Process for preparing cellulose ether with low degree of polymerization and cellulose ether prepared therefrom
A cellulose ether, low degree of polymerization technology, applied in the field of cellulose ether, can solve problems such as discoloration and yellowing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0025] It is preferable to carry out the preparation of alkali cellulose and the depolymerization reaction while sufficiently stirring. This makes it possible to distribute the alkali metal hydroxide solution, oxygen or oxygen-containing gas and heat evenly into the slurry, thereby obtaining the advantageous results of the invention.
[0026] The reaction temperature of the first depolymerization of alkali cellulose with oxygen is preferably 20 to 100°C, more preferably 30 to 90°C, still more preferably 40 to 90°C. The reaction time for the depolymerization of alkali cellulose with oxygen is generally 5 minutes to 2 hours, but depends on the temperature.
[0027] The percent viscosity reduction in the depolymerization reaction of alkali cellulose with oxygen is preferably from 10 to 95%. The term "percent viscosity reduction" as used herein can be determined by the following equation:
[0028] Viscosity reduction percentage (%)={1-(V 1 / V 0 )}×100
[0029] where V 0 (mPa...
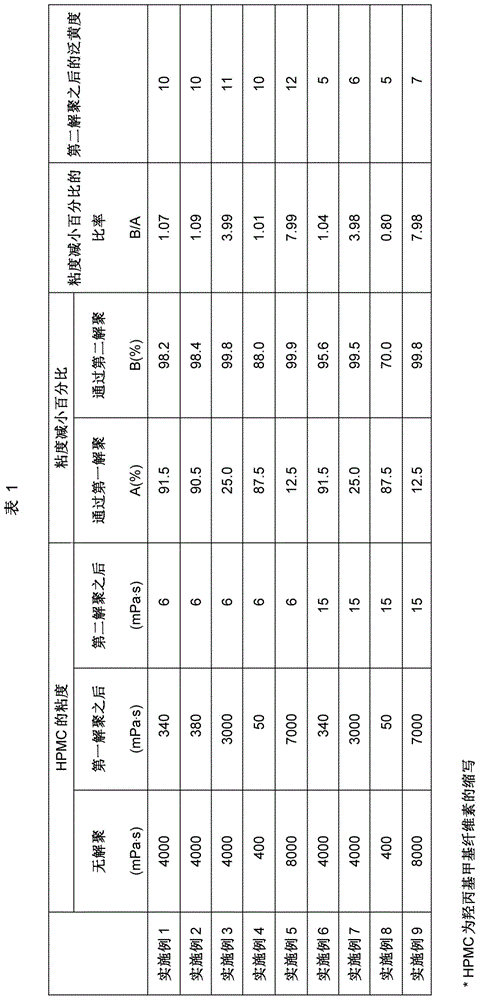
Embodiment 1
[0058] (a) Preparation of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) without depolymerization
[0059] Wood pulp in the form of chips (degree of polymerization Dpw=2100) was immersed in 44% by weight aqueous sodium hydroxide solution, followed by centrifugation to obtain alkali cellulose. The weight ratio of the alkali metal hydroxide in the alkali cellulose to the solid component in the slurry was determined by titration and was found to be 1.25. The resulting alkali cellulose (5.5 kg, as a solid component in the slurry) was placed in a 100 L pressure-resistant reactor. After vacuum treatment, 11 kg of methyl chloride and 2.7 kg of propylene oxide were added thereto and reacted with alkali cellulose. The reaction product was washed with hot water and then dried in a drier using a combination of jacket heating and hot air heating until the weight loss on drying reached 2% by weight. Subsequently, impact crushing was performed to obtain HPMC. Regarding the degree of substitution of...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Prepare HPMC in the same manner as in Example 1, the difference is that the weight ratio of the alkali metal hydroxide in the alkali cellulose and the solid component in the slurry is 1.05, and the gained alkali cellulose (5.5kg, as the solid component in the slurry points) were placed in a 100L pressure-resistant reactor, and after vacuum treatment, 10 kg of methyl chloride and 1.3 kg of propylene oxide were added. Regarding the degree of substitution of the HPMC thus obtained measured using the method of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia, DS was 1.80 and MS was 0.15. The results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com