Method for fabricating gradient ultra-fine metal grains
A production method and ultra-fine grain technology, which are applied in the field of material processing, can solve the problems of ultra-fine grain materials such as elasticity, low toughness, no work hardening performance, and low shear band height.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] A method for producing graded ultra-fine grained titanium metal is disclosed, including the following steps:
[0038] A. Immerse a 36mm secondary commercial pure Ti plate in liquid nitrogen and cool it to -170°C~-90°C. The purpose of cooling the metal plate to this temperature is to reduce the increase in material temperature during the subsequent rolling process. Prevent heat from recrystallizing and growing the refined grains;
[0039] B. Roll the Ti plate with a compression amount of 2mm each time, and cool the rolled Ti plate to -170°C~-90°C. Gradually rolling can make the stress distributed along the material surface to the internal gradient. Continuing to cool afterwards can keep the surface metal crystal grains in a nano-sized state;
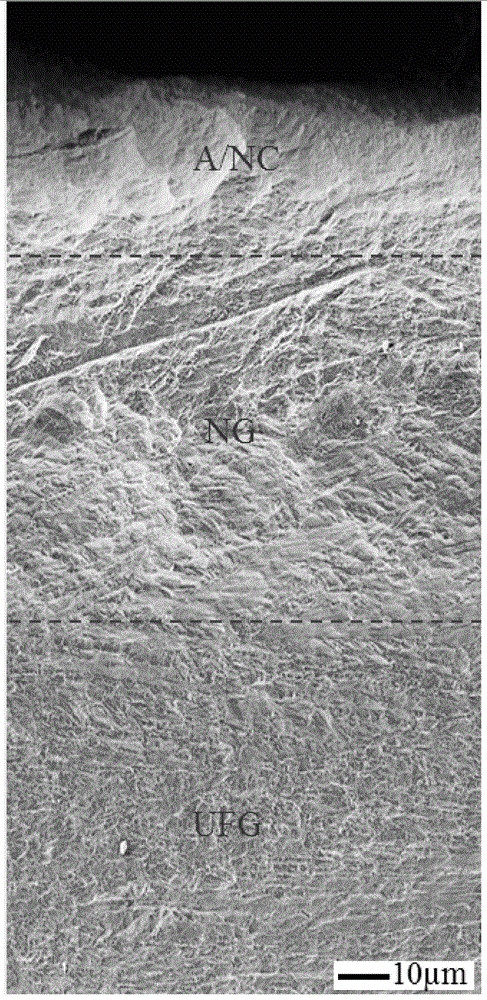
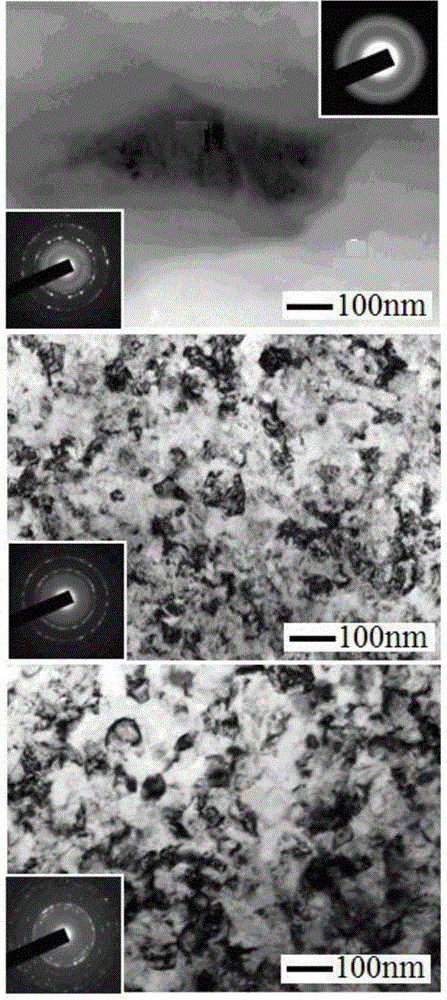
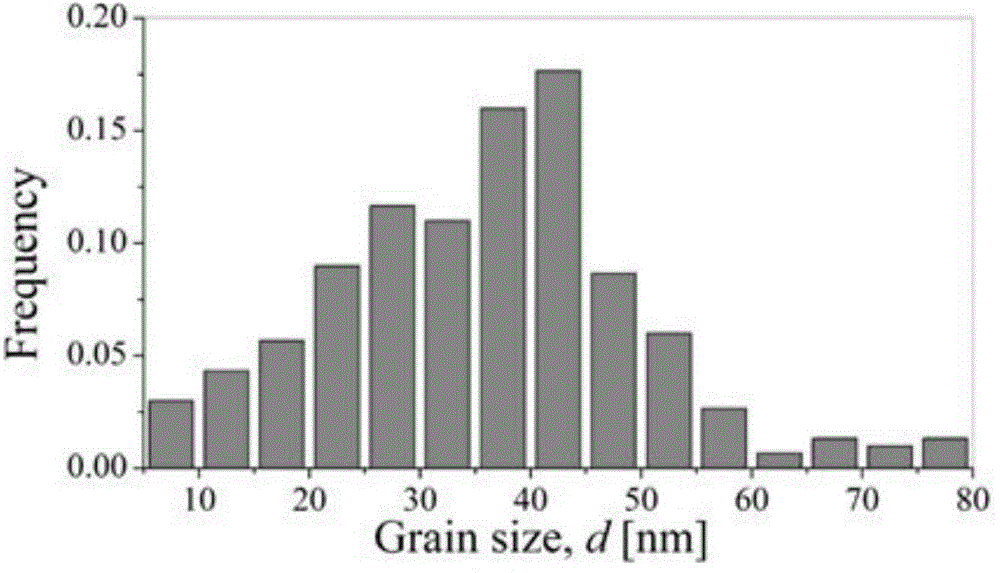
[0040] C. Repeat step B until the thickness of the Ti plate is 5mm, and the weak gradient ultra-fine processing stage is completed. At this time, the grain size of the Ti plate decreases gradually from the surface to the inside, and the ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] A. Immerse a 30mm secondary commercial pure Mg plate in liquid nitrogen and cool it to -170°C~-90°C. The purpose of cooling the metal plate to this temperature is to reduce the increase in material temperature during the subsequent rolling process. Prevent heat from recrystallizing and growing the refined grains;
