Tension-compression and torsion vibration fatigue test device
A fatigue test and torsional vibration technology, applied in the direction of applying repetitive force/pulsation force to test the strength of materials, can solve the problems of time-consuming, labor-intensive, and long-time consumption, and achieve the effects of improving test efficiency, reducing operating temperature, and reducing heat
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
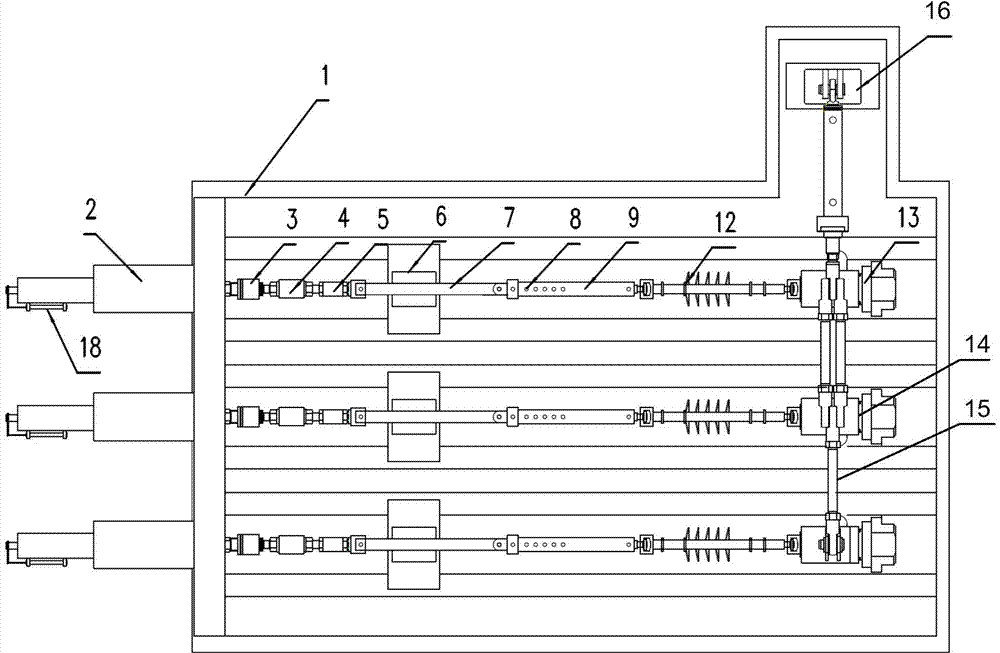
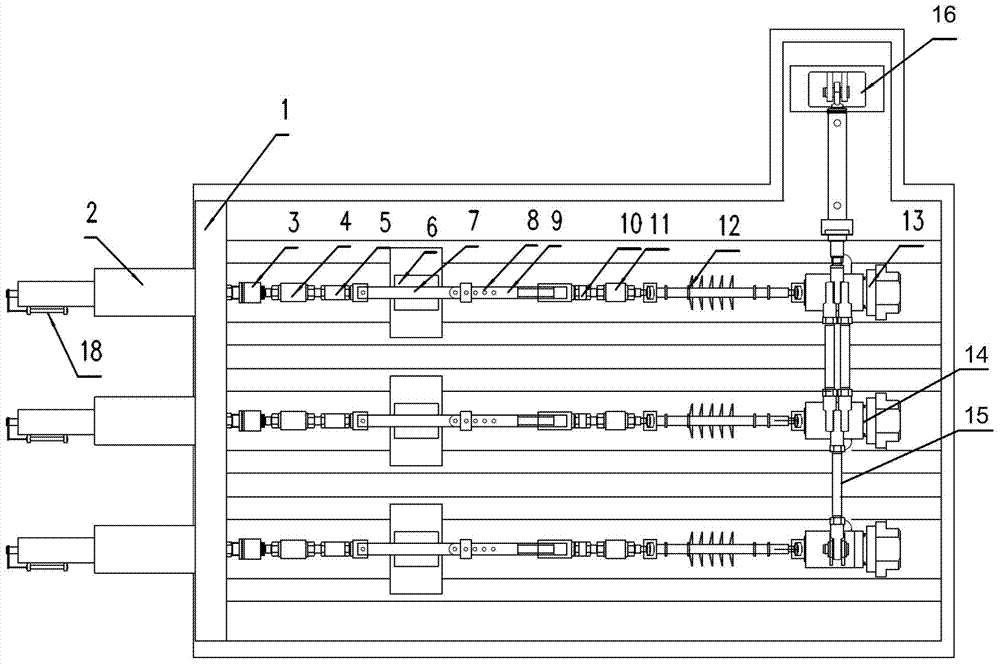
[0025] figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of the tension-compression and torsional fatigue vibration test device of this embodiment, which includes a test device bench 1, 3 sets of tension-compression test mechanisms and 1 set of torsion test mechanisms. This embodiment only takes 3 stations as an example. In practice, more workstations can be designed according to needs and space. In this embodiment, the tension-compression and torsional fatigue vibration tests of three tested workpieces can be completed simultaneously.
