Method of utilizing human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells as feed layer to culture human induced pluripotent stem cells
A technology of pluripotent stem cells and pluripotent stem cells, which is applied in the direction of cells modified by introducing foreign genetic material, can solve the problems of limiting the clinical application of human iPSCs, the culture generation is only 14 generations, and the feeder-free medium is expensive. The effect of clinical application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
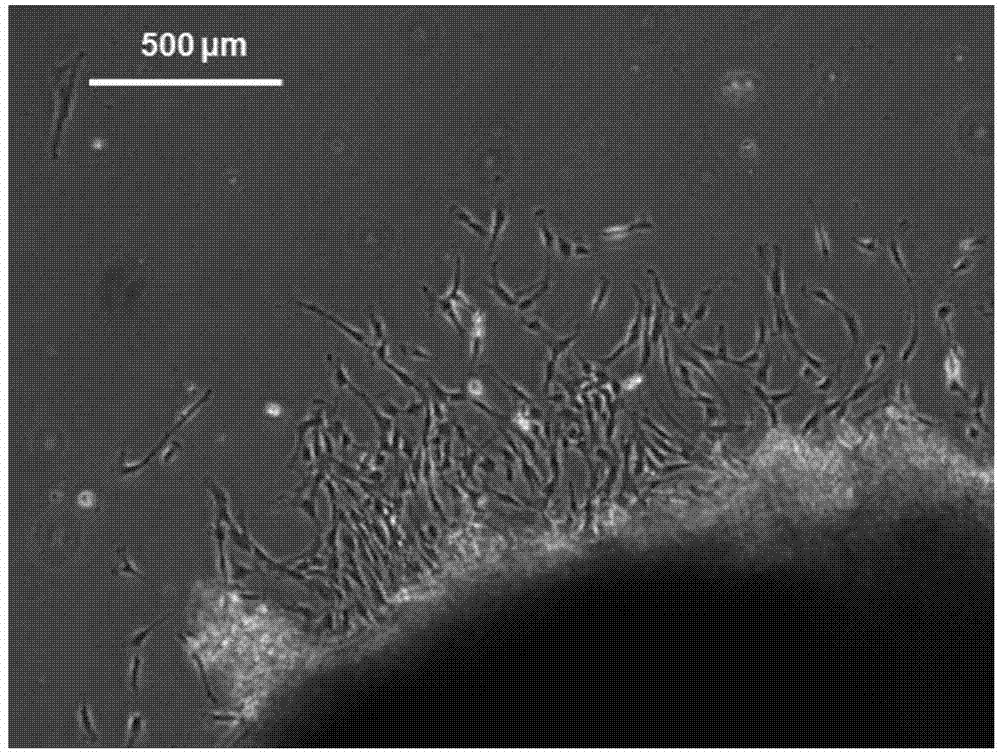
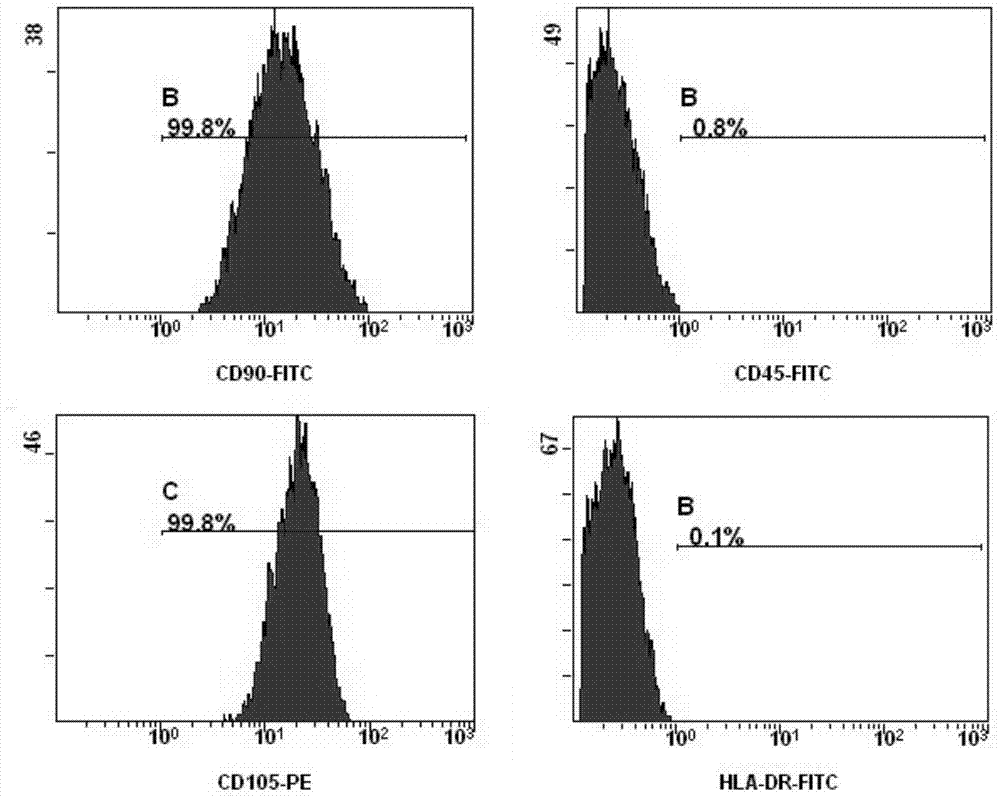
[0045] Example 1 Isolation, cultivation and identification of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
[0046] 1. Test method
[0047] 1.1 Isolation and culture method
[0048] Human umbilical cord tissue with a length of about 10 cm was aseptically obtained from the delivered fetus, and the umbilical cord was cut longitudinally in an aseptic manner, and the umbilical artery and umbilical vein were removed, and then washed three times with PBS. Mechanically cut the remaining tissue to about 0.2cm 3 Size, use the tissue block attachment method to attach the tissue block to a 10cm cell culture dish, add the mesenchymal stem cell serum-free medium (Lonza) containing 1% double antibody, and place it at 37°C in 5% CO 2 The cells were cultured in an incubator, and the medium was changed every 3 days. After the cells reached 90% confluence, they were digested with 0.05% trypsin, and subcultured into P1 cells at a ratio of 1:4, and then continued to be subcultured at a ratio of...
