Selective-failure-based 3D (three-dimensional) printing method for preparing mold
A 3D printing and selective technology, applied in the field of 3D printing, can solve the problems of difficult to improve the performance of molded parts, low surface finish, high temperature resistance, etc., to achieve the effect of improving molding speed and efficiency, high dimensional accuracy requirements, and protecting details.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
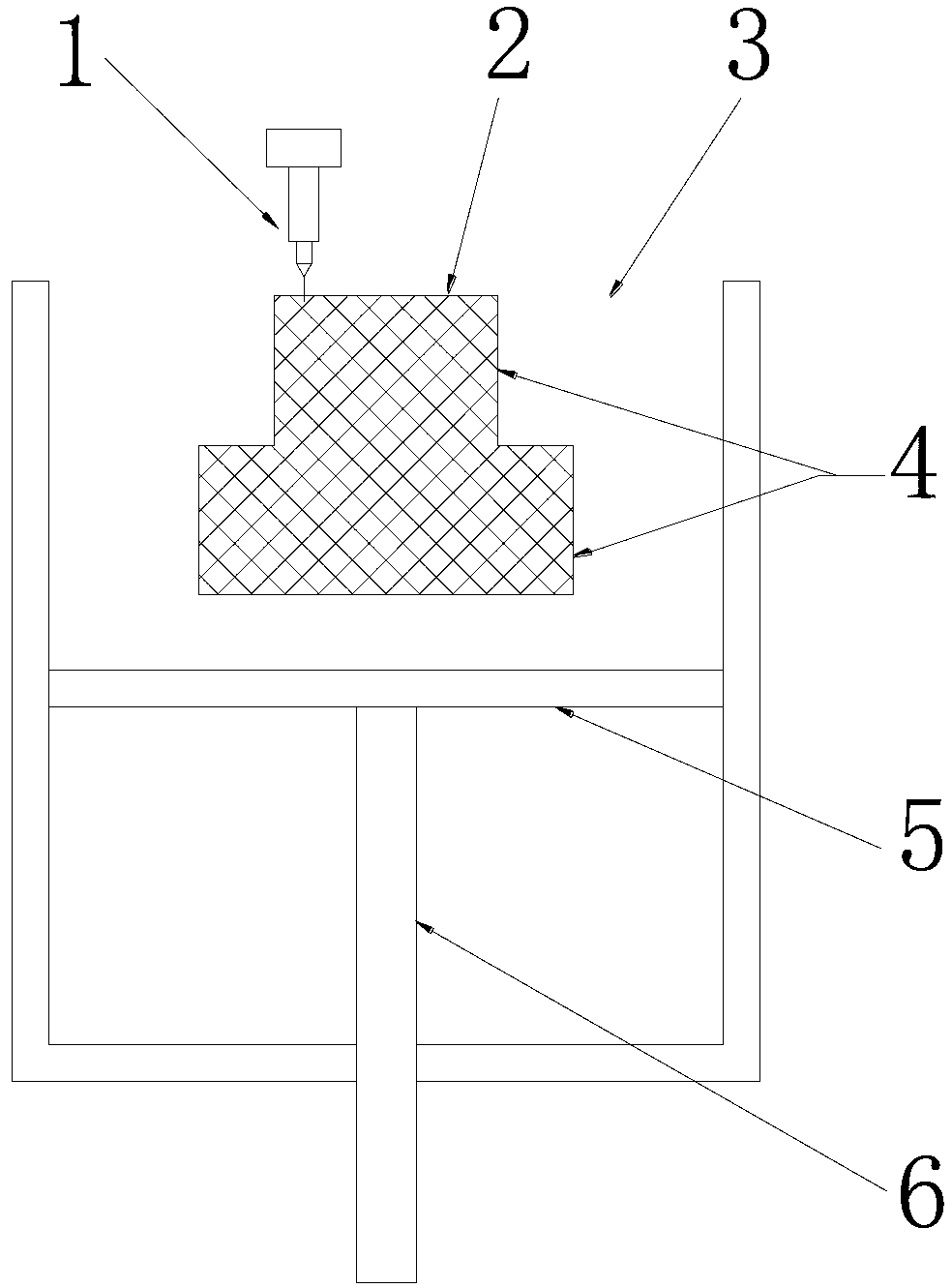
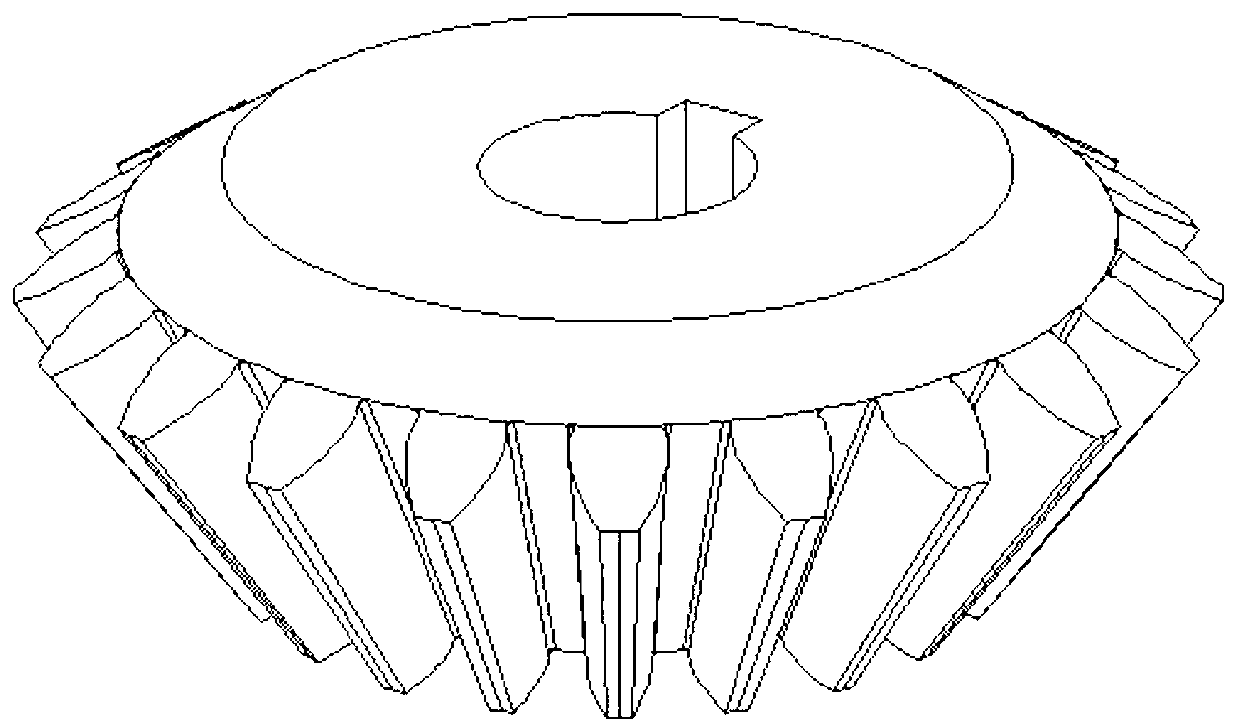
[0031] Example 1: 3D printing of "straight bevel gear" mold, using laser selective failure method
[0032] Firstly, draw the 3D CAD solid model of the "straight bevel gear" casting, and process it with the computer to get the 3D CAD solid model of the "straight bevel gear" casting mold. The casting corresponds to the cavity inside the mold, forming a "straight bevel gear" Toothed bevel gear" casting - 3D CAD solid model of the casting mold.
[0033] Then, the above-mentioned solid model is sliced in layers in the Z direction, and the slice thickness is 0.3 mm, and each layer slice generates a casting-mold boundary contour line. The part corresponding to the outside of the contour line is the "straight bevel gear casting", and the part corresponding to the contour line and the inside of the contour line is the "straight bevel gear casting". This part is the area that needs selective failure processing.
[0034] Then, the 3D printer control system starts to lay the coated san...
