Pair of polypeptides specifically identifying porcine NFkappaBp65 gene, and coding gene and application thereof
A pair of coding technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problem of low gene knockout efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1, the construction of TALE target recognition module
[0039] 1. Description of the four modules and the mechanism of combining modules
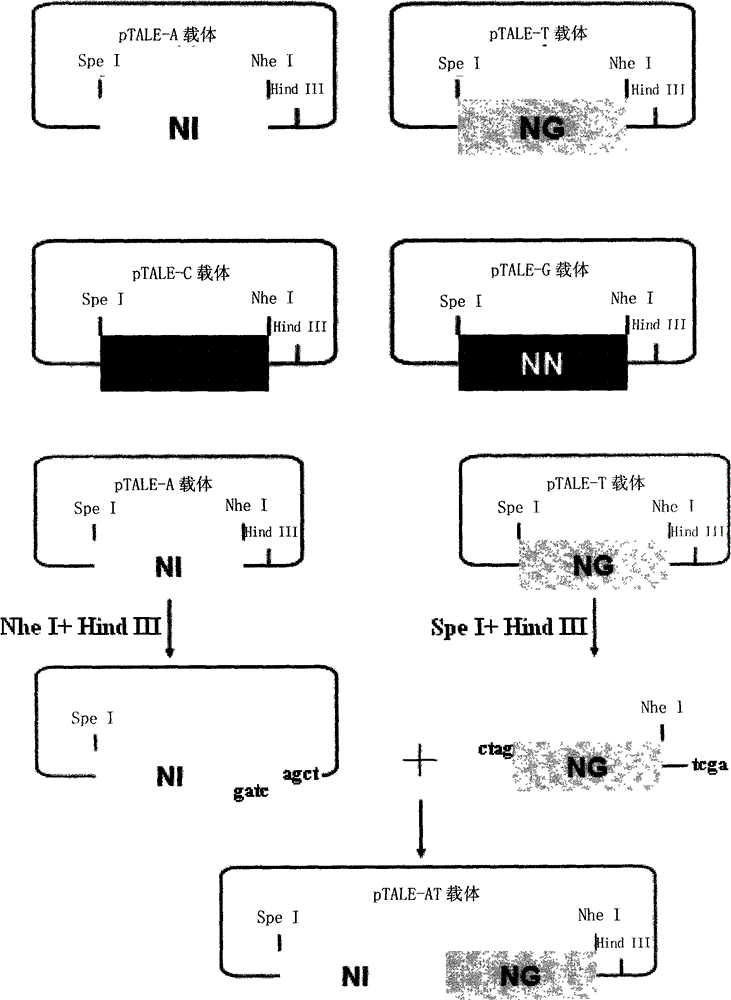
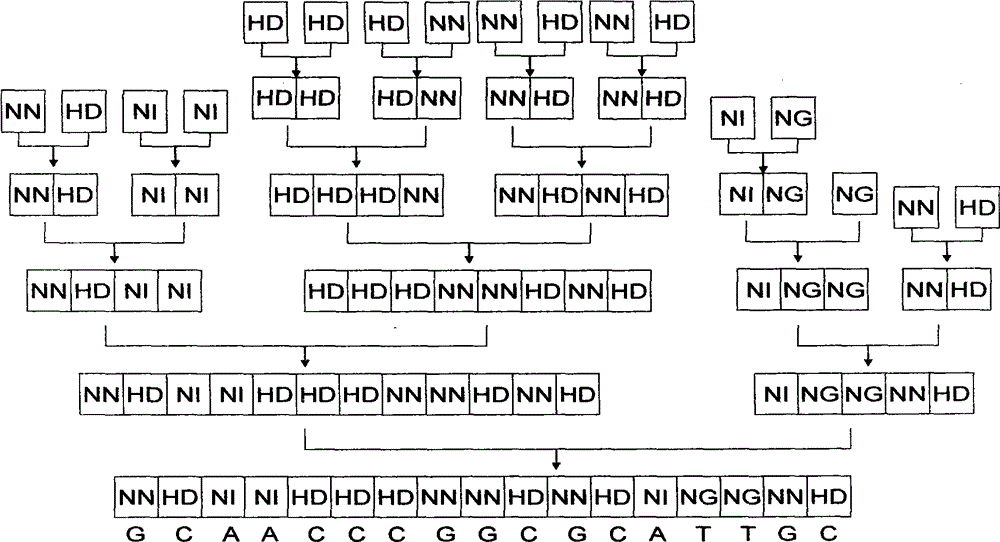
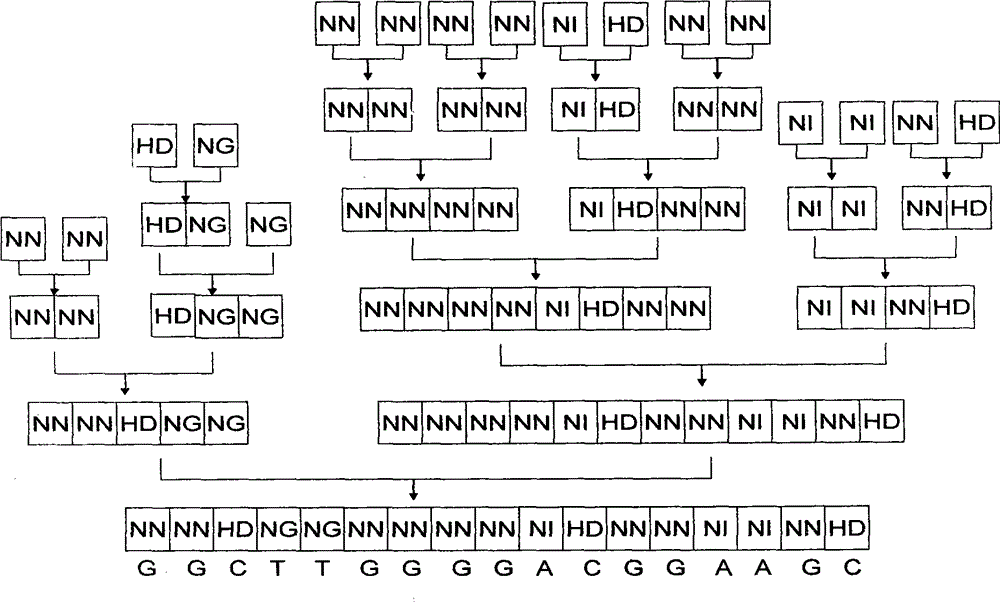
[0040] The nucleic acid recognition unit of TAL is a double-linked amino acid (that is, two adjacent amino acids) separated by 32 constant amino acid sequences. Double-linked amino acids have a constant correspondence with A, G, C, and T, that is, NI recognizes A, NG recognizes T, HD recognizes C, and NN recognizes G. The pTALE-A plasmid, pTALE-G plasmid, pTALE-C plasmid, and pTALE-T plasmid are single-module vectors, which are plasmids encoding DNA for the nucleic acid recognition units of the above four TALs respectively, and at the 5' end of the encoding DNA. Spe I restriction recognition sequence, 3' end has continuous Nhe I restriction recognition sequence and Hind III recognition sequence. Through the Spe I, Nhe I, and Hind III restriction sites on the single-module vector, the TAL unit corresponding to the target ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2, the construction of reporter plasmid
[0056] 1. Synthesize the double-stranded DNA molecule (target fragment) shown in sequence 6 of the sequence listing.
[0057] 2. Using the double-stranded DNA molecule synthesized in step 1 as a template, perform PCR amplification with a primer pair composed of NFκB p65F and NFκB p65R to obtain a PCR amplification product.
