Rotation piezoelectric energy collecting device
A technology for collecting device and electrical energy, applied in piezoelectric effect/electrostrictive or magnetostrictive motors, electrical components, generators/motors, etc. and other problems, to achieve the effects of reducing vibration and noise, improving power-to-weight ratio, suppressing residual pulsating torque and unbalanced magnetic pull
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
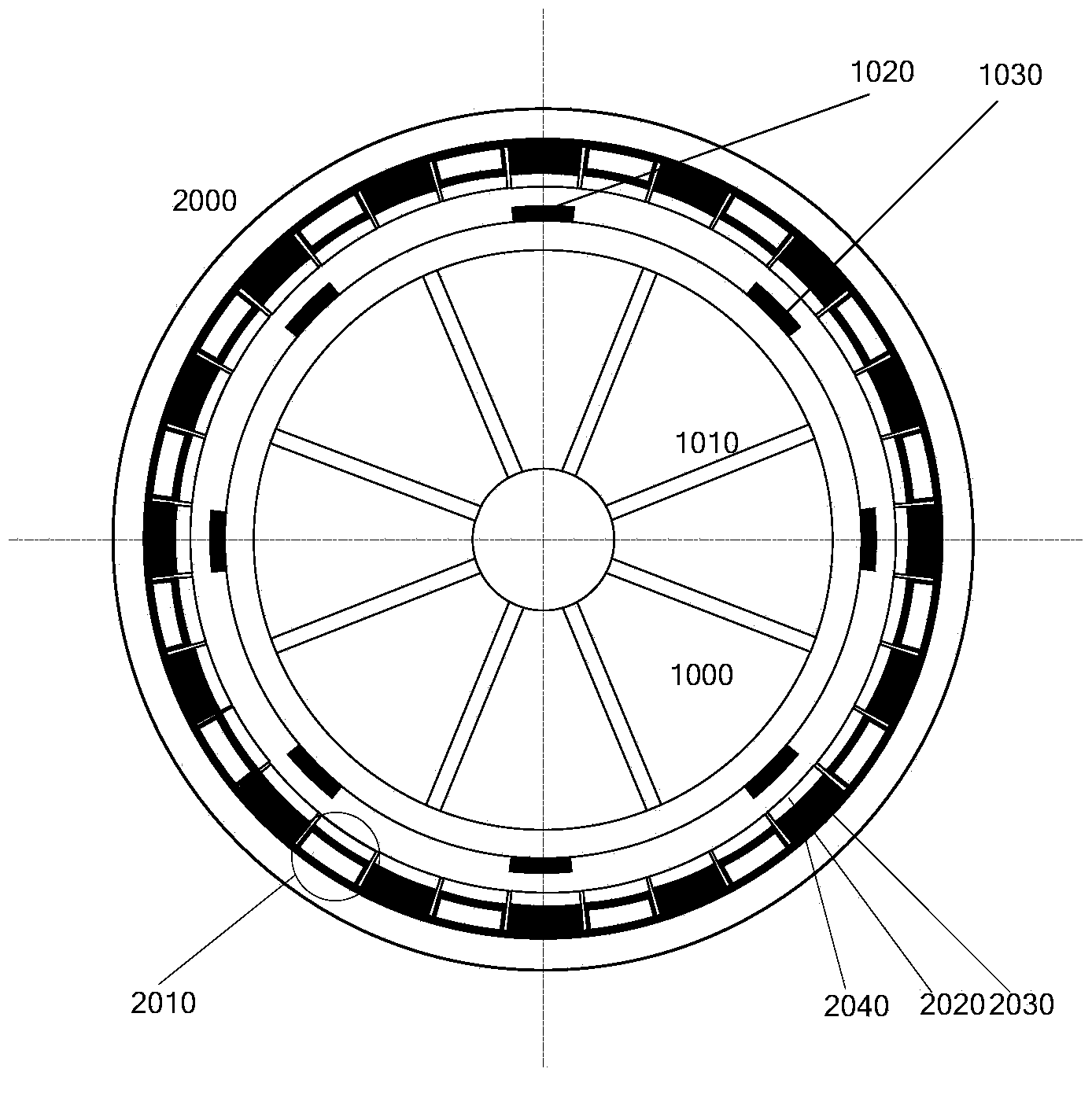
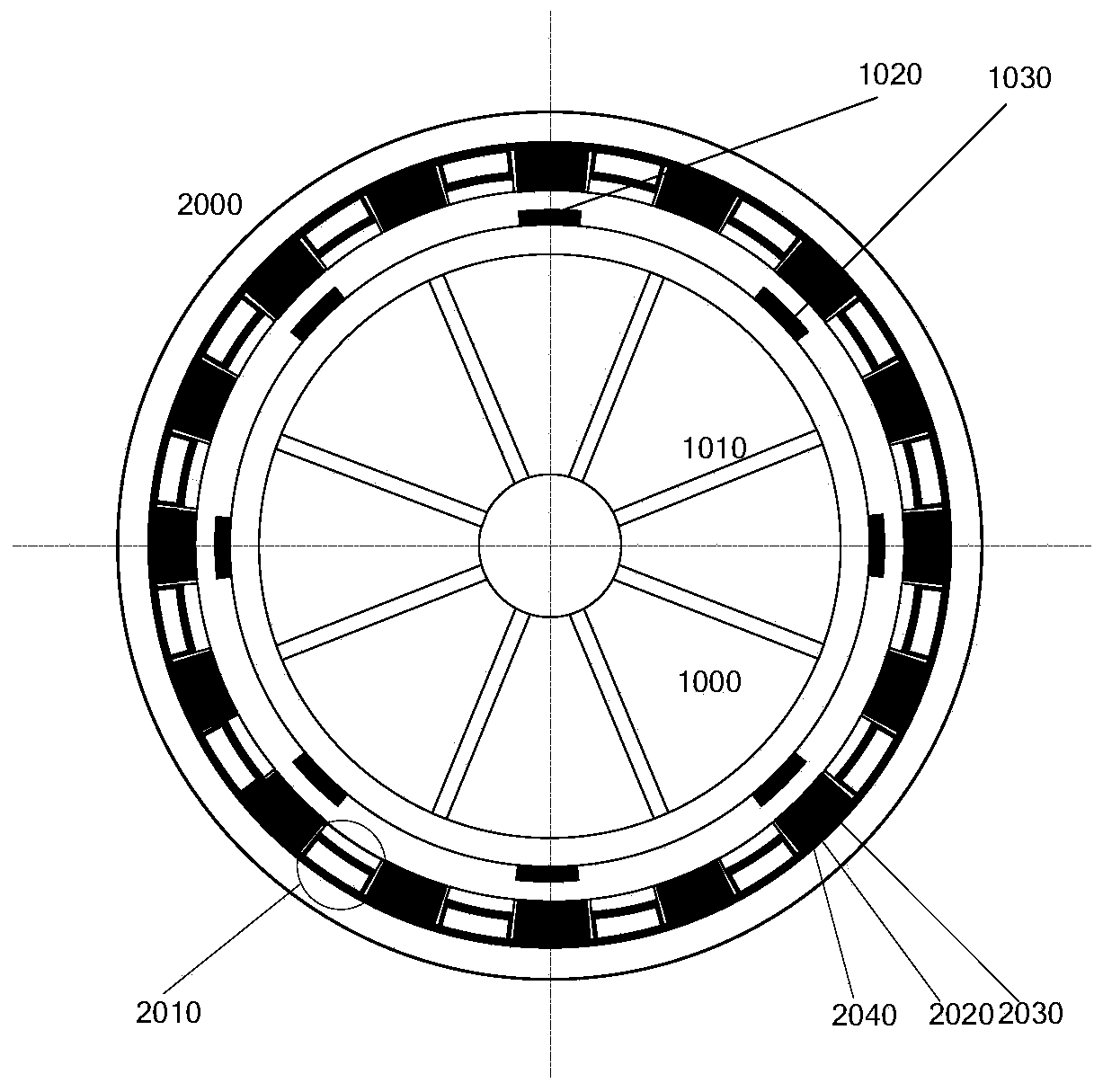
[0129] This embodiment provides a rotating piezoelectric generator with an eight-pole rotor, such as figure 1 shown. The stator and rotor bodies of the device are all made of silicon steel with good magnetic permeability. The magnetic steel is evenly distributed along the circumference of the stator and rotor, and radial magnetization is used to improve power generation efficiency, or tangential magnetization is used to reduce torque ripple. The number of stator magnets can be odd or even, and the number of magnets on the rotor side can be the same or different. The power generation components are connected in series to increase the voltage amplitude, or connected in parallel to reduce the output voltage, which is convenient for the processing of external circuits. In addition, the rotating speed can be adjusted according to the needs to obtain the output voltage of the required frequency. According to the present invention, the rigid-flexible vibration and voltage output c...
Embodiment 2
[0133] image 3 As another topological configuration of the present invention, the motor is similar to Embodiment 1, except that the stator and rotor magnets are arranged in opposite polarity. Therefore, the number of magnetic poles of the stator and rotor is an even number, so the magnetic pulling force of the stator magnet steel and the voltage pulsation frequency of the corresponding power generation components are related to the number of pole pairs of the rotor. According to the theoretical analysis of the present invention, the law of rigid-flexible vibration and voltage output described in Table 2 can be obtained. Apparently, the parity of the excitation force harmonics and the number of magnetic poles jointly determine the vibration and voltage output laws of this embodiment.