Embodiment 2
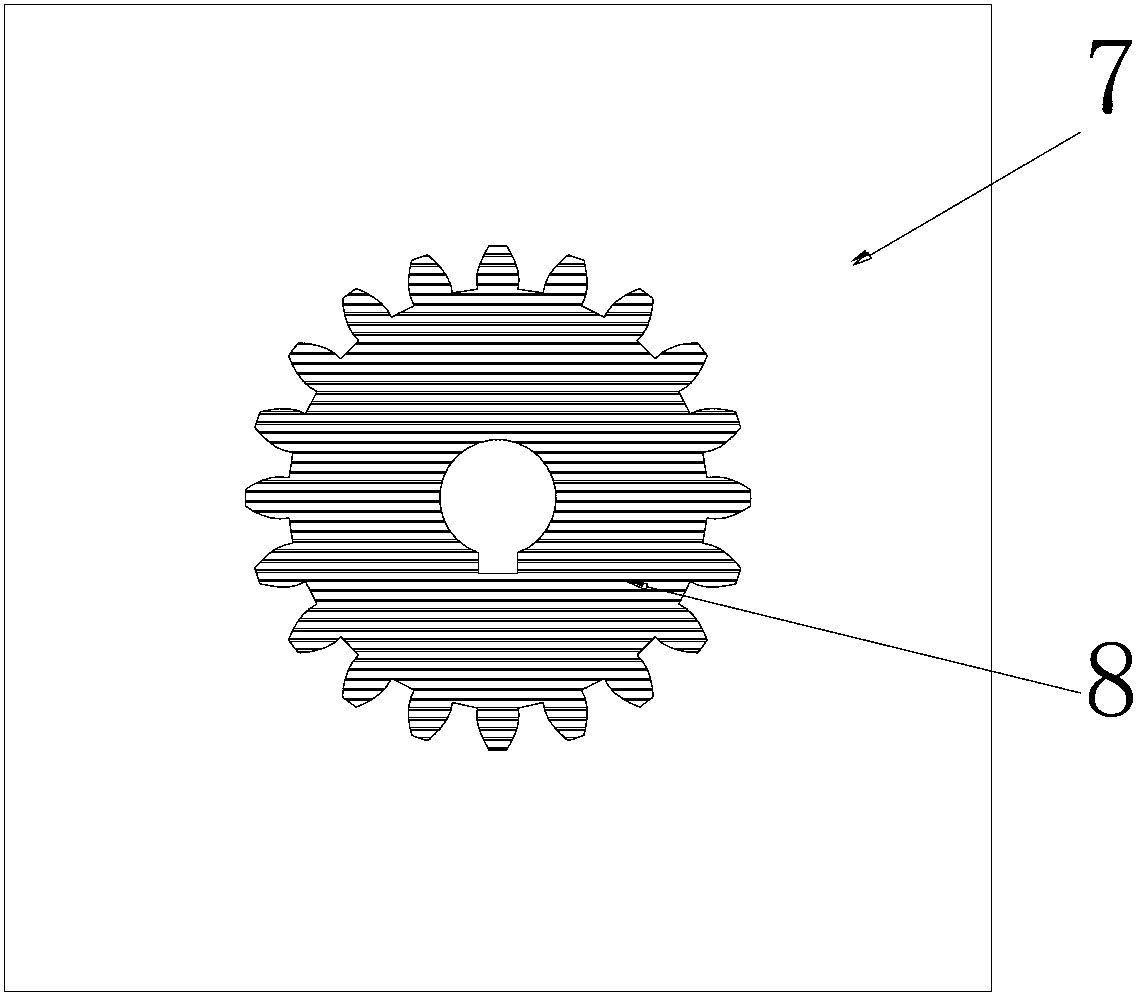
[0037] Example 2: 3D printing of the "cam" mold, using a laser selective failure method
[0038] First, draw the 3D CAD solid model of the "cam" casting, and the computer will process it to get the 3D CAD solid model of the "cam" casting mold. The casting corresponds to the cavity inside the casting mold to form a "cam" casting - mold 3D CAD solid model.
[0039] Then, the above-mentioned solid model is sliced in layers in the Z direction, and the slice thickness is 0.3 mm, and each layer slice generates a casting-mold boundary contour line. The part corresponding to the outside of the contour line is the "cam casting mold", and the part corresponding to the contour line and the inside of the contour line is the "cam casting part". This part is the area that needs selective failure processing.
[0040] Then, the 3D printer control system starts to process the coated sand powder body. According to the boundary contour line of the casting-mold of each slice, the computer cont...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com