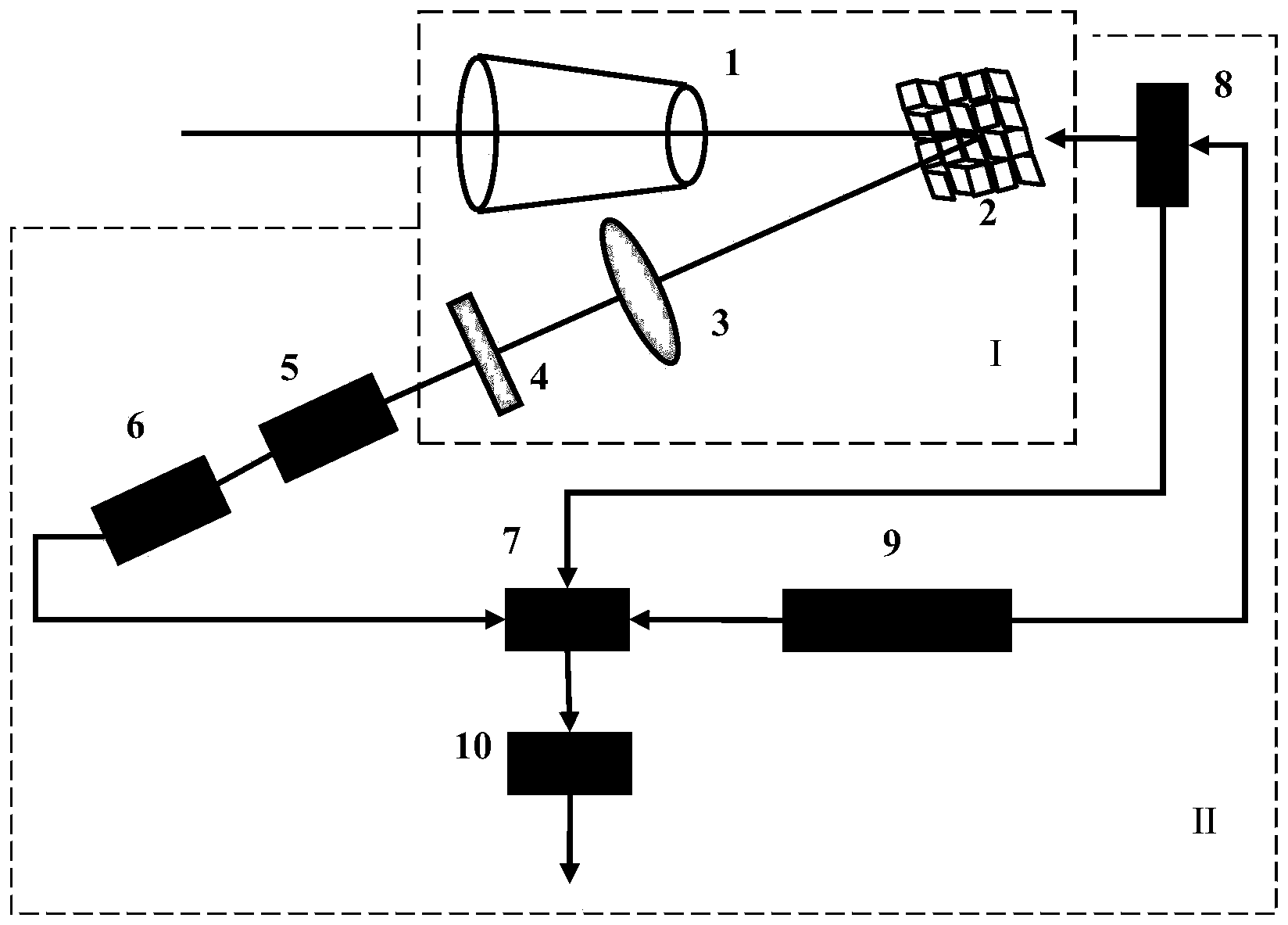
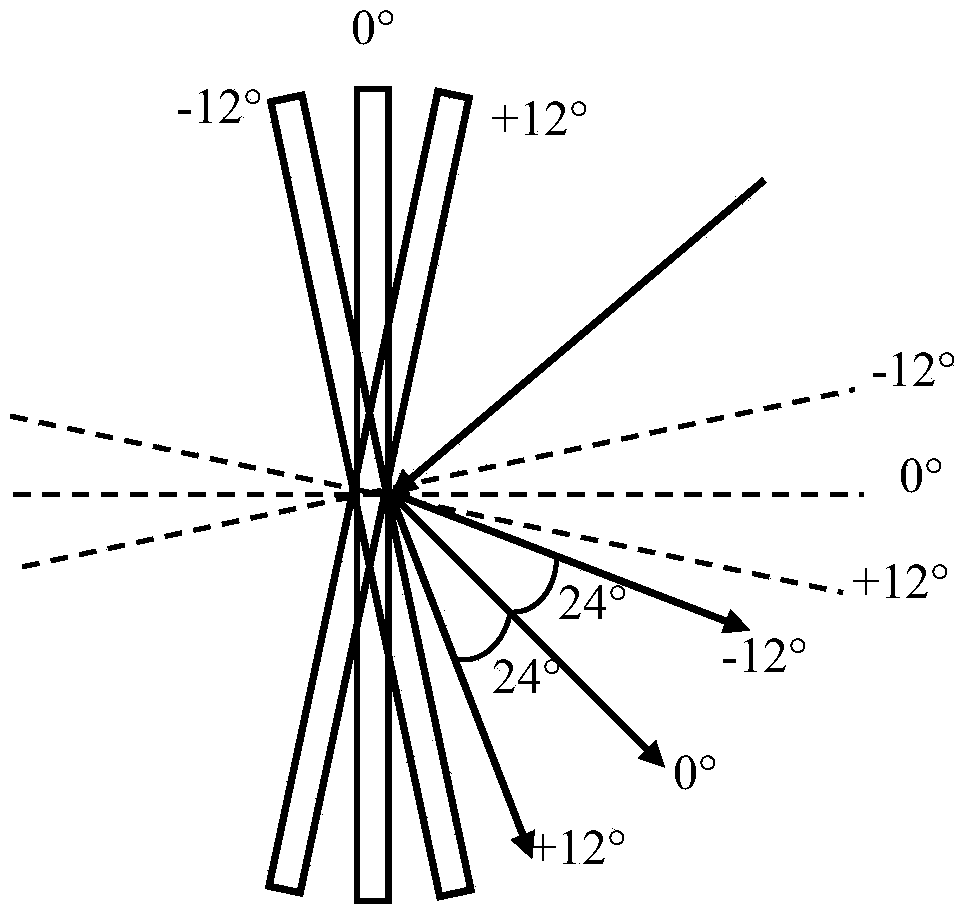
Ultrasensitive astronomical telescope and astronomical image acquisition method
A technology for astronomical telescopes and astronomical images, applied in the field of astronomy, can solve the problems of reduced imaging resolution, duty cycle, high cost, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing errors, high-sensitivity image detection, and improving uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0049] The present invention will be further described now in conjunction with accompanying drawing.
[0050] The ultra-sensitive astronomical telescope of the present invention utilizes the principle of Compressive Sensing (CS for short), which is a brand-new mathematical theory proposed by Donoho, Tao and Candès et al. According to compressed sensing, by randomly sampling the signal, the signal information can be sampled with a sampling number far lower than that required by the Nyquist / Shannon sampling theorem, and the original signal can be perfectly restored through a mathematical algorithm, and it has many advantages. High robustness. Compressed sensing is mainly divided into three steps: compressed sampling, sparse transformation and algorithm reconstruction; among them, compressed sampling refers to the process of sampling a signal with a measurement number less than the number of signals y=Ax, where x is the signal to be tested, and A is the measurement matrix, and y...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com