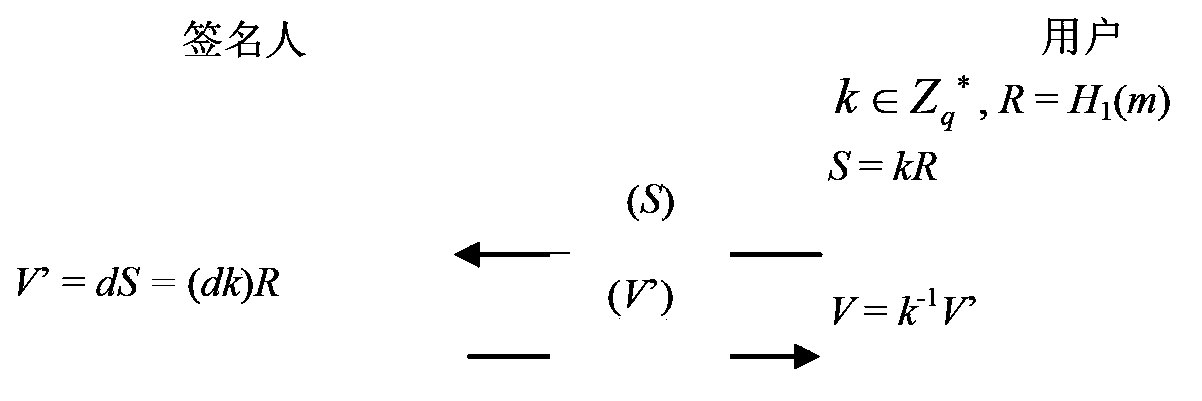Blind signature method based on elliptic curve and device thereof
An elliptic curve and blind signature technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of untraceable signed messages, the signer does not know the specific content of the message, and the signer cannot know, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
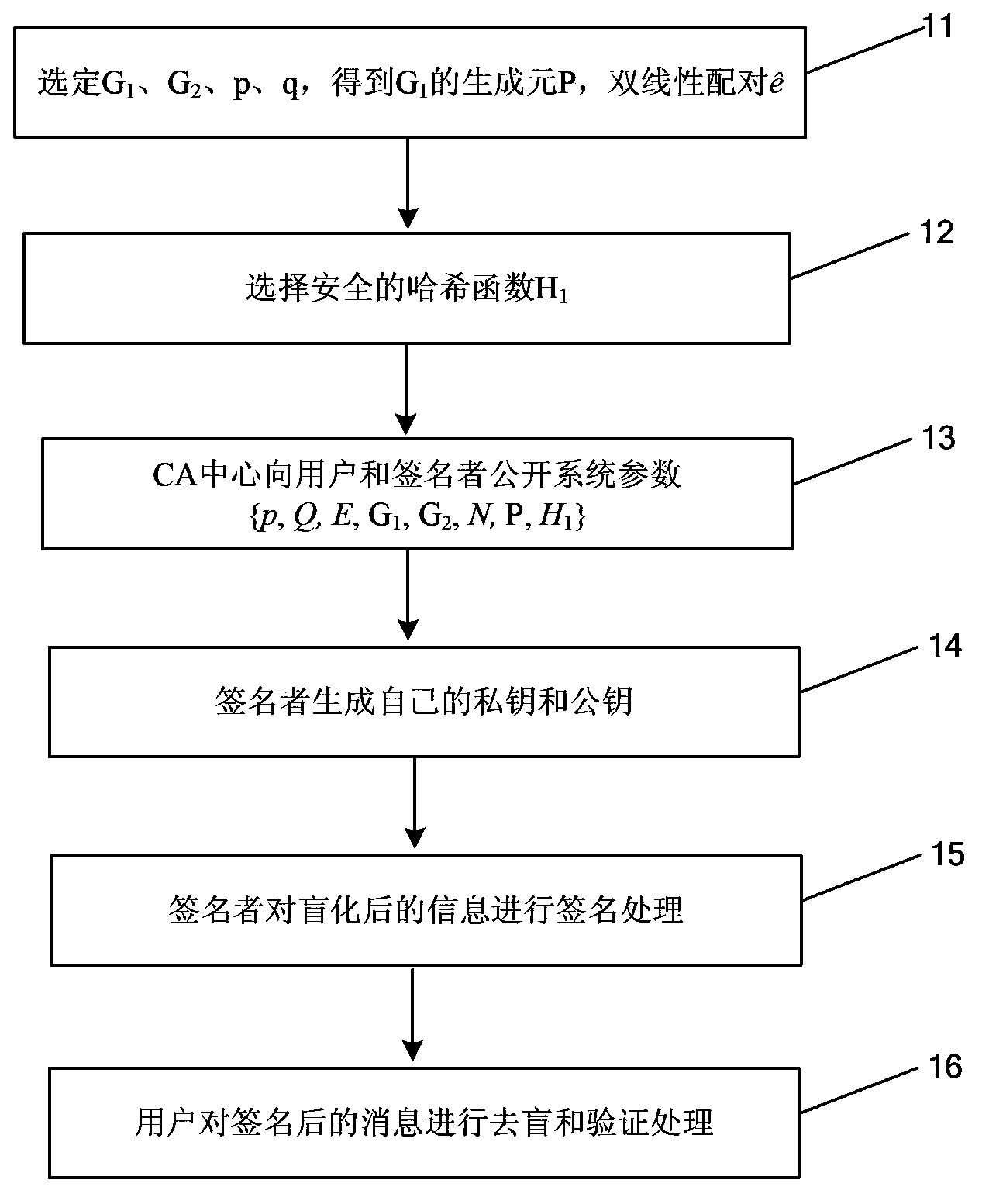
[0025] The processing flow of an elliptic curve-based blind signature method provided in this embodiment is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the following processing steps are included:
[0026] Step 11: Select G 1 , G 2 , p, q, get G 1 The generator P of the bilinear pairing
[0027] selected G 1 , G 2 are two groups of order q, p and q are two large prime numbers (where p is at least 512 bits, and q is at least 160 bits), and q is a prime factor of p+1, and the number of bits of q is given by n said. G 1 is F p A subgroup of the additive group of elliptic curves E on the above F p Represents a field composed of integers from 0 to p-1, the above elliptic curve E can be shaped like: y 2 =f(x), G 2 is the domain A multiplicative group on , where by F p Obtained by the second expansion, the shape is F p [x] / f, F p [x] is F p The ring of polynomials on , f is a quadratic irreducible reduction polynomial. P is G 1 The generator of , namely q*P=O, "O" is the po...
