Preparation method of tannin-based adsorbent resin
An adsorption resin and tannin-based technology, applied in the field of preparation of tannin-based adsorption resins, can solve problems such as selective adsorption limitation, and achieve the effects of low cost, strong adsorption capacity and strong adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
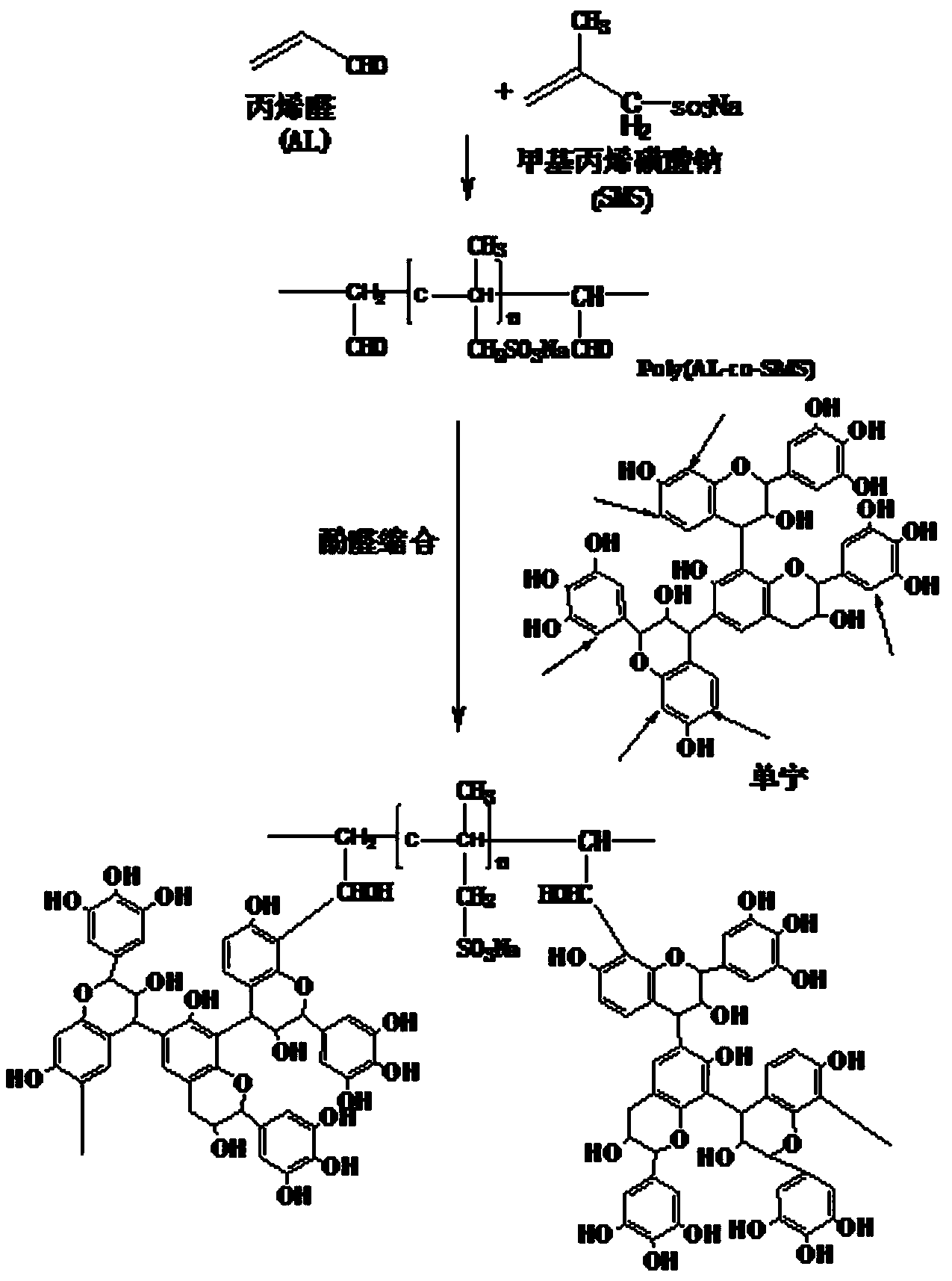
[0014] (1) Synthesis of the copolymer, dissolve a certain amount of methacrylic acid and acrolein in deionized water, the molar ratio of methacrylic acid and acrolein is 1.92:1, and then add potassium peroxodisulfate to initiate After stirring and dissolving, nitrogen was flushed for 13 minutes, sealed, placed in a water bath at 60°C, and reacted for 2.1 hours under magnetic stirring.
[0015] (2) Synthesis of tannin-based adsorption resin, dissolving tannin with 70% of the total mass of methacrylic acid and acrolein in deionized water, adjusting the pH of the solution to 9.5, and then, using (1) synthesized The copolymer solution and the tannin solution were mixed, stirred in an environment of 70° C. for 31 minutes, and left to stand to obtain a tannin-based adsorption resin.
[0016] The tannin-based adsorption resin obtained by the above method has an adsorption capacity of 1.3 mmolg / g for lead ions when the pH value is 5.5.
Embodiment 2
[0018] (1) Synthesis of the copolymer, dissolve a certain amount of methacrylic acid and acrolein in deionized water, the molar ratio of methacrylic acid and acrolein is 1.99:1, and then add potassium peroxodisulfate to initiate After stirring and dissolving, nitrogen was flushed for 14 minutes, sealed, placed in a water bath at 56°C, and reacted for 2.5 hours under magnetic stirring.
[0019] (2) Synthesis of tannin-based adsorption resin, dissolving tannin with 52% of the total mass of methacrylic acid and acrolein in deionized water, adjusting the pH of the solution to 9.8, and then, using (1) synthesized The copolymer solution and the tannin solution were mixed, stirred in an environment of 74° C. for 22 minutes, and left to stand to obtain a tannin-based adsorption resin.
[0020] When the pH value of the tannin-based adsorption resin obtained by the above method is 5.5, the adsorption capacity of lead ions is 2.55mmolg / g.
Embodiment 3
[0022] (1) Synthesis of the copolymer, dissolve a certain amount of methacrylic acid and acrolein in deionized water, the molar ratio of methacrylic acid and acrolein is 2.08:1, and then add potassium peroxodisulfate to initiate After stirring and dissolving, nitrogen was flushed for 11 minutes, sealed, placed in a water bath at 63°C, and reacted for 2.8 hours under magnetic stirring.
[0023] (2) Synthesis of tannin-based adsorption resin. Dissolve tannin with 86% of the total mass of methacrylic acid and acrolein in deionized water, adjust the pH of the solution to 9.1, and then, the The copolymer solution and the tannin solution were mixed, stirred in an environment of 67° C. for 38 minutes, and left to stand to obtain a tannin-based adsorption resin.
[0024] When the pH value of the tannin-based adsorption resin obtained by the above method is 5.5, the adsorption capacity of lead ions is 3.45mmolg / g.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com