[0058] NFκB p65F: 5'-ACTTATGTTA CCCGGG CGGATTGAGGAGAAACGCAAAAGG-3';
[0059] NFκB p65R: 5'-ATACATGTAT CCCGGG AGAAACAGGAGCCCAACAGAGGG-3'.
[0060] 3. Digest the PCR amplified product in step 2 with restriction endonuclease XmaI, and recover the digested product.
[0061] 4. Digest the pGL4-SSA vector with restriction endonuclease XmaI, and recover the vector backbone of about 5.7 kb.
[0062] 5. Ligate the digested product of step 3 with the vector backbone of step 4 to obtain recombinant plasmid pGL4-SSA-p65 (reporter plasmid). According to the sequencing results, the structure of the reco...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Example 3, verifying the TALEN activity of the plasmid constructed in Example 1 by the luciferase reporter gene method
[0064] Carry out the following 2 groups of experimental treatments respectively (each experimental treatment carries out three repeated experiments, each repeated experiment is set 3 repeated treatments, the average value of three repeated treatments is taken as the result; the transfection reagents are all DNA Fect Transfection Reagent DNA transfection reagents, CWBIO, Cat No.CW0860, the amount of transfection reagent added in each treatment is 6 μl, and the operation is carried out according to the instructions):
[0065] Group 1: 0.4 μg pRL-TK plasmid (reference control plasmid), 2.0 μg recombinant plasmid pGL4-SSA-p65, 4.0 μg plasmid vector pCS2-Fok I (PEAS type) and 4.0 μg plasmid vector pCS2-Fok I (PERR type) co-transfection 1×10 6 293T cells;
[0066] Group 2: 0.4 μg pRL-TK plasmid (reference control plasmid), 2.0 μg recombinant plasmid pGL4-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com