One-step synthetic method of palladium tetraammine acetate dihydrate (II)
A technology of acetic acid dihydrate and palladium acetate, applied in the field of chemistry and chemical industry, can solve problems such as difficulty in mass production, difficult control of reaction end points, application limitations, etc., and achieves the effects of high reaction yield, simple operation, and high product purity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0012] Example 1 Measure 500 mL of concentrated ammonia water, add 100.00 g (446.4 mmol) of palladium acetate solid in batches under stirring, after the addition is complete, stir at 40-50°C until the palladium acetate is completely dissolved to obtain a light yellow solution, filter to remove a small amount of insoluble The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to 80-100mL, and then 5mL of concentrated ammonia water was added and stirred to obtain a light yellow tetraamminepalladium(II) acetate solution; the concentrated solution was added to 2000 mL of acetone under vigorous stirring, and the After stirring for 30 minutes, filter, wash the filter cake once with 50 mL of acetone, concentrate the filtrate again, reverse analysis with acetone, combine the obtained light yellow solids, and dry at 40-50°C for 3 hours to obtain 144.2 g of tetraamminepalladium(II) acetate Pale yellow solid, yield 98%.
[0013] Feature structure parameters:
[0014] Elemental analy...
Embodiment 2
[0018] Example 2 Measure 1500 mL of concentrated ammonia water, add 500.00 g (2.232 mol) of palladium acetate solid in batches under stirring, after the addition is complete, stir at 40-50°C until the palladium acetate is completely dissolved to obtain a light yellow solution, filter to remove a small amount of