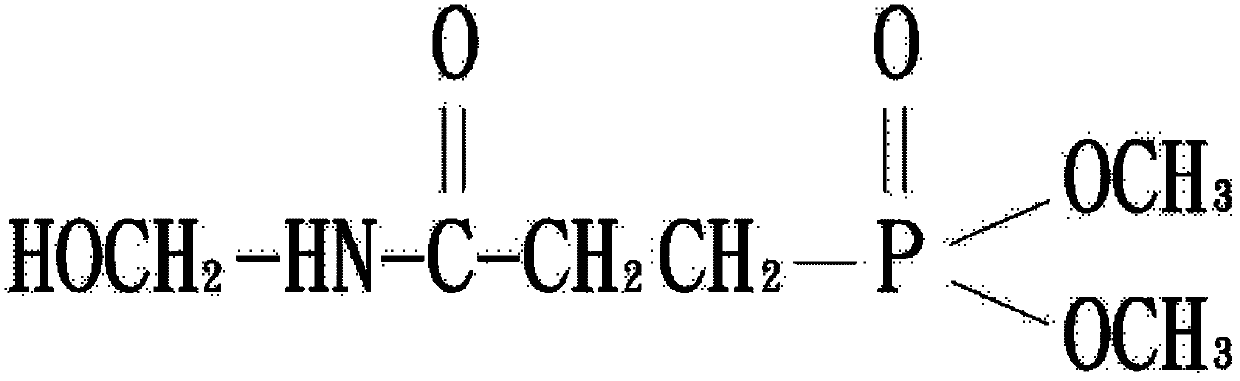Manufacture method of native cellulose fiber with flameproof function
A natural cellulose and cellulose technology, applied in the field of fiber production, can solve the problems of personal safety hazards in the home, increase of non-dissolving fiber waste, poor flame resistance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1 (sample numbers D1~D12 and F1~F12 of the present invention):
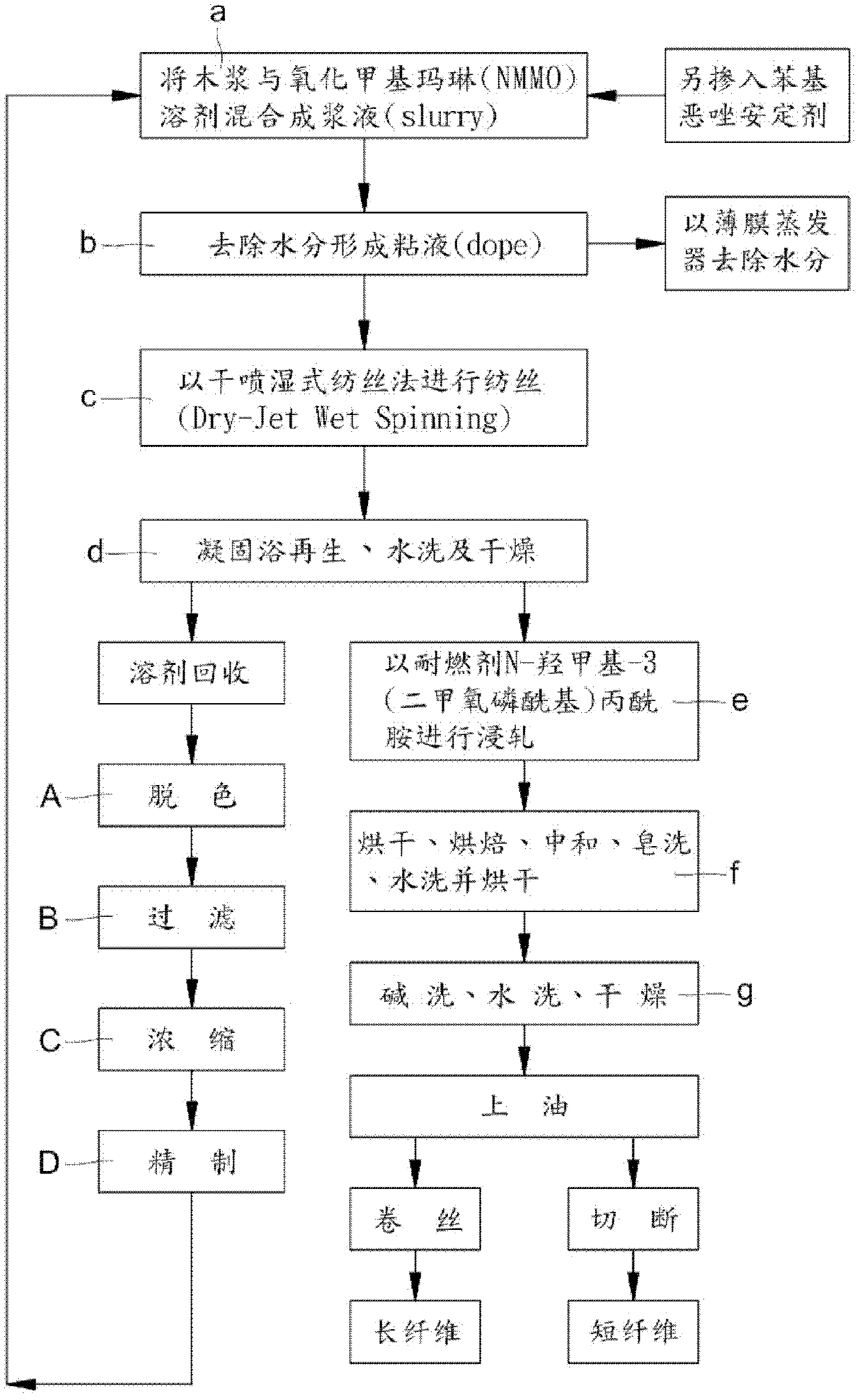
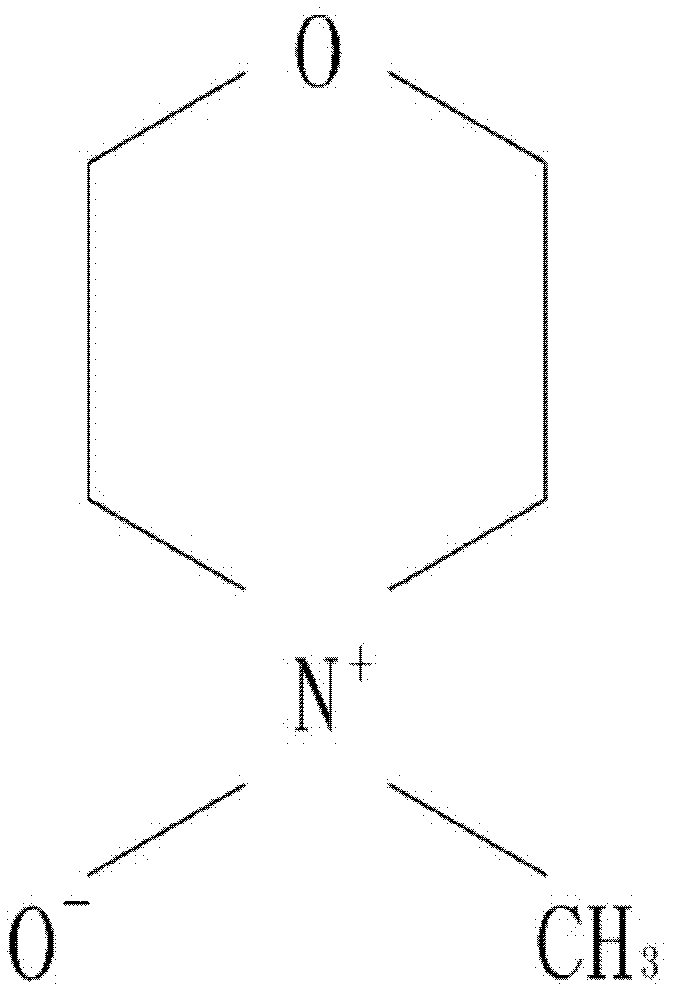
[0034] Mix wood pulp cellulose with a degree of polymerization of 650 and oxidized methyl marlene (NMMO) solvent to form a slurry, and add different proportions of phenyloxazole (1,3-phenylene-bis 2-oxazoline, BOX) to stabilize Then use a vacuum thin film evaporator to evaporate the excess water, heat at 80°C to 120°C, remove the water to 5% to 13% within 5 minutes, and then dissolve the cellulose into mucus (dope). The composition of the mucus is shown in the table As shown in the sample numbers D1 to D12 in Table 1, the viscous liquid is sent to the spinning machine with a metering pump for spinning, extruded through the spinning port by extrusion, and dry-jet wet spinning method (Dry-jet Wet Spinning) After being regenerated in a coagulation bath, washed with water and dried to make natural cellulose fibers, the natural cellulose fibers are padded with N-hydroxymethyl-3-(dimethoxyphosphoryl)p...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment two (sample numbers D13~D24 and F13~F24 of the present invention):
[0036] Mix wood pulp cellulose with a degree of polymerization of 1050 and methyl marin oxide (NMMO) solvent to form a slurry, and add different proportions of phenyloxazole (1,3-phenylene-bis 2-oxazoline, BOX) to stabilize Then use a vacuum thin film evaporator to evaporate the excess