Embodiment 2
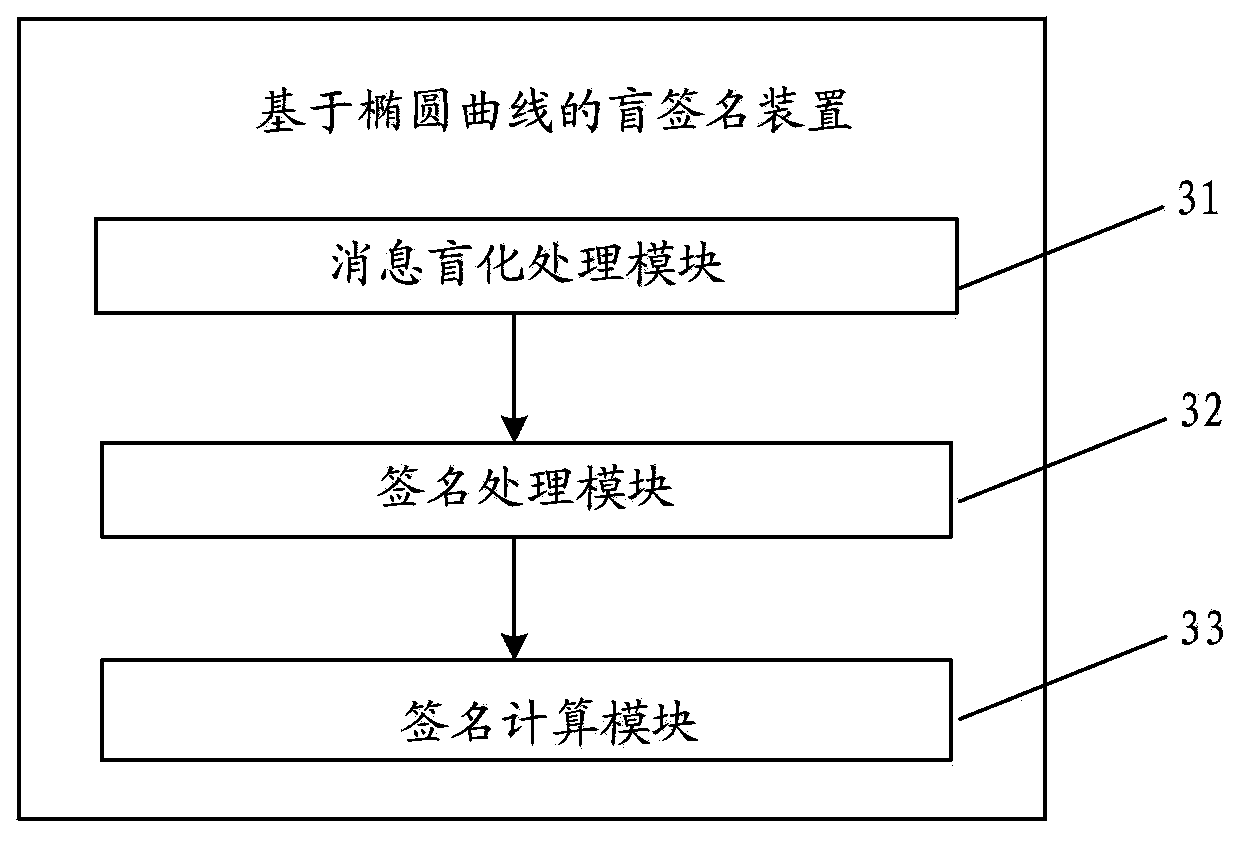
[0077] This embodiment provides a blind signature device based on elliptic curve, its specific structure is as follows image 3 As shown, the following modules are included:
[0078] The message blinding processing module 31 is used to randomly select the blinding factor k∈Z by sending the user q * , calculate R=H 1 (m), S=kR, the m is an arbitrary length 0, 1 string m in the information to be signed, the S is a blinded message, the q is a set large prime number, and the Z q * Represents an integer within the range of 1~(q-1), the H 1 is a one-way hash function that maps m to G 1 A point on the elliptic curve E, the G 1 is F p A subgroup of order q on the additive group of elliptic curves E, the F p It is a field composed of integers from 0 to p-1, the p is a set large prime number, and the q is a prime factor of p+1;
[0079] The signature processing module 32 is used to sign S with the private key d of the signer, calculate V'=dS=dkR, and send V' to the receiving us...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com