insoluble The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to 150-200mL, then 5mL of concentrated ammonia water was added and stirred to obtain a light yellow tetraamminepalladium(II) acetate solution; the concentrated solution was added to 5L of acetone under vigorous stirring, and stirred at room temperature Filter after 30 minutes, wash the filter cake once with 100 mL of acetone, concentrate the filtrate again, reverse analysis with acetone, combine the obtained pale yellow solids, and dry at 40-50°C for 3 hours to obtain 721.21 grams of tetraammine palladium (II) acetate Yellow [Pd(NH 3 ) 4 ](CH 3 COO) 2 2H 2 O, yield 98%.
Embodiment 3
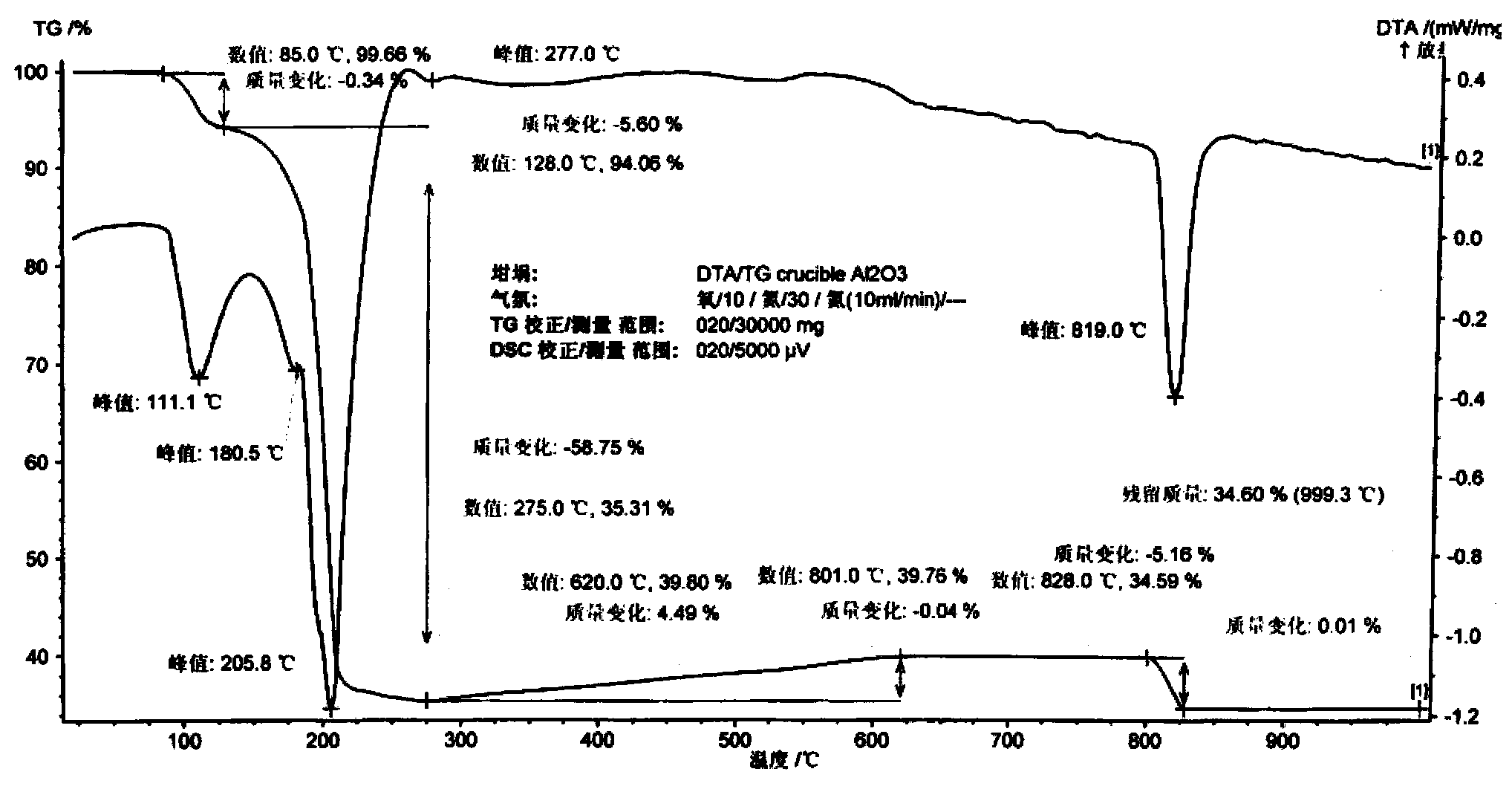
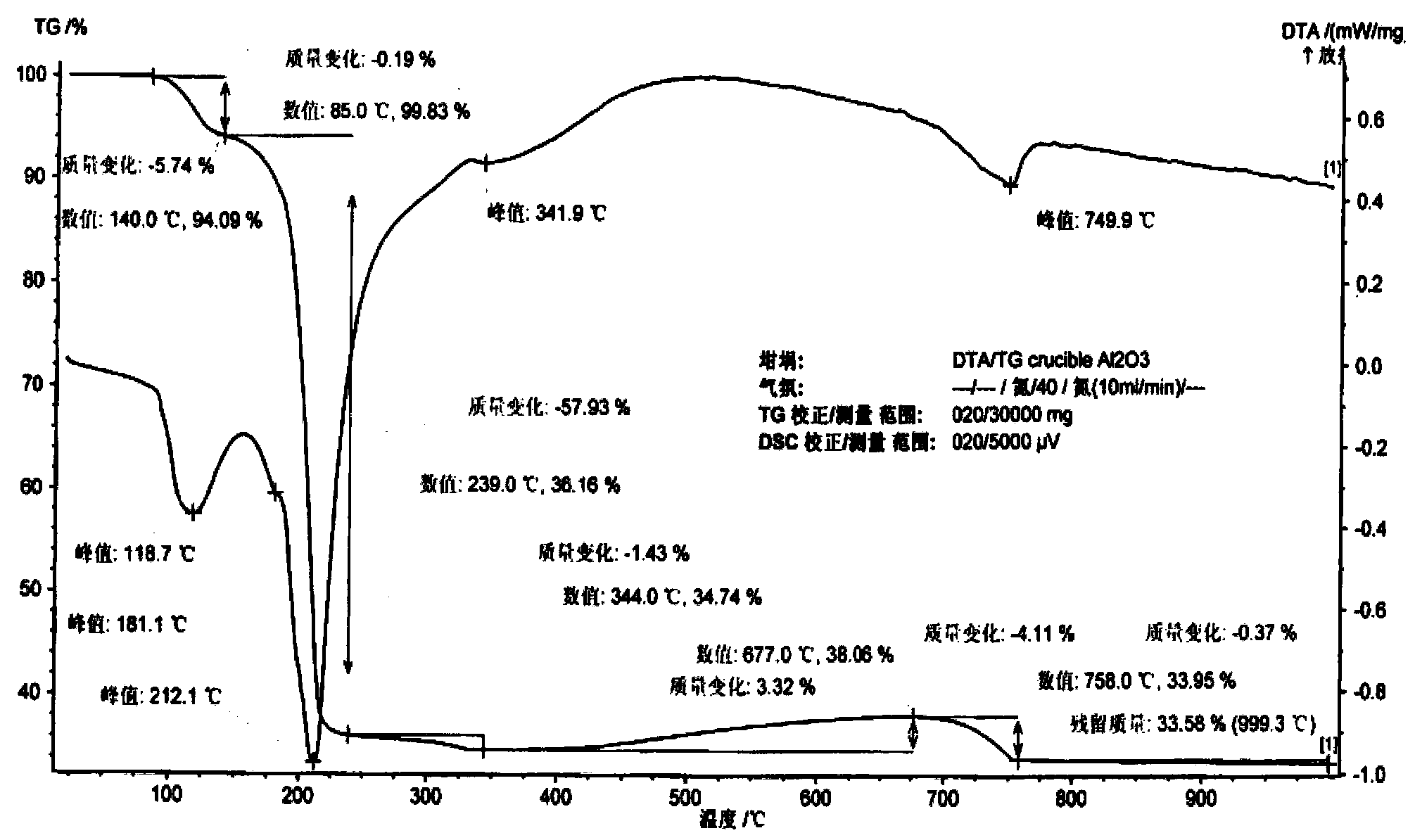
[0019] Example 3 The thermal decomposition behavior of tetraammine palladium acetate dihydrate in air was determined by thermogravimetric analysis (DTA / TG), and the gas phase products of thermal decomposition were determined by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
[0020] Table 1. The main products of pyrolysis of tetraamminepalladium acetate dihydrate at 270℃
[0021]
[0022] The thermal cracking reaction formula of tetraammine palladium acetate dihydrate is as follows:
[0023]
[0024] Such as figure 1 , it can be known from the DTA / TG diagram in air that [Pd(NH 3 ) 4 ](CH 3 COO) 2 2H 2 O starts endothermic weight loss at 85°C, and an endothermic peak appears at 111°C, and the weight loss is 5.6% at 85-128°C; for the removal of two crystal waters, and then intense endothermic weight loss, the endothermic peak appears at 205°C, The peak and valley of the weight loss curve is 275 ° C, and the weight loss is 58.8%, which is equivalent to losing four ammonia...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com