Method for preparing OBSC (4,4'-oxo-bis-benzenesulfonyl chloride) from basic chemical raw materials
A chemical raw material and a basic technology, applied in the field of preparing OBSC from basic chemical raw materials, can solve the problems of low product yield and purity, excessive sulfonating agent raw materials, complicated product post-processing, etc., so as to avoid raw material consumption and yield. And the effect of excellent purity and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
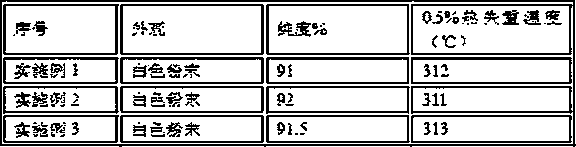
Embodiment 1
[0023] (1) Under the catalysis of ferric chloride, chlorine gas is homogeneously split into chlorine free radicals by light; the dosage of catalyst ferric chloride is 1% of the mass of chlorine gas.
[0024] (2) Sulfur dioxide gas is produced by burning sulfur in the air.
[0025] (3) Put the diphenyl ether into the reaction kettle, pass the chlorine gas treated in step (1) 0.9 times the mass of diphenyl ether and the sulfur dioxide gas prepared in step (2) and 0.8 times the mass of diphenyl ether into the reaction In the kettle, react with diphenyl ether for 5 hours at a temperature of 55°C, a pressure of 0.5KPa, and a stirring rate of 100 r / min, and then keep the pressure and stirring conditions constant and react at a temperature of 30°C for 4 hours.
[0026] (4) Feed chlorine gas into the reaction kettle again, react at a temperature of 35°C and a pressure of 0.05MPa, stop feeding chlorine gas when the oxidation-reduction potential suddenly rises, and then continue to reac...
Embodiment 2
[0028] (1) Under the catalysis of ferric chloride, chlorine gas is homogeneously split into chlorine free radicals by light; the amount of catalyst ferric chloride is 2% of the mass of chlorine gas.
[0029] (2) Sulfur dioxide gas is produced by burning sulfur in the air.
[0030] (3) Put the diphenyl ether into the reactor, and pass the chlorine gas with 1.1 times the mass of diphenyl ether treated in step (1) and the sulfur dioxide gas with 0.95 times the mass of diphenyl ether prepared in step (2) into the reactor , react with diphenyl ether for 4 hours at a temperature of 70°C, a pressure of 3KPa and a stirring rate of 200 r / min, and then keep the pressure and stirring conditions constant and react at a temperature of 45°C for 3 hours.
[0031] (4) Feed chlorine gas into the reaction kettle again, react at a temperature of 45°C and a pressure of 0.09MPa, stop feeding chlorine gas when the oxidation-reduction potential suddenly rises, and then continue to react at a tempera...
Embodiment 3
[0033] (1) Under the catalysis of ferric chloride, chlorine gas is homogeneously split into chlorine free radicals by light; the amount of catalyst ferric chloride is 3% of the mass of chlorine gas.
[0034] (2) Sulfur dioxide gas is produced by burning sulfur in the air.
[0035] (3) Put the diphenyl ether into the reactor, and pass the chlorine gas with 1.2 times the mass of diphenyl ether treated in step (1) and the sulfur dioxide gas with 1.1 times the mass of diphenyl ether prepