Bioartificial proximal tubule systems and methods of use
A bioartificial, renal proximal tubule technology, applied in the field of bioartificial proximal tubule devices, can solve the problems of inability to measure the influence of renal tubules, inability to measure flow changes, physiological and dynamic conditions, laborious separation techniques, species differences, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0097] Example 1: Seeding and Differentiation of hKDCs on Extracellular Matrix Scaffolds
[0098] This experiment tests the attachment, growth and differentiation of human kidney-derived cells ("hKDC") on various configurations of extracellular (ie, acellular) matrix scaffolds as well as traditional culture on collagen-coated cell chambers.
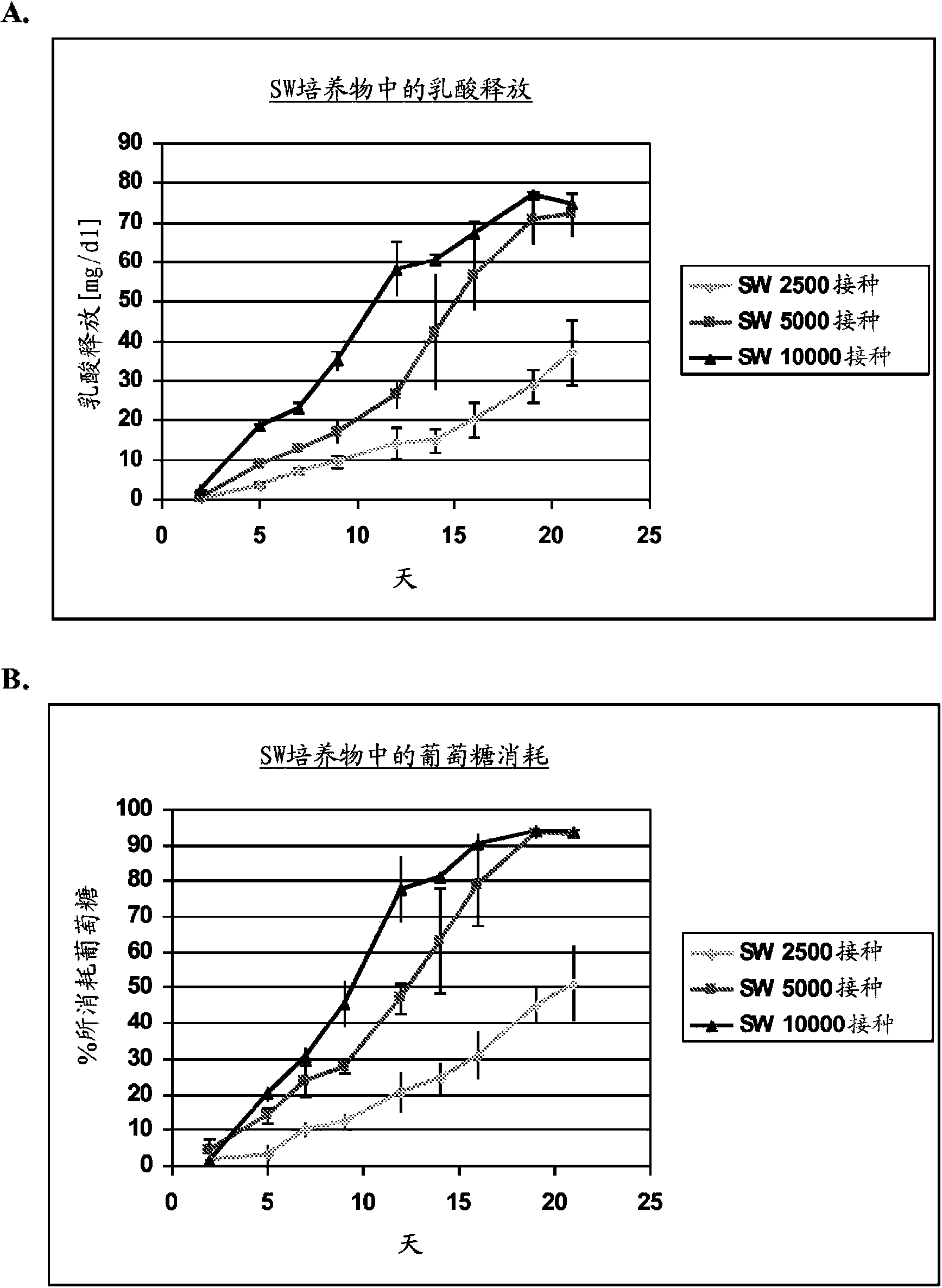
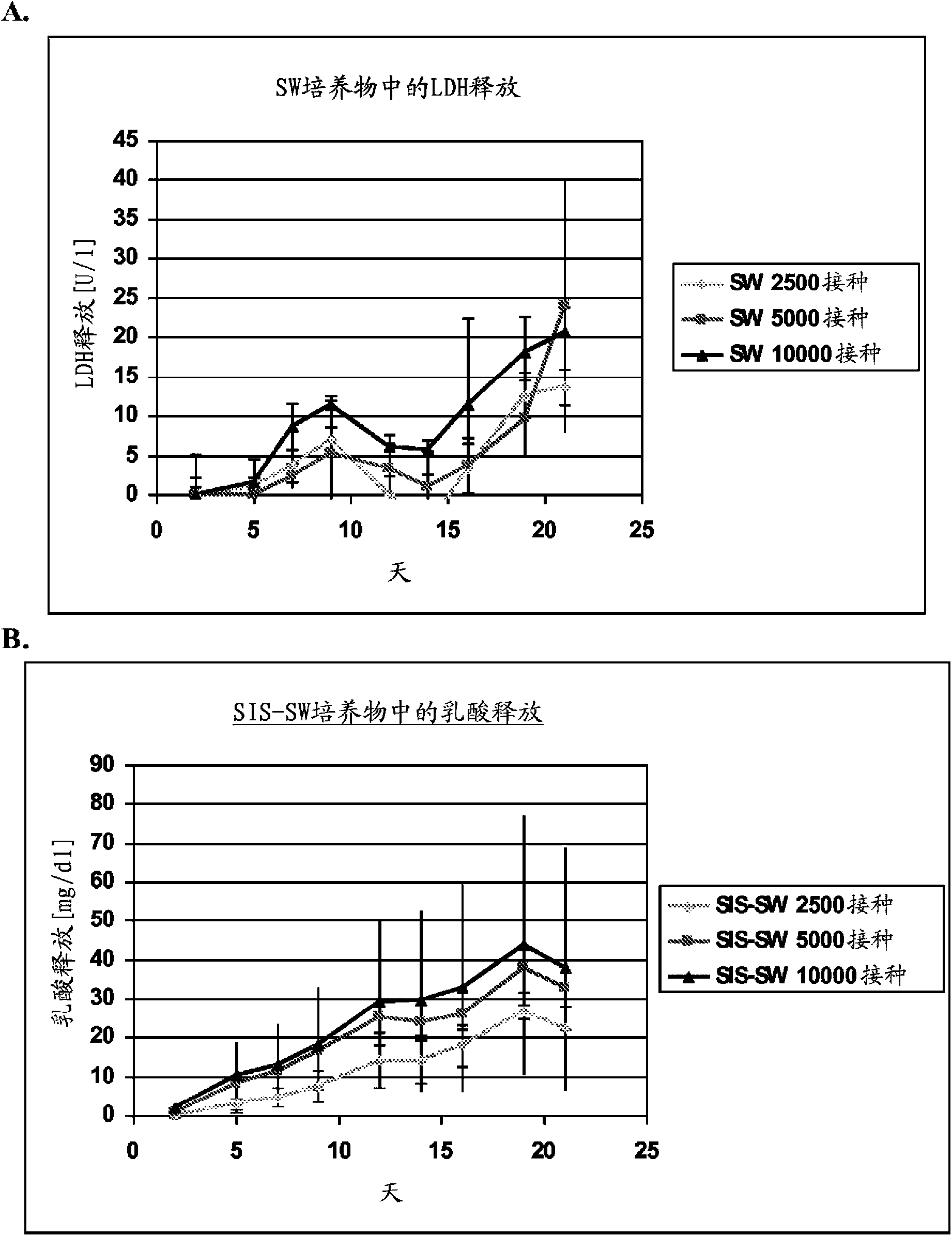
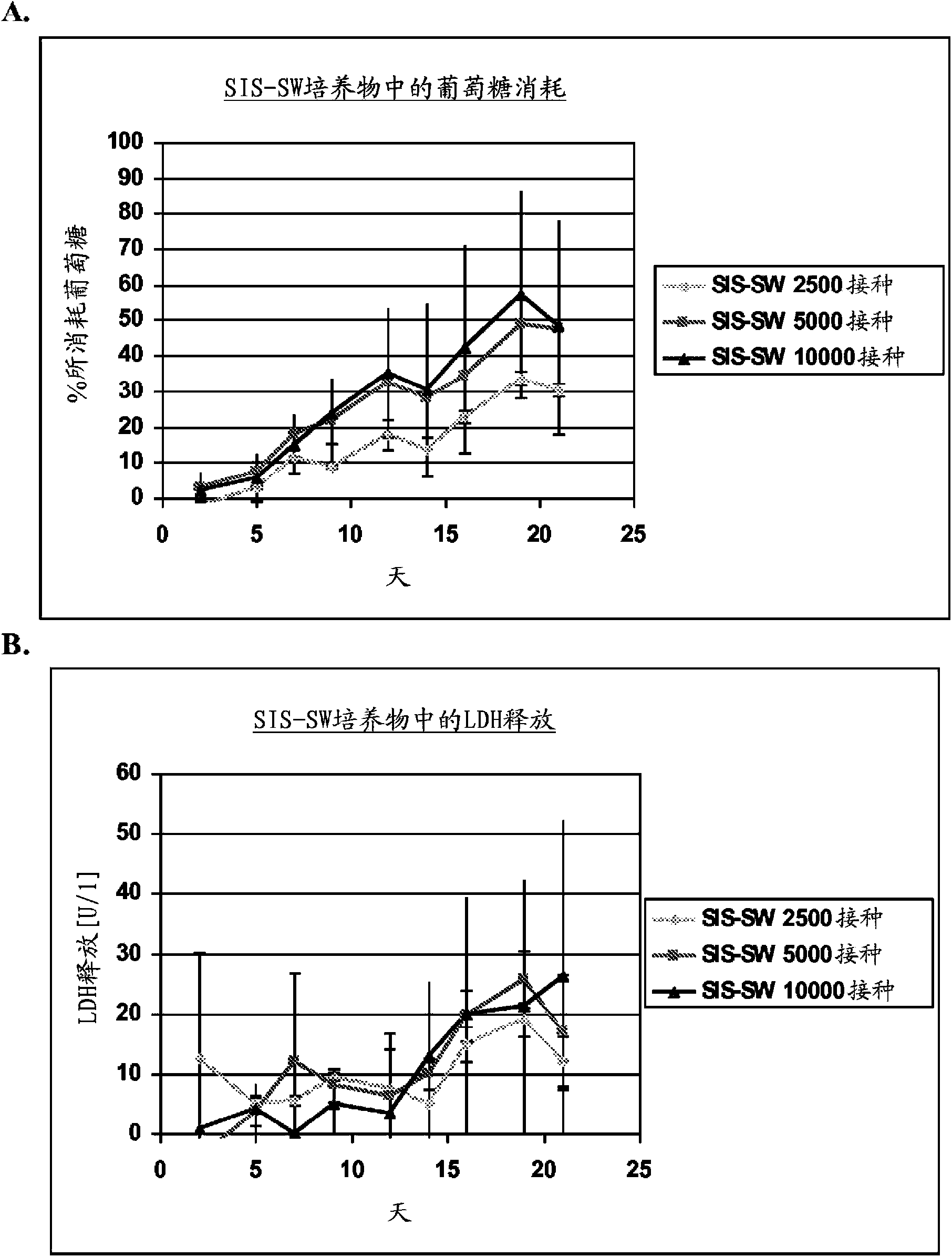
[0099] Four passages of hKDC were seeded onto three different scaffold configurations and cell chambers (Coming, Coming NY). use REGM TM Kidney epithelial cell growth medium (Lonza, Walkersville MD) cells were cultured for a period of more than three weeks. Each scaffold configuration was tested with