Process for treating free alkali in red mud by microorganisms
A technology of microbial treatment and process method is applied in the field of environmental treatment of non-ferrous metal metallurgical waste, which can solve the problems of complex process and unfavorable soil reclamation, and achieve the effects of simple process, short cycle and cost reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
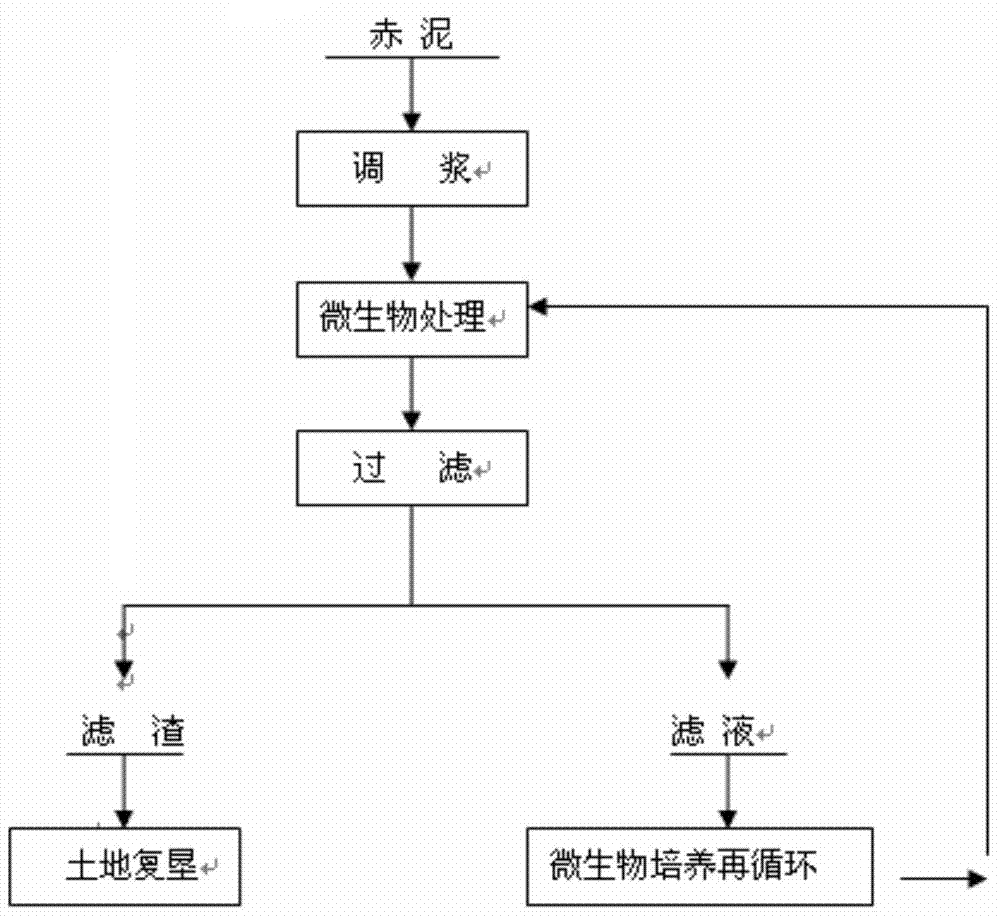
[0024] a. Red mud contains 2.8% by weight of free alkali Na2O, 0.3% by weight of K2O, and 3.1% by weight of total free alkali. The percentage by weight of adding water to the red mud is 10%;
[0025] b. Pour the pulp after pulping into the stirring tank, under the conditions of controlling the temperature at 25°C and the pressure at 0.1MPa, add the acidic solution of domesticated lactic acid bacteria, and control the pH of the solution to 7; directly stir for 10 hours.
[0026] c. Filter the treated pulp to obtain a solution containing microorganisms and send it to a microorganism cultivation tank to cultivate microorganisms for recycling.
[0027] d. After removing free alkali, the red mud filter cake contains 0.8% of total free alkali, which reduces the environmental damage to the soil and can be used for land reclamation.
Embodiment 2
[0029] a. Red mud contains 3.1% by weight of free alkali Na2O, 0.2% by weight of K2O, and 3.3% by weight of total free alkali. Add water to the red mud to adjust the weight percentage to 20%.
[0030] b. Pour the pulp after pulping into the stirring tank, under the condition of controlling the temperature at 15°C and the pressure at 0.1MPa, add the domesticated acidic solution of Thiobacillus ferrothiobacillus, and control the pH of the solution to 7.5.
[0031] Direct stirring treatment for 20 hours.
[0032] c. Filter the treated pulp to obtain a solution containing microorganisms and send it to a microorganism cultivation tank to cultivate microorganisms for recycling.
[0033] d. After removing free alkali, the red mud filter cake contains 0.9% of total free alkali, which reduces the environmental damage to the soil and can be used for land reclamation.
Embodiment 3
[0035] a. Red mud contains 4.38% by weight of free alkali Na2O, 0.04% by weight of K2O, and 4.42% by weight of total free alkali. Add water to the red mud to adjust the weight percentage to 30%.
[0036] b. The ore pulp after pulping is poured into the stirring tank. Under the conditions of controlling the temperature at 20°C and the pressure at 0.1MPa, add the acidic solution of domesticated lactic acid bacteria, and control the pH of the solution to 8.
[0037] Direct stirring treatment for 30 hours.
[0038] c. Filter the treated pulp to obtain a solution containing microorganisms and send it to a microorganism cultivation tank to cultivate microorganisms for recycling.
[0039] d. The red mud filter cake after the free alkali removal treatment contains 0.95% of the total free alkali, which reduces the environmental damage to the soil and can be used for land reclamation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com