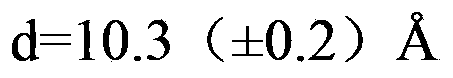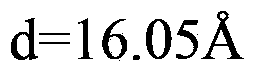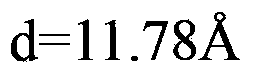Metal azo pigments and pigment preparations produced from same, and production method and use thereof
A metal azo pigment technology, applied in the field of metal azo pigments, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory brightness and color purity requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0275] Example 1: Preparation of Pigment A (non-inventive (non-inventive)):
[0276] Azobarbituric acid (0.3 mol) prepared according to Guideline 1 was mixed with 1500 g of distilled water at 82 °C. Thereafter 75.7 g of melamine (0.6 mol) were introduced. Then 0.3 mol of about 30% strength zinc chloride solution was added dropwise. After 3 hours at 82°C, the pH was adjusted to about 5.5 using KOH. Then dilute with about 300 g of distilled water at 90°C. Then 34 g of 30% strength hydrochloric acid were added dropwise and a temperature of 90° C. was fixed for 12 hours. Thereafter the pH was adjusted to about 5 using aqueous potassium hydroxide solution. The pigment is then separated on a suction filter, washed, dried in a vacuum oven at 80° C., and ground in a standard laboratory mill for about 2 minutes. (Pigment A = adduct of zinc azobarbiturate and melamine).
Embodiment 2
[0277] Example 2: Preparation of Pigment B (non-inventive (non-inventive)):
[0278] Azobarbituric acid (0.3 mol) prepared according to Guideline 1 was mixed with 1500 g of distilled water at 82 °C. Then 10 g of 30% strength hydrochloric acid were added dropwise to adjust the pH to 2-2.5. Thereafter 79.4 g of melamine (0.63 mol) were introduced. Then 0.3 mol of about 25% strength nickel chloride solution was added dropwise. After 3 hours at 82°C, the pH was adjusted to about 5.5 using KOH. Then dilute with about 100 g of distilled water at 90°C. 21 g of 30% strength hydrochloric acid are then added dropwise and a temperature of 90° C. is maintained for 12 hours. Thereafter the pH was adjusted to about 5 using aqueous potassium hydroxide solution. The pigment is then separated on a suction filter, washed, dried in a vacuum oven at 80° C., and ground in a standard laboratory mill for about 2 minutes. (Pigment B = adduct of nickel azobarbiturate and melamine).
Embodiment 3-5
[0279] Examples 3-5: Preparation of Pigments C, D, and E (Inventive (Inventive))
[0280] In the following inventive (inventive) Examples 3 to 5, the operation of Example 2 was repeated, but the nickel chloride solution was replaced by a mixed solution of nickel chloride and zinc chloride.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com