three different cell concentrations: 2.5 × 10 3 , 5×10 3 , and 1×10 4 cells. The configurations tested were: 1) collagen sandwich culture; 2) collagen-SIS sandwich culture; 3) SIS monolayer culture; and 4) collagen coated cell chambers.
[0100] Collagen sandwich culture
[0101] hKDCs were cultured between two collagen gel layers ...
example 2
[0114] Example 2: Optimization of Cell Seeding Concentration for hKDCs on Decellularized Scaffolds
[0115] Example 1 shows that cells seeded onto a collagen-free two-dimensional decellularized scaffold form a confluent monolayer of epithelial cells that express proximal tubule markers after three weeks in culture. Perform the following experiments to optimize cell seeding density and attempt to shorten the culture period required to form a monolayer.
[0116] Scaffolds were prepared by decellularizing certain fragments of the small intestinal submucosa (SIS) as described in Example 1 . at three different concentrations (1×10 4 , 5×10 4 and 1×10 5 cells / well) hKDCs of 4 passages were seeded on SIS scaffolds and treated with REGM TM Kidney Epithelial Cell Growth Medium (Lonza, Walkersville) was used to culture them for three weeks. Samples were removed for histological analysis after two and three weeks and fixed with Bouin's fixative for 1 hour. Then, they were washed ...
example 3
[0124] Example 3: Immunohistochemistry of p-glycoprotein-1
[0125] Scaffolds were prepared by decellularizing certain fragments of the small intestinal submucosa (SIS) as described in Example 1 . Take 5×10 4 Four passages of hKDCs were seeded onto SIS scaffolds at a concentration of 3 cells / scaffold and treated with REGM TMKidney Epithelial Cell Growth Medium (Lonza, Walkersville) was used to culture them for three weeks. Samples were removed for histological analysis after three weeks and fixed with Bouin's fixative for 1 hour. Afterwards, the samples were washed in water for at least 4 hours and embedded in paraffin. Subsequently, 3 μm thick sections were prepared. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed to confirm the expression of p-glycoprotein-1 (pgp-1, also known as MDR1), an efflux transporter expressed by proximal tubule cells. Target retrieval of dewaxed segments was achieved by enzymatic treatment with proteinase K, heating in citrate buffer pH 6 (Dako, #S2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com