Medical image segmentation algorithm
A technique for medical images, segmentation algorithms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
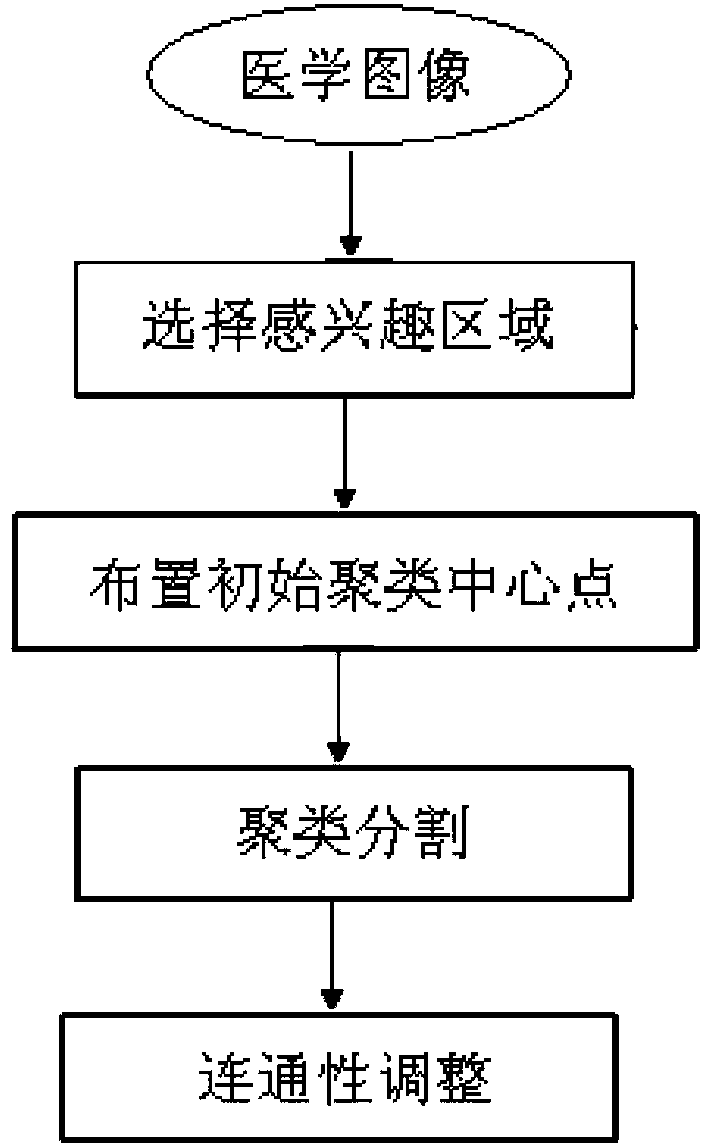
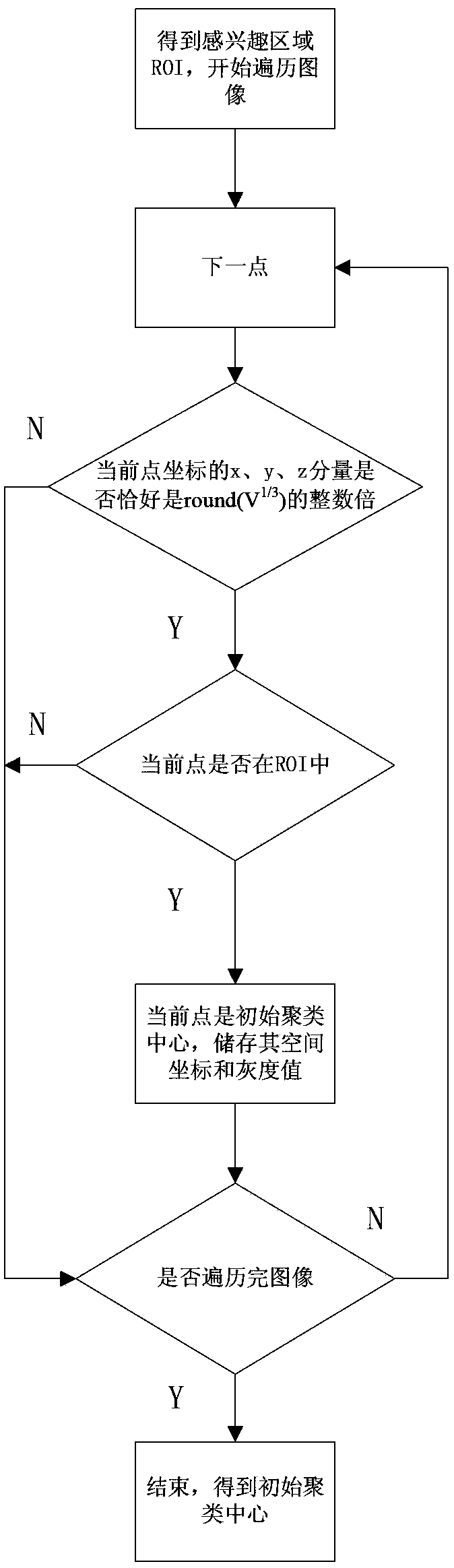
[0040] Such as figure 1 As shown, the medical image segmentation algorithm of the present invention processes a three-dimensional medical image composed of multi-layer two-dimensional images, and the specific steps include selecting a region of interest, arranging initial cluster center points, cluster segmentation and connectivity adjustment.
