Method for Comprehensive Recovery of Valuable Minerals from River Tailings
A tailings and river channel technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, wet separation, solid separation, etc., can solve the problems of comprehensive recovery difficulties, low recovery rate, single element recovery, etc., to save a lot of money and reduce emissions , Optimizing the effect of the ecological environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
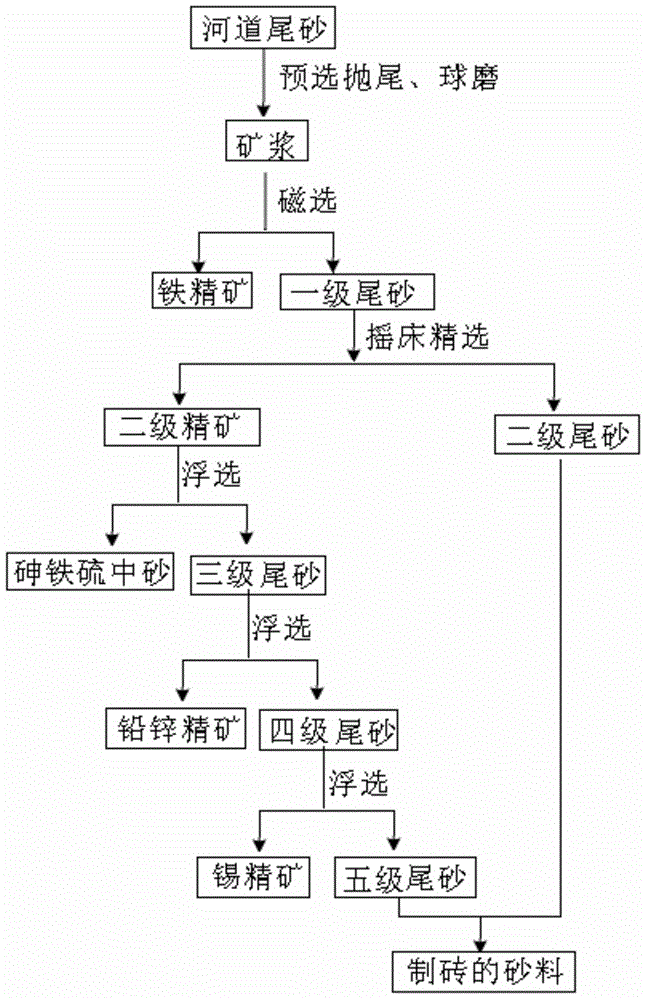
[0015] Specific implementation mode one: the method for comprehensive recovery of valuable minerals from river tailings in this embodiment is carried out according to the following steps:
[0016] 1. The river tailings are pre-selected and thrown by a sawtooth wave jig and / or spiral classifier to obtain river tailings with a particle size d≤2mm, and then ball milled by a ball mill to obtain ore pulp;
[0017] 2. Pass the ore pulp obtained in step 1 through a magnetic separator to obtain iron concentrate and first-grade tailings after magnetic separation;
[0018] 3. The primary tailings are selected by shaking table to obtain the secondary concentrate and secondary tailings;
[0019] 4. Secondary concentrate flotation of arsenic-iron-sulfur ore to obtain arsenic-iron-sulfur ore and third-grade tailings;
[0020] 5. Three-stage tailings flotation lead-zinc concentrate to obtain lead-zinc concentrate and four-stage tailings;
[0021] Sixth, the fourth-grade tailings flotation ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0023] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that during the pre-selection of tailings in step 1, the river tailings with a particle size of d are pre-selected and discarded, and the river tailings of 0.45mm≤d≤2mm use sawtooth The wave jig pre-selects the tailings; for the river tailings with a particle size d<0.45mm, the spiral classifier pre-selects the tailings. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0024] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that the particle size d≤0.165mm of the river tailings in the pulp in step one, and the mass percentage of the river tailings in the pulp is 95% to 98%; other It is the same as the specific embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com