Zero discharge treatment method for wastewater of lead-acid battery
A lead-acid battery and treatment method technology, applied in water/sewage multi-stage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, dehydration/drying/concentrated sludge treatment, etc. The problem of low utilization rate, etc., to achieve the effect of stable sodium ion content, less environmental damage, and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
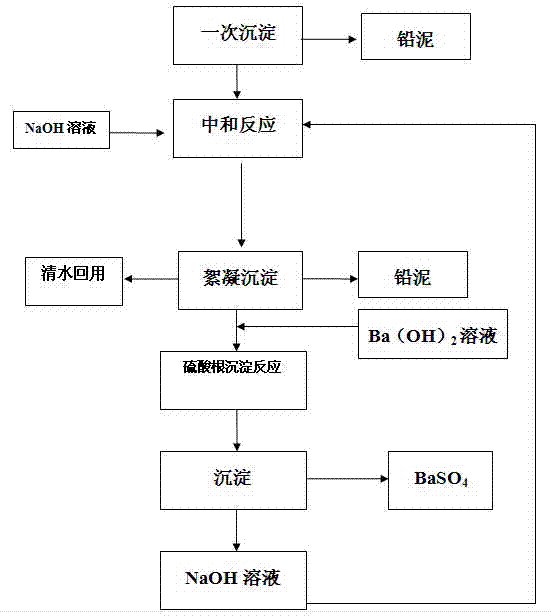
[0049] A zero-discharge treatment method for lead-acid battery wastewater, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0050] (1) Primary sedimentation: lead-acid battery wastewater is introduced from the bottom of the primary sedimentation tank, passes through the inclined tube sedimentation area (using the existing conventional layout method), is discharged from the upper part of the primary sedimentation tank into the regulating tank, and the lead at the bottom of the primary sedimentation tank is collected. Sludge is discharged into the sludge tank.
[0051] (2) Neutralization reaction: NaOH solution is passed into the regulating tank to adjust the pH of the wastewater to 5. NaOH solution is obtained using step (5) Ba(OH) 2 The solution is carried out with the reaction product NaOH in the water after the sulfate ion precipitation reaction. If NaOH is not enough to achieve complete neutralization, an additional part of NaOH needs to be added to adjust the pH ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] A zero-discharge treatment method for lead-acid battery wastewater, comprising the steps of:
[0059] (1) Primary sedimentation: The lead-acid battery wastewater is introduced from the bottom of the primary sedimentation tank, passes through the inclined tube sedimentation area, is discharged from the upper part of the primary sedimentation tank into the regulating tank, and the lead sludge at the bottom of the primary sedimentation tank is collected and discharged into the sludge tank.
[0060] (2) Neutralization reaction: NaOH solution is passed into the regulating tank to adjust the pH of the wastewater to 8. NaOH solution is obtained using step (5) Ba(OH) 2 The solution is carried out with the reaction product NaOH in the water after the sulfate ion precipitation reaction. If NaOH is not enough to achieve complete neutralization, an additional part of NaOH needs to be added to adjust the pH value, and finally adjust the pH of the wastewater to the set value.
[006...
Embodiment 3
[0073] A zero-discharge treatment method for lead-acid battery wastewater, comprising the steps of:
[0074] (1) Primary sedimentation: The lead-acid battery wastewater is introduced from the bottom of the primary sedimentation tank, passes through the inclined tube sedimentation area, is discharged from the upper part of the primary sedimentation tank into the regulating tank, and the lead sludge at the bottom of the primary sedimentation tank is collected and discharged into the sludge tank.
[0075] (2) Neutralization reaction: NaOH solution is passed into the regulating tank to adjust the pH of the wastewater to 7.
[0076] NaOH solution is obtained using step (5) Ba(OH) 2 The solution is carried out with the reaction product NaOH in the water after the sulfate ion precipitation reaction. If NaOH is not enough to achieve complete neutralization, an additional part of NaOH needs to be added to adjust the pH value, and finally adjust the pH of the wastewater to the set value...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com