Relative navigation method for autonomous rendezvous of space non-operative target
A non-cooperative target and relative navigation technology, applied in the field of spatial autonomous relative navigation, can solve problems such as difficult implementation, low estimation accuracy, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
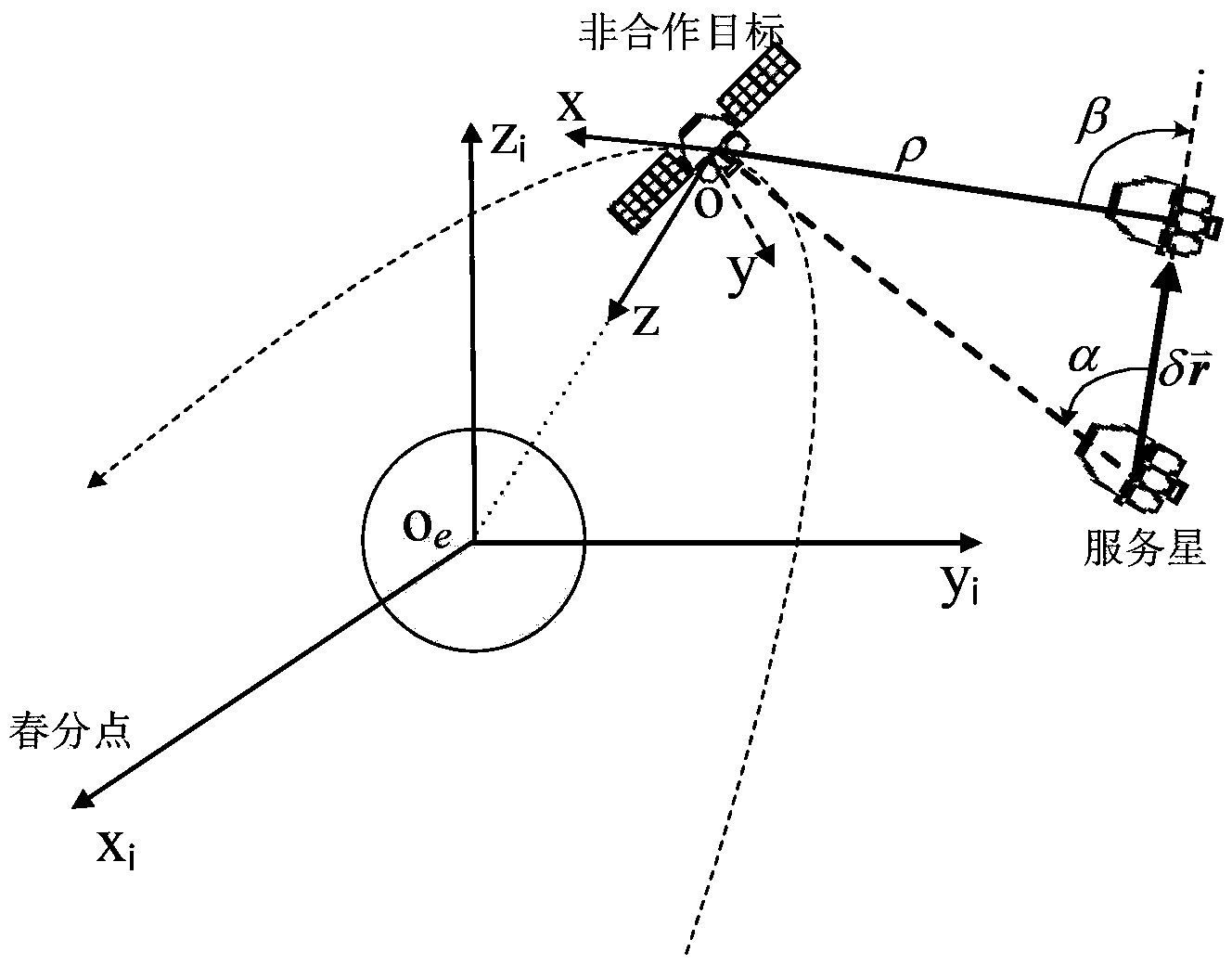
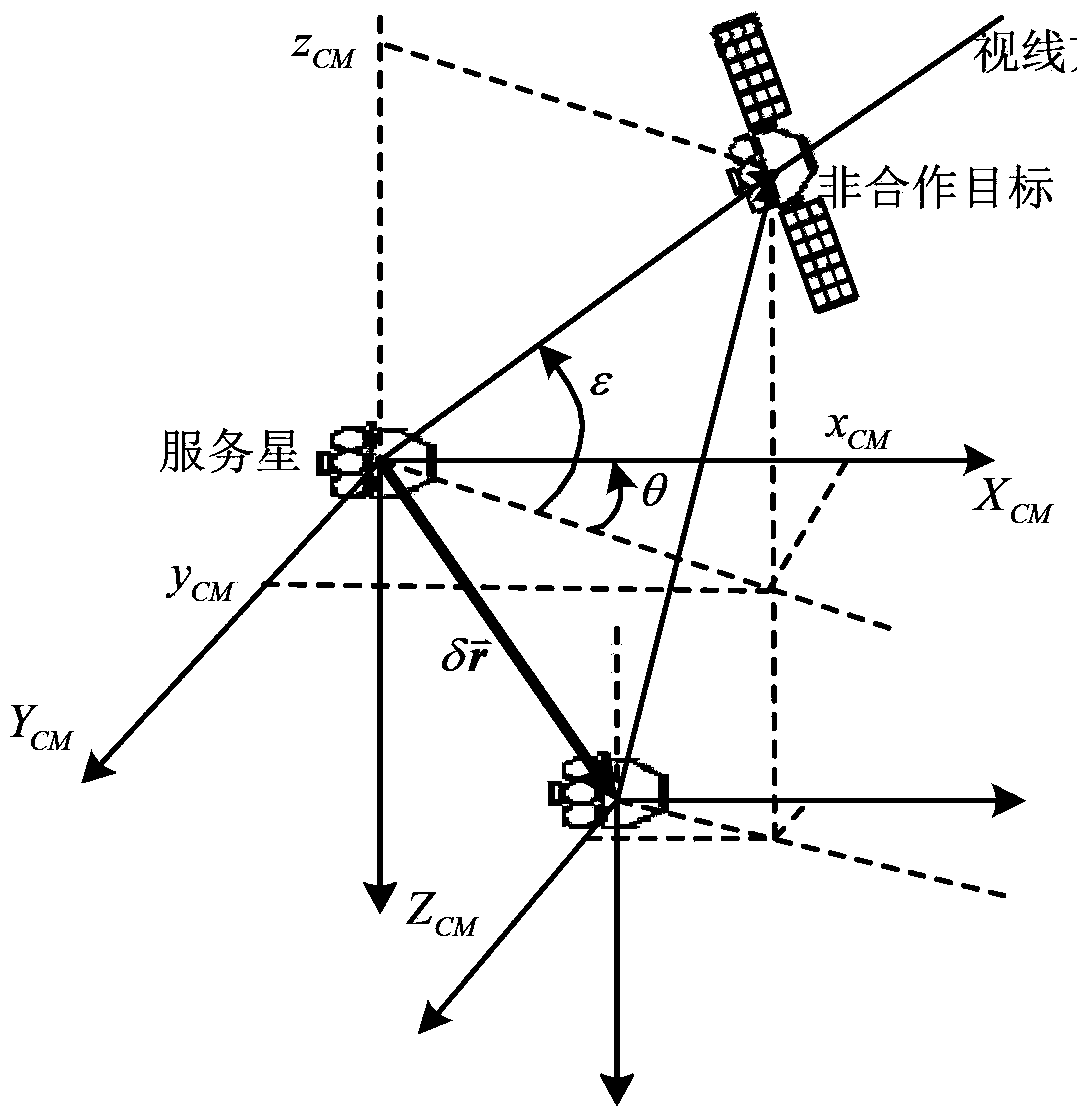
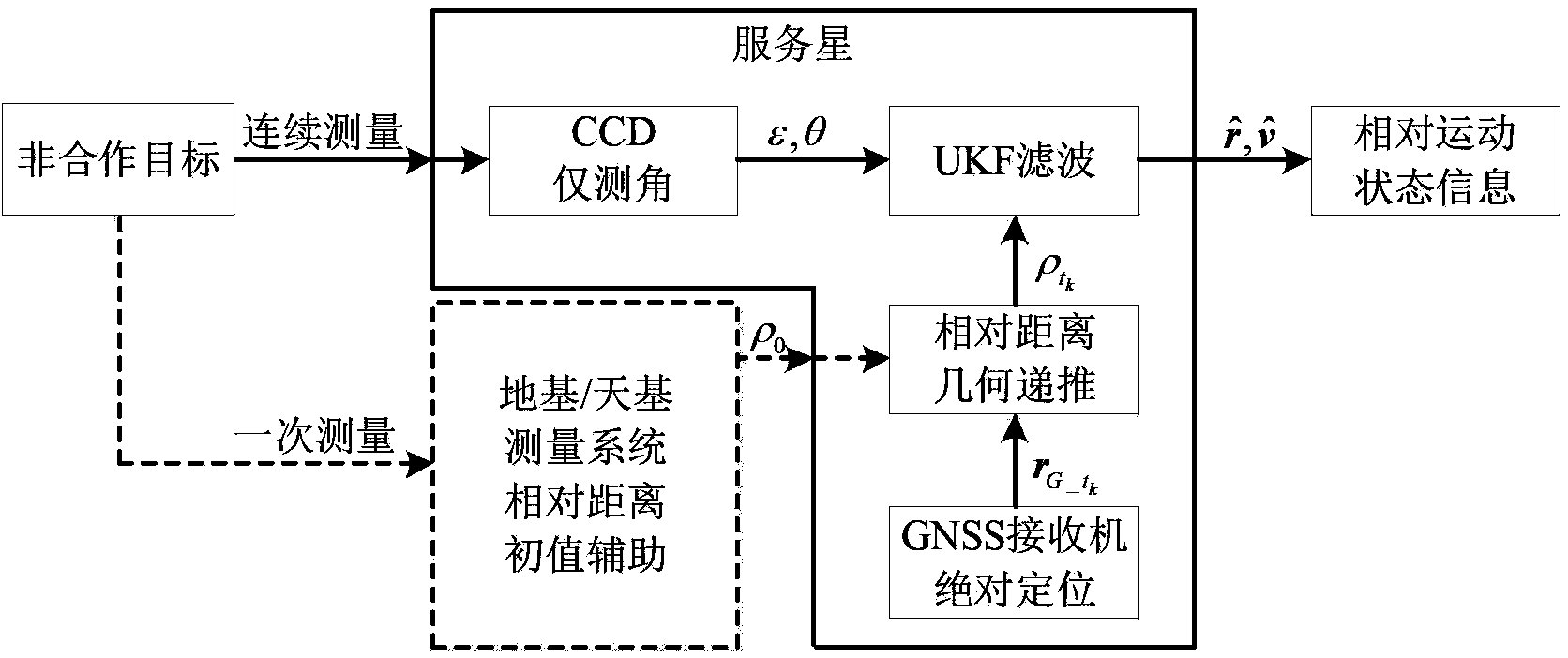
[0035] Specific examples: combining Figure 5 Illustrate the example verification of the present invention, set following calculation condition and technical parameter:
[0036] 1) The semi-major axis of the orbit of the non-cooperative target is 6678km, the eccentricity is 0.01, the orbital inclination is 60°, the argument of perigee is 120°, the right ascension of ascending node is 40°, and the true anomaly is 70°;
[0037] 2) The initial relative position is [-40;0;-10]km, and the initial relative velocity is [20;0;10]m / s;
[0038] 3) CCD camera installation error 10 -3 rad, measurement noise mean square error 10 -3 rad, output frequency 1Hz;
[0039] 4) The probability error of GNSS receiver positioning circle is 20m, the mean square error of noise is 2m, and the output frequency is 1Hz;
[0040] 5) The mean square error of the relative distance auxiliary initial value error of the ground-based or space-based measurement system is 10m
[0041] 6) The initial value of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com