[0026] Such as figure 1 As shown, each tension-compression test mechanism includes a tension-compression cylinder 2 , a first connector 3 , a force sensor 4 , a second connector 5 , a guide mechanism 6 , a guide rod 7 and an adjustment rod 9 .
[0027] Wherein, the tension-compression actuator 2 is a linear motion conversion mechanism, which is installed on the test bench 1, and the piston rod of the tension-compression actuator 2 is connected t...
Embodiment 2
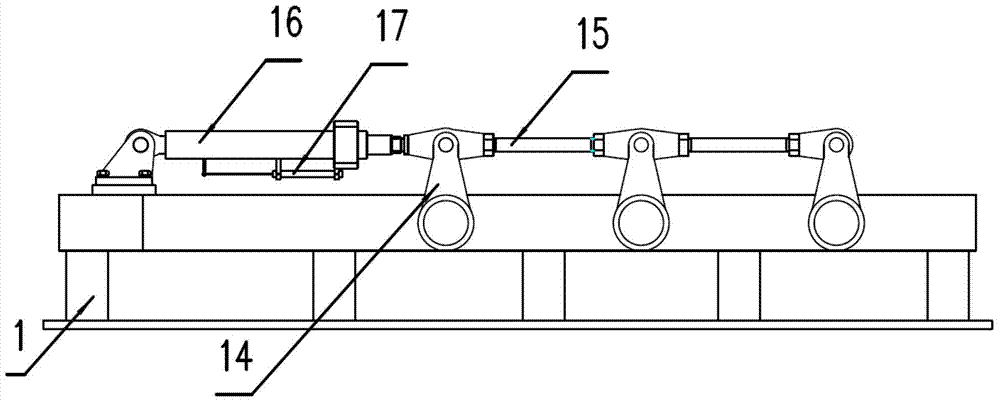
[0035] Such as image 3 As shown, this embodiment is an improvement on Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, in order to monitor the torsional moment generated under the applied torsion angle, a third connecting piece 10 and a torque sensor 11 are added, the adjusting rod 9 is connected with the torque sensor 11 through the third connecting piece 10, and the torque sensor 11 is then It is connected to one end of the workpiece 12 under test.
[0036] In addition, this embodiment also improves the adjusting rod 9 . Such as image 3 As shown, a row of equally spaced positioning holes 8 is designed at one end of the adjusting rod 9 , and the other end is connected to the screw hole provided by the third connecting piece 10 through threads. The adjusting rod 9 can be connected with the guide rod 7 through any positioning hole 8, and the space occupied by the tested workpiece 12 can be fine-tuned by adjusting the thread connection depth of the third connecting piece 10 and the adjust...
Embodiment 3
[0038] In the tension-compression fatigue test, a constant static force is usually applied to the workpiece to be tested, and then an alternating force is superimposed on this basis. In the prior art, the pulling and pressing actuator 2 usually uses a hydraulic actuator to carry out the above test. Because the test time required for the fatigue test is long, the energy consumed is very large, and the actuator will be exhausted when it works for a long time. A lot of heat is generated, causing seal damage and piston rod wear.
[0039] Therefore, the pulling and pressing actuator 2 of the present embodiment adopts a composite actuator. The composite actuating cylinder is a structure in which the static loading cylinder and the dynamic loading cylinder are integrated, as shown in FIG. 4(a), which includes a coaxially connected static loading cylinder 2-1 and a dynamic loading cylinder 2-2. The inner chambers of the static loading cylinder 2-1 and the dynamic loading cylinder 2-2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com