High-throughput, sensitive detection of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
A technology of gluconic acid and phosphoric acid, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of lack and inability to detect G6PDH, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0073] Example 1: DBS sample
[0074] Filter paper with Dried Blood Spot (DBS) obtained from a neonatal screening program was utilized in the present examples. The 3 mm diameter disc was removed from the filter paper and the blood sample from this disc was added to a 1.5 mL Eppendorf tube using 50 μL of "Reagent 1". "Reagent 1" was prepared by mixing 3 volumes of double distilled water, 3 volumes of 250mM K 2 HPO 4 , 2 volumes of 1% saponin for molecular biology, 1 volume of 7.5mM nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate and 1 volume of 10mM glucose-6-phosphate. The Eppendorf tubes were sealed and after gentle mixing, the tubes were placed in an incubator at 37°C for 30 minutes. The reaction was quenched by adding 100 [mu]L of a 1:1 acetonitrile:methanol (LC-MS grade) mixture. After centrifugation, 10 μL of the clarified supernatant was diluted with 240 μL of 20 mM Butyl-Dimethyl-Ammonium Bicarbonate (BDMAB) in water.
[0075] Inject 2 μL of this solution into an LC / ...
example 2
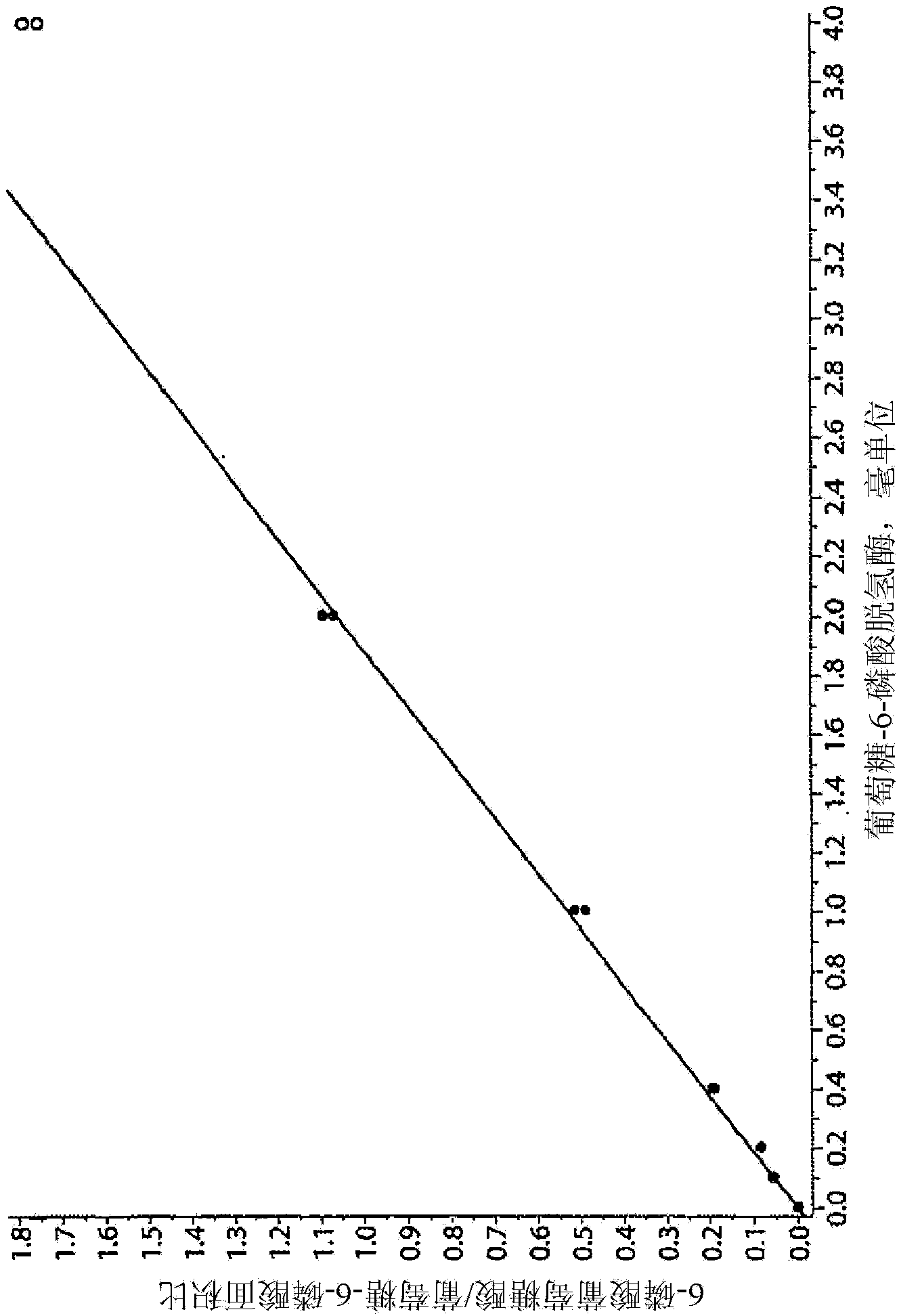
[0082] Example 2: Enzyme Calibration
[0083] With 50% double distilled water, 30% 250mM K 2 HPO 4 and 20% of a solution of 1% Molecular Biology Saponin to dissolve a commercially available enzyme standard (eg, Sigma #G5885) to obtain 100 milliunits / ml. In 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes, add 0, 1, 2, 4, 10, 20, and 40 µL of this solution (corresponding to 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 1.0, 2.0, and 4.0 milliunits of enzyme) to 50 μL of "Reagent 1" (described in Example 1). The Eppendorf tubes were sealed and after gentle mixing, the tubes were placed in an incubator at 37°C for 30 minutes. The reaction was quenched by adding 100 [mu]L of a 1:1 acetonitrile:methanol (LC-MS grade) mixture. After centrifugation, 10 μL of the clear supernatant was diluted with 240 μL of 20 mM butyl-dimethyl-ammonium bicarbonate (BDMAB) in water. As in Example 1, 2 μL of this solution was injected into the LC / MS / MS system. In "Quant" or "MultiQuant" mode, traces corresponding to transitions 275.2 > 79.0 and 25...