water, heat at 80°C to 120°C, remove the water to 5% to 13% within 5 minutes, and then dissolve the cellulose into mucus (dope). The composition of the mucus is shown in the table As shown in the sample numbers D13-D24 in Table 1, the viscous liquid is sent to the spinning machine with a metering pump for spinning, extruded through the spinning port by extrusion, and dry-jet wet spinning method (Dry-jet Wet Spinning) After being regenerated in a coagulation bath, washed with water and dried to make natural cellulose fibers, the natural cellulose fibers are padded with N-hydroxymethyl-3-(dimethoxyphosphoryl)pro...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment three (flame-resistant function test):
[0042] Wood pulp cellulose with a degree of polymerization of 650 and 1050 was mixed with oxidized methyl marin (NMMO) solvent to form a slurry and mixed with phenyloxazole (1,3-phenylene-bis 2-oxazoline, BOX) stabilizer, Then use a vacuum thin film evaporator to evaporate the excess water, heat at 80°C to 120°C, and remove the water to 5% to 13% within 5 minutes to dissolve the cellulose into mucus (dope), and then measure the mucus The pump is sent to the spinning machine for spinning, extruded through the spinning port by extrusion, and regenerated in the coagulation bath by dry-jet wet spinning method (Dry-jet Wet Spinning), and then washed and dried to make natural cellulose fibers , the natural cellulose fiber is padded with N-methylol-3-(dimethoxyphosphoryl)propionamide flame retardant, and the squeeze rate is 65% to 70%, and the N-methylol-3 -(Dimethoxyphosphoryl)propionamide flame retardant concentration is 0...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| oxygen index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| oxygen index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com