Optical interferometer used for detecting inner arc surface of annular guide rail
An annular guide rail and optical interference technology, applied in the field of optical interferometers, can solve the problems of the influence of interferometer detection accuracy and reliability, detection profile deviation, and inability to obtain three-dimensional surface profile at one time, so as to improve test efficiency and precision. , Improve the accuracy and reliability, the effect of low external environment requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
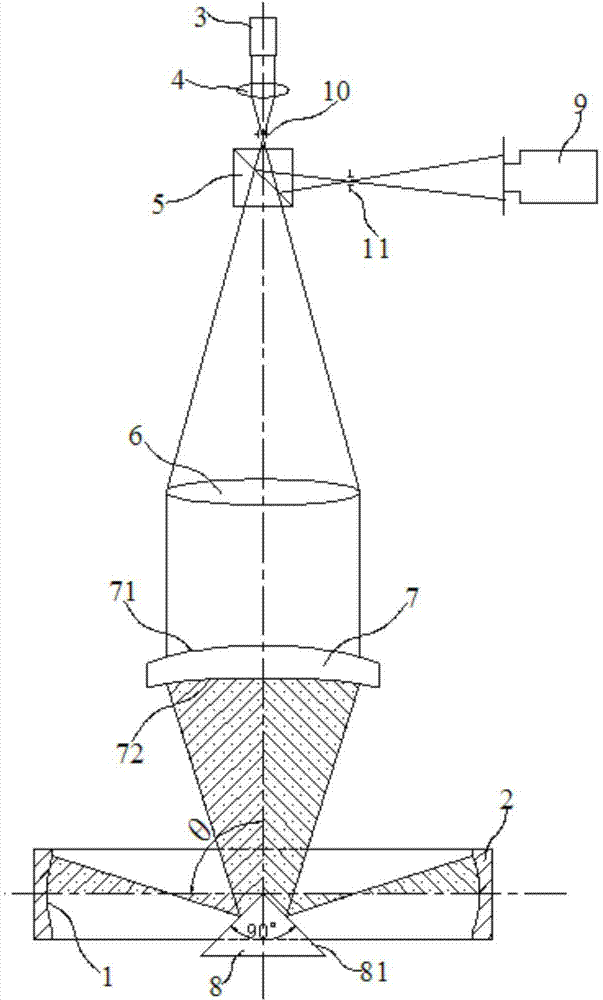
[0026] Embodiment 1: An optical interferometer for detecting the inner arc surface of the circular guide rail, the inner arc surface 1 is located along the circumference of the annular guide rail 2 and is located on the inner side, including a laser 3, a condensing convex lens 4, and a beam splitter 5 , as the collimating convex lens 6 of objective lens, reference lens 7 and conical mirror 8, described condensing convex lens 4 is positioned between laser 3 and collimating convex lens 6 and the focal point of condensing convex lens 4 coincides with the focal point of collimating convex lens 6; The beam splitter 5 is located between the condensing convex lens 4 and the collimating convex lens 6, and is used to divide the light from the collimating convex lens 6 into a first beam and a second beam; the reference lens 7 is located between the collimating convex lens 6 and the collimating convex lens 6. On the opposite side of the beam splitter 5, the surface opposite to the collima...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2: An optical interferometer for detecting the inner arc surface of the ring guide rail, the inner arc surface 1 is located along the circumference of the ring guide rail 2 and is located on the inner side, including a laser 3, a condensing convex lens 4, and a beam splitter 5 , as the collimating convex lens 6 of objective lens, reference lens 7 and conical mirror 8, described condensing convex lens 4 is positioned between laser 3 and collimating convex lens 6 and the focal point of condensing convex lens 4 coincides with the focal point of collimating convex lens 6; The beam splitter 5 is located between the condensing convex lens 4 and the collimating convex lens 6, and is used to divide the light from the collimating convex lens 6 into a first beam and a second beam; the reference lens 7 is located between the collimating convex lens 6 and the collimating convex lens 6. On the opposite side of the beam splitter 5, the surface opposite to the collimating co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com