[0134] Table 2 The vibration and voltage output characteristics of the eight-pole rotor rotating piezoelectric generator (the polarity of the magnetic steel adjacent to the rotor is opposite) ...
Embodiment 3
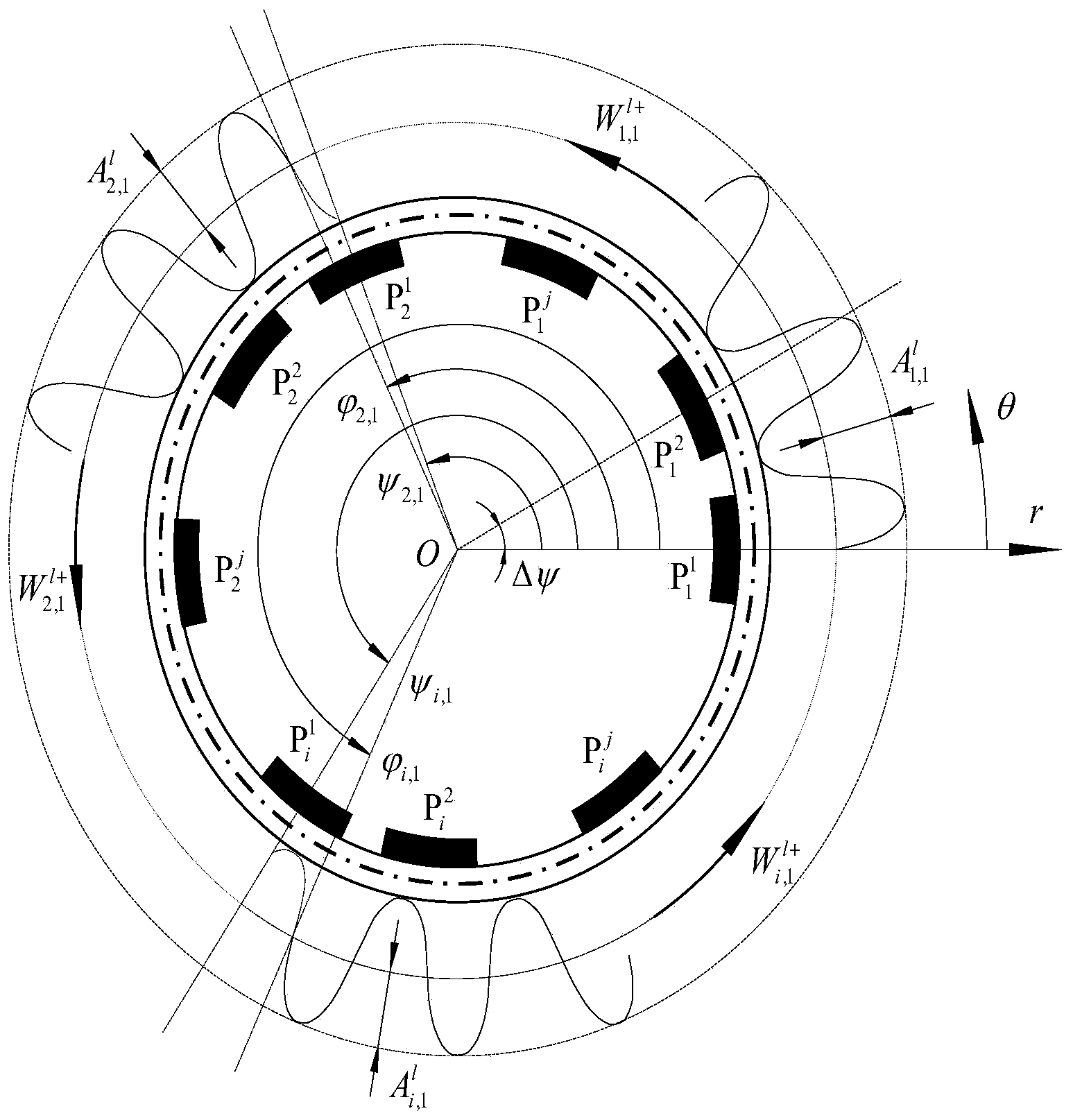
[0138] In order to increase the output power of the motor and at the same time improve the stress state of the piezoelectric components, Figure 4 Taking the 8-pole stator as an example, a cross-section of the two-stage dislocation axis is given. The misalignment angle of the two stators in the figure is π / 8. The rotor magnets can be arranged with the same polarity or adjacent opposite polarities (not shown). In this embodiment, the vibration characteristics and voltage quality can be optimized by adjusting the number of segments and the misalignment angle. It should be pointed out that although the dislocation method is adopted, the excitation frequency and waveform acting on the piezoelectric component have not changed. In fact, only the excitation force and voltage phase of the two stators have been changed, and the wave response has also been changed. amplitude. It should also be pointed out that if only the force and vibration state in the shaft section are considered,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com