Embodiment 2
[0055] The preparation of embodiment 2 feeder layers
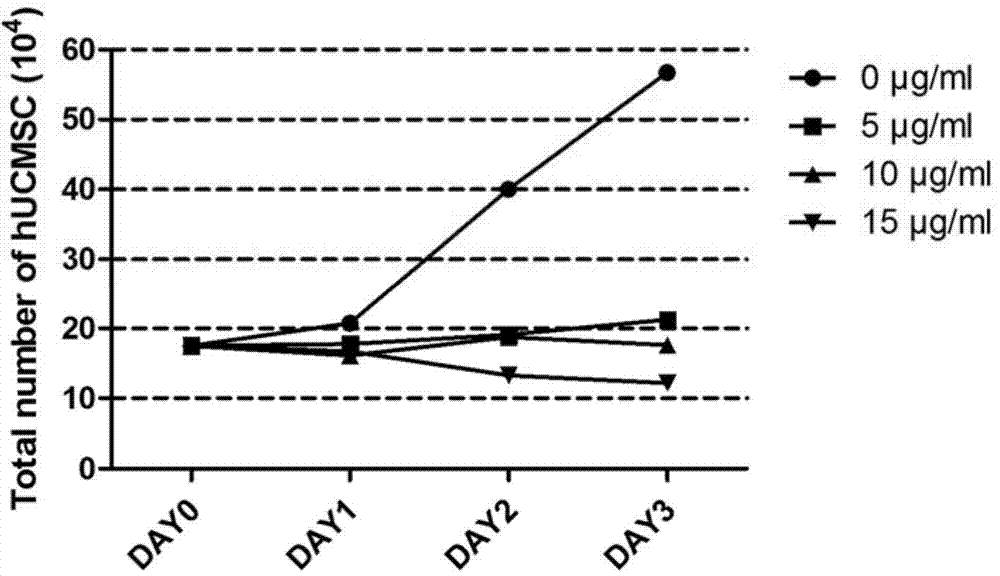
[0056] 1. Screening of mitomycin C concentration
[0057] Experimental method: Take the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUCMSC) isolated in Example 1, inoculate them into a 6cm cell culture dish after subculture, and culture them with mesenchymal stem cell serum-free medium (Lonza), and use 5 μg / ml , 10 μg / ml and 15 μg / ml mitomycin C for 3 hours, the group without mitomycin C was used as the blank control group, and the experimental group was washed with PBS for 3 times after treatment, and replaced with serum-free medium for mesenchymal stem cells (Lonza) at 37°C 5% CO 2 cultured in a cell culture incubator. Trypsinization was performed on the 0th day, the 1st day, the 2nd day and the 3rd day after treatment in each group, counted by trypan blue staining, and three replicate wells were set up.
[0058] Experimental results: The cells in the blank control group proliferated normally, while the proliferation...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The preparation of embodiment 3 feeder layer
[0064] Experimental method: the third to seventh generation human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUCMSC) isolated in Example 1 were used as feeder layer. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells were digested with 0.05% trypsin, stained with trypan blue and counted at 0.7×10 4 cells / cm 2 The density was seeded on a 10cm culture dish, cultured in serum-free medium (Life), and the confluence of the cells was about 40% the next day. Add mitomycin C with a final concentration of 10 μg / ml, place it in a cell culture incubator for 2 hours, wash it with PBS three times after treatment, and replace it with a serum-free medium (Life) to obtain human umbilical cord mesenchyme Stem cell feeder layer and used within 24 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com