example 3
[0087] Example 3: Analysis of Dried Blood Samples
[0088] Correlation studies were organized using anonymous excess samples from routine analysis in the hospital and pre-collected and used according to local ethical committee guidelines. Blood samples were spotted on Guthrie cards, dried and sent for LC / MS / MS measurements. Analysis was performed by LC / MS / MS as described in Example 1 above. As a reference, BioVision kit (BioVision Kit) (Cat. No. K757-100 from BioVision, 980 Linda Vista Drive, Mountain View, CA 94043, USA, was used as implemented in a routine hospital laboratory. Samples were premeasured by Research Products (BioVision Research Products, 980 Linda Vista Avenue, Mountain View, CA 94043 USA).
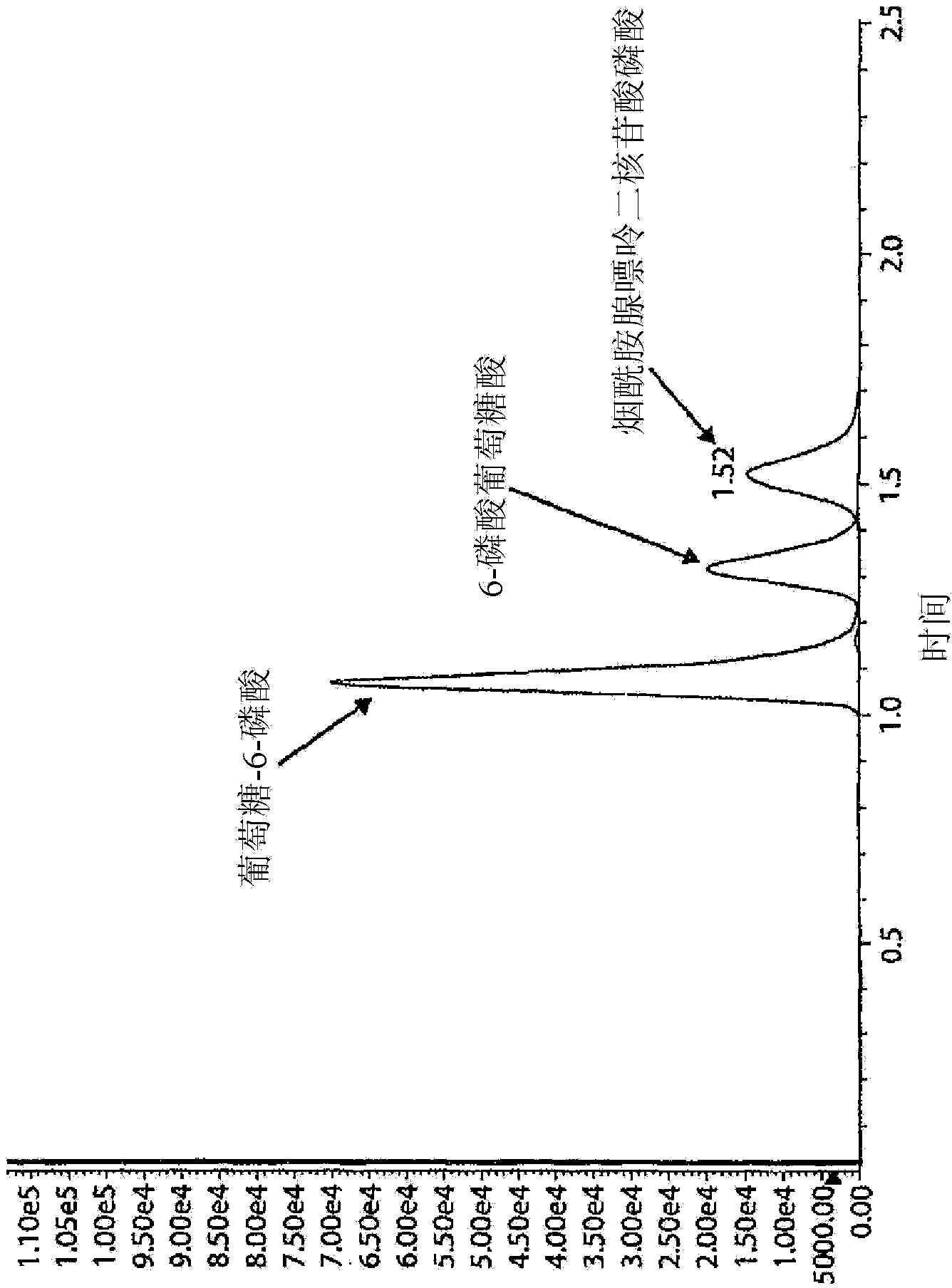
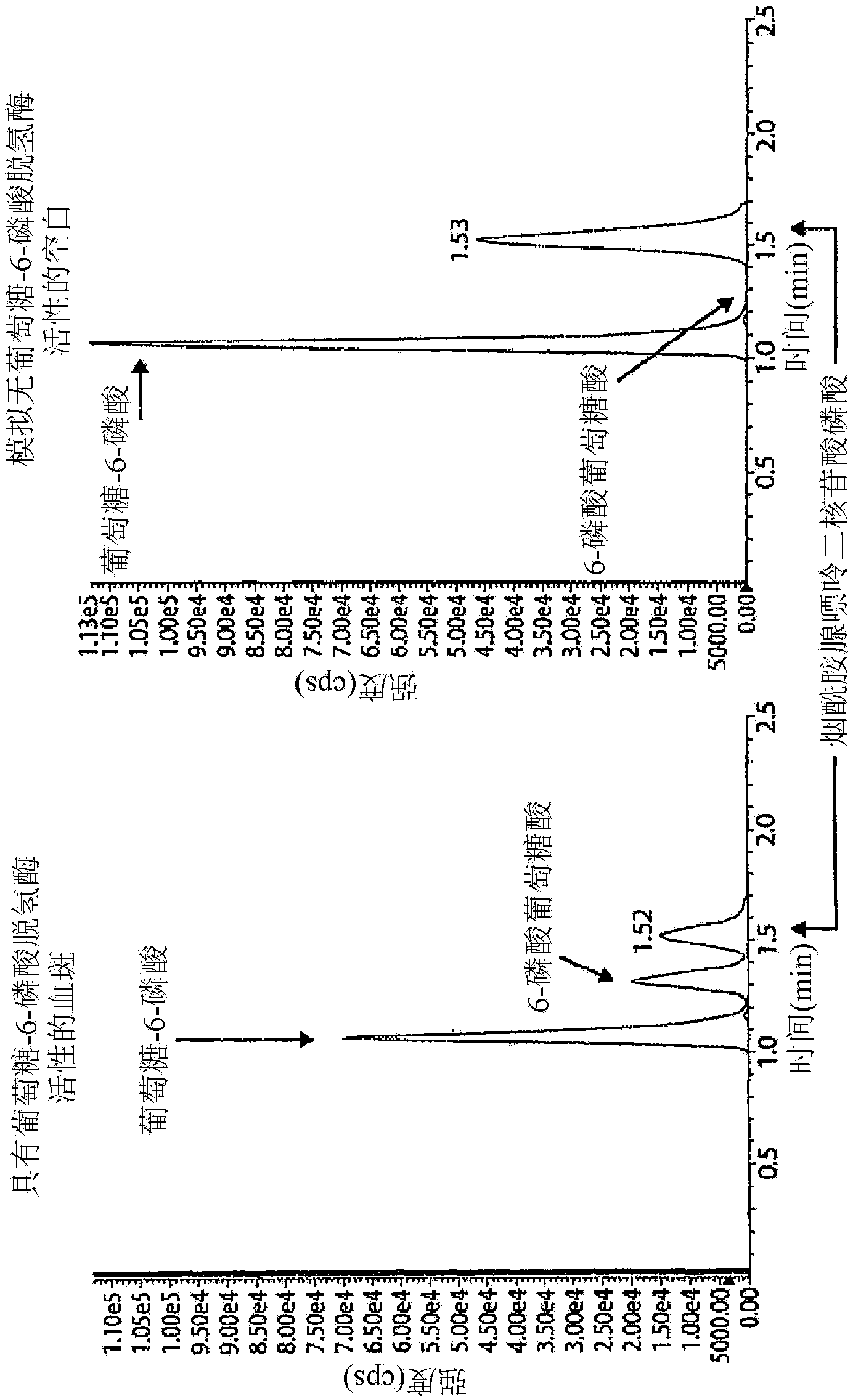
[0089] Figure 4A and 4B Shown are two exemplary mass spectrometer readings in MRMs obtained from two dried blood samples, indicating high and low G6PDH activity as measured by the Bovison kit (BV). As can be seen from these figures, LC-MS / MS is capable of measuring...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com