[0046] B. Roll the Mg plate with a compression of 2mm each time, and cool the rolled Mg plate to -170°C~-90°C. Gradually rolling can make the stress distributed along the material surface to the internal gradient. Continuing to cool afterwards can keep the surface metal crystal grains in a nano-sized state;
[0047] C. Repeat step B until the thickness of the Mg board is 4mm, and the weak gradient ultra-fine processing stage is completed. At this time, the grain size of the Mg board decreases gradually from the surface to the inside, ranging from 50 to 250 nm;
[0048] D. After the completion of step C, proceed to the strong gradient ultra-fine processing stage, cu...
Embodiment 3
[0052] A. Immerse a 40mm secondary commercial pure Al plate in liquid nitrogen and cool it to -170°C~-90°C. The purpose of cooling the metal plate to this temperature is to reduce the increase in material temperature during the subsequent rolling process. Prevent heat from recrystallizing and growing the refined grains;
[0053] B. Roll the Al plate with a compression of 2mm each time, and cool the rolled Al plate to -170°C~-90°C. Gradually rolling can make the stress distribution along the material surface to the internal gradient. Continuing to cool afterwards can keep the surface metal crystal grains in a nano-sized state;
[0054] C. Repeat step B until the thickness of the Al plate is 6mm, and the weak gradient ultra-fine processing stage is completed. At this time, the grain size of the Al plate decreases gradually from the surface to the inside, and the range is 50~250nm;
[0055] D. After the completion of step C, perform a strong gradient ultra-fine processing stage, cut th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com