Method for making high simulation specimens of medicinal plants
A technology of medicinal plants and production methods, which can be used in educational utensils, instruments, teaching models, etc., can solve the problems of waste of resources, differences, and color distortion of organs, and achieve the effects of being easy to carry and display, not easy to damage, and easy to store.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
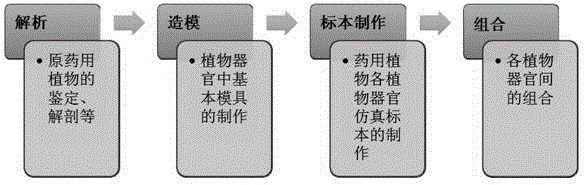
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Example 1 (making of high-simulation specimens of the medicinal plant Platycodon grandiflorum)
[0067] 1. Analysis method of medicinal plants
[0068] 1.1 Identification: Through morphological observation, document checking, specimen checking, plant growth process observation, etc., it is determined that the selected medicinal plants are Plantae, Angiosperms, Dicotyledons, Compositae, Platycodonaceae, Campanulaceae, Campanulaceae, and Campanulaceae (Platycodon grandiflorum (Jacq.) A. DC.).
[0069] 1.2 Analysis
[0070] 1.2.1 The identified medicinal plants were taken, and their organs were analyzed respectively, and the morphological characteristics of the various parts of the medicinal plants were obtained: it is a perennial herb, the root is oblong or long spindle, the lower part is tapering, and there are occasional branches , 7-20cm long, 0.7-2cm in diameter; white or light yellowish white surface, with horizontally long lenticel-like spots. There are horizonta...
Embodiment 2
[0115] Embodiment 2 (making of high imitation specimen of medicinal plant Curcuma curcuma)
[0116] 1. Analysis method of medicinal plants
[0117] 1.1 Identification Through morphological observation, checking literature, checking specimens, observing plant growth process and other studies, it is determined that the selected medicinal plants are Plantae, Angiosperms, Monocots, Musaceae, Zingiberaceae, Curcuma, Curcuma ( Curcuma wenyujin Y.H. Chen et C.Ling).
[0118] 1.2 Analysis
[0119] 1.2.1 Take the identified medicinal plants, analyze their organs respectively, and conclude that the morphological characteristics of the various parts of the medicinal plants are: perennial herbs, with oval, long ovate, conical or long spindle-shaped roots , the top is blunt, the base is blunt, 2~8cm long, 1.5~4cm in diameter, the surface is light grayish brown or grayish brown; the rhizome is fleshy, oval or long oval, yellow, visible links and fibrous root scars, aromatic, leaf base , ...
Embodiment 3
[0164] Embodiment 3 (making of the artificial specimen of medicinal plant Cistanche deserticola)
[0165] 1. Analysis method of medicinal plants
[0166] 1.1 Identification Through morphological observation, checking literature, checking specimens, observing plant growth process, etc., it is determined that the selected medicinal plants are Plantae, Angiosperms, Dicotyledons, Labiatae, Ledanaceae, Cistanche, Cistanche deserticola (Cistanche deserticola Ma).
[0167] 1.2 Analysis
[0168] 1.2.1 Take the identified medicinal plants, analyze their organs respectively, and conclude that the morphological characteristics of the various parts of the medicinal plants are: perennial parasitic herbs, 40-160 cm high, mostly underground; unbranched or free-standing parts 2-4 branches, the diameter of the lower part can reach 5-10 (-15) cm, and it gradually becomes thinner upwards, with a diameter of 2-5 cm. Leaves broadly ovate or triangular ovate, 0.5-1.5cm long, 1-2cm wide, denser i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com