[0041] Step 1. Select an area of interest
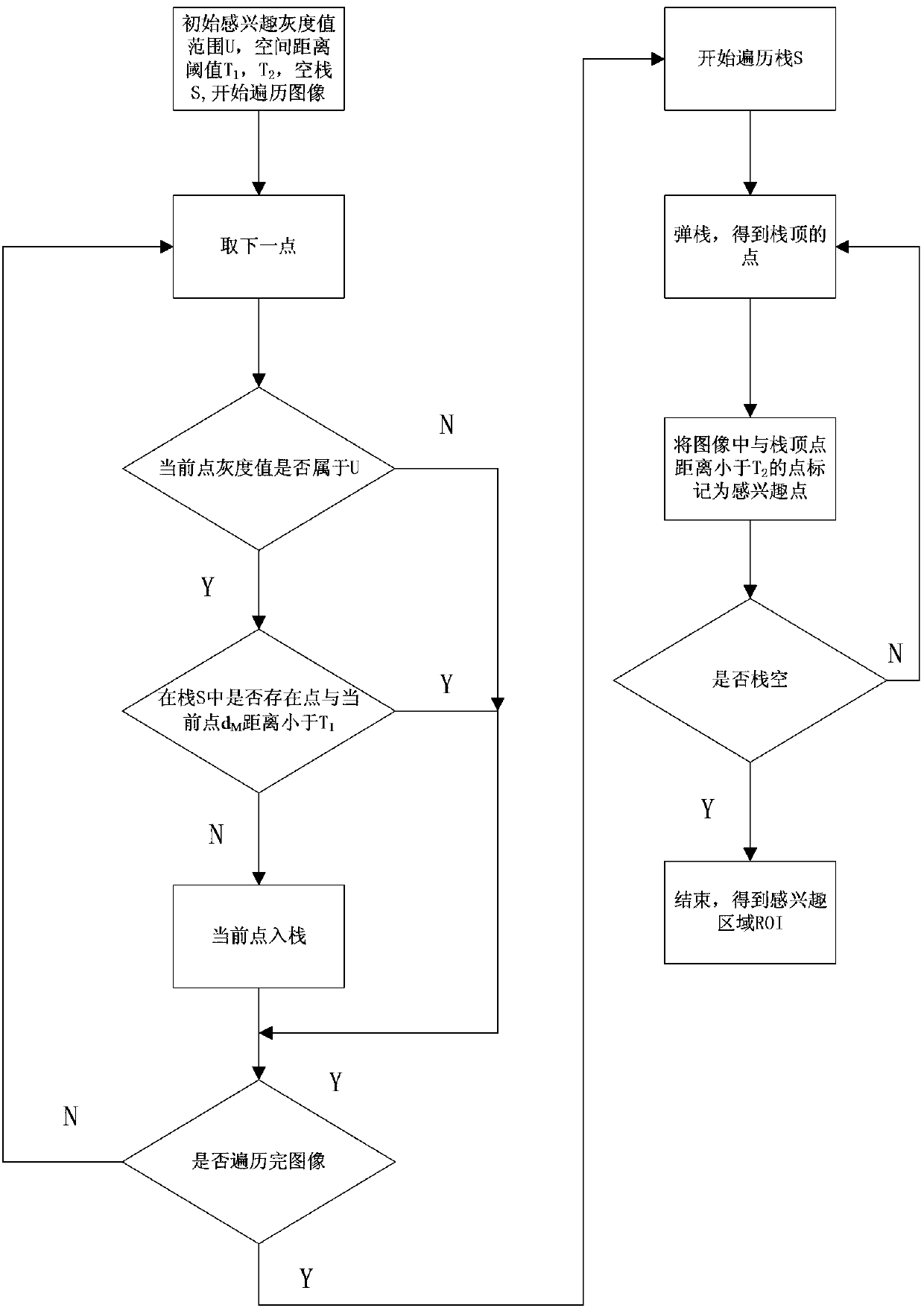
[0042] In practical applications, the image region of interest is often not the entire medical image. Therefore, in order to reduce the calculation time of the algorithm, the region of interest (ROI) of the medical image must first be selected, and the subsequent clustering and segmentation are only performed on the region of interest. . When the ROI is not all medical images, this step removes the segmentation operation on the uninterested regions, which will significantly reduce the running time of the algorithm. Such as figure 2 As shown, step one specifically includes the following ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com