Brushless harmonic excitation motor with initial self-starting capacity
A brushless harmonic and self-starting technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, electromechanical devices, synchronous machine parts, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to achieve weak magnetic speed expansion, difficult to adjust, etc., and achieve simple structure, good performance, and convenient manufacture Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
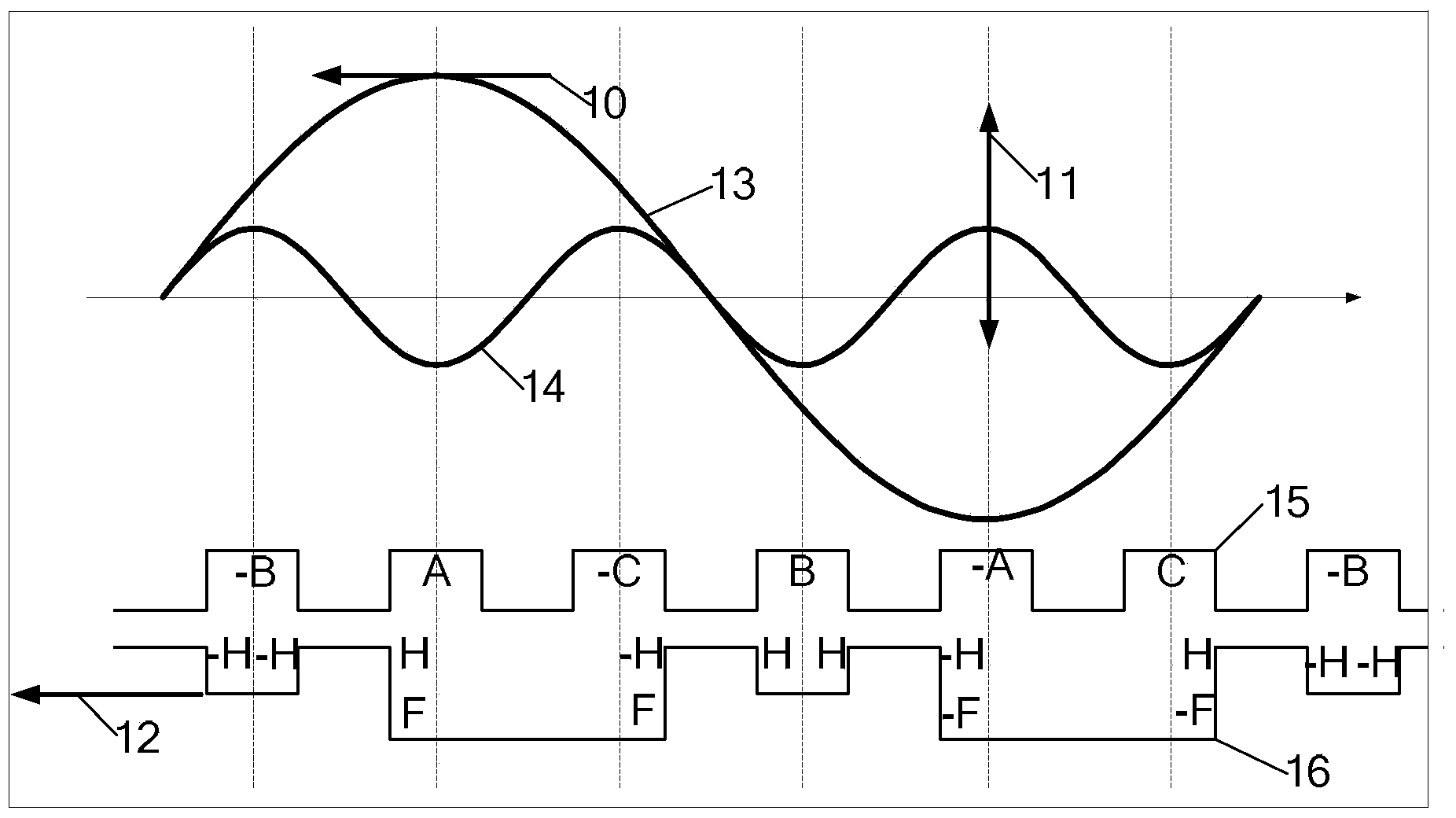
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
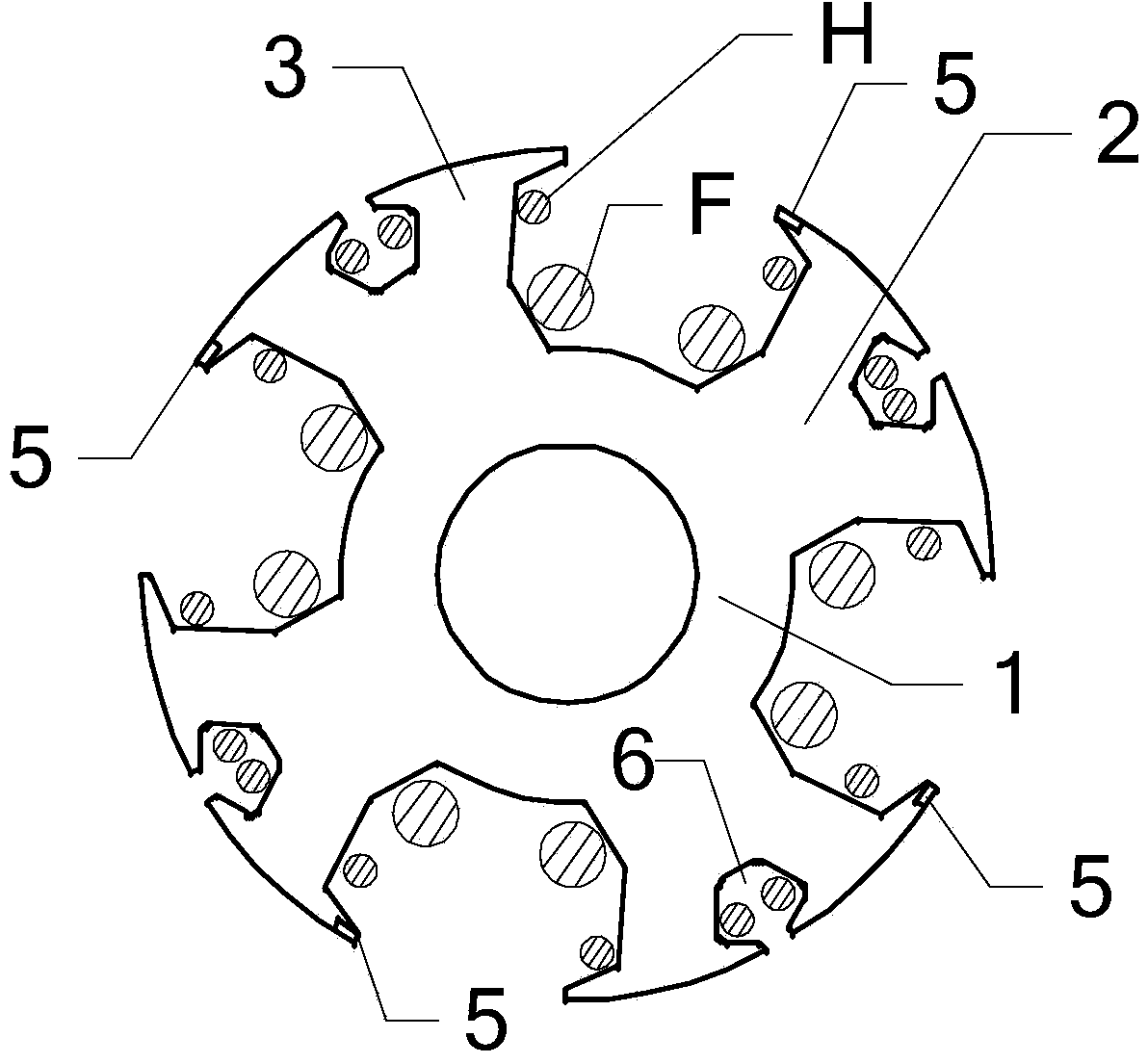
[0022] Specific implementation mode one: see figure 1 Describe this embodiment, a brushless harmonic excitation motor with initial self-starting capability described in this embodiment, the rotor core 1 of the motor has a 4-pole structure, each pole has a rotor main tooth,
[0023] Each rotor main tooth is covered with an excitation winding F, and one end of the pole shoe 2 of each rotor main tooth is provided with a permanent magnet 5 of NdFeB material, and one end of the pole shoe 2 of each rotor main tooth is adjacent to it The other ends of the pole pieces 2 of the rotor main teeth are oppositely arranged, and the excitation directions of the permanent magnets 5 of NdFeB material on the two adjacent rotor main teeth are opposite,
[0024] The middle position of the pole piece 2 of each main tooth of each rotor is provided with a winding slot 6, and the four winding slots 6 divide the four pole pieces 2 into eight rotor teeth 3, and each rotor tooth 3 is nested with a harmo...
specific Embodiment approach 2
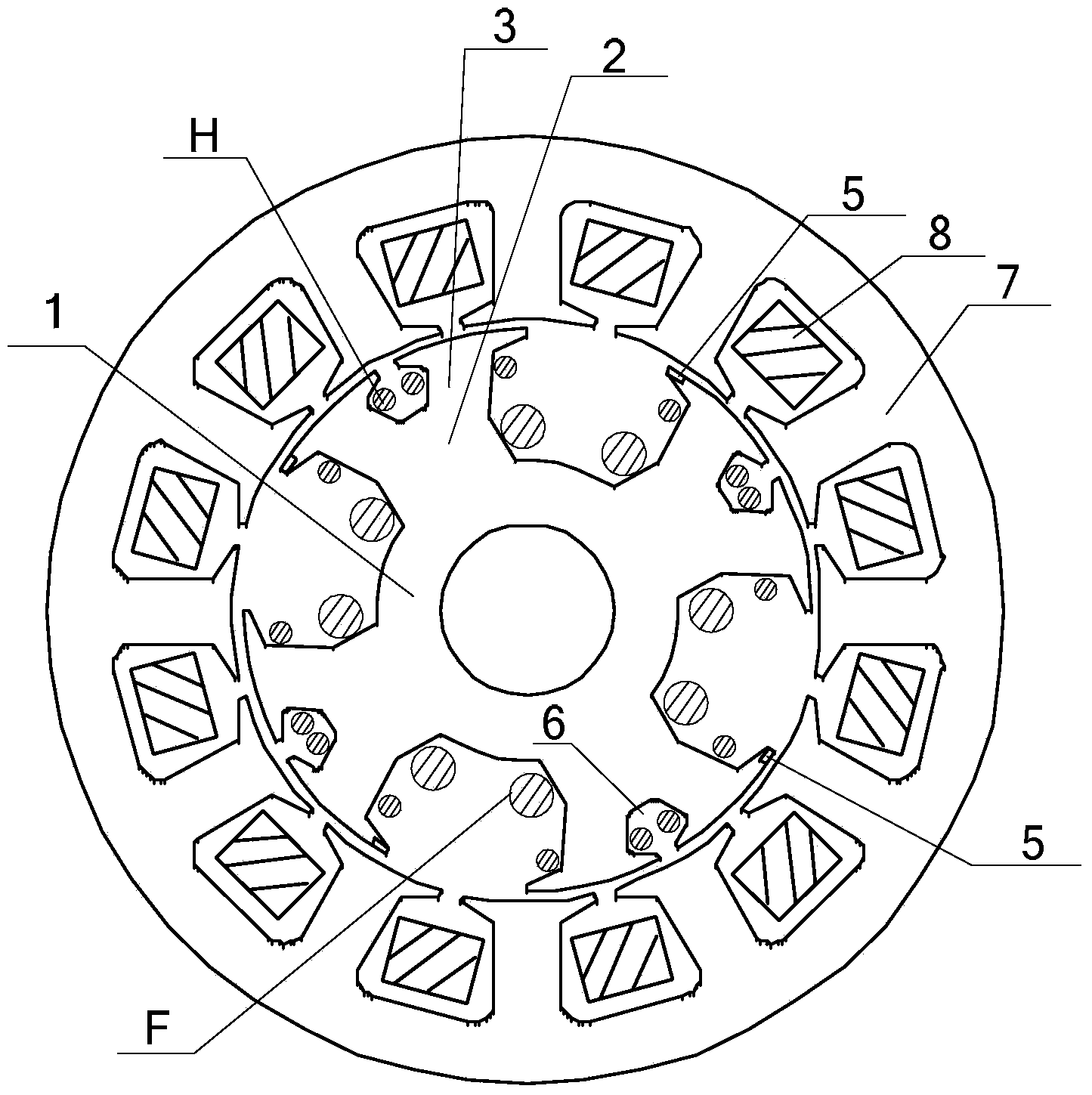
[0028] Specific implementation mode two: see figure 1 and figure 2 Describe this embodiment. The difference between this embodiment and the brushless harmonic excitation motor with initial self-starting capability described in Embodiment 1 is that the stator core 7 of the motor has a 12-slot structure, and the stator is three-phase The winding 8 has a single-layer structure and is an open winding with a pitch of 3.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0029] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and the brushless harmonic excitation motor with initial self-starting capability described in Embodiment 1 is that the stator core 7 of the motor has a 12-slot structure, and the stator is three-phase The winding 8 has a double-layer structure and is an open winding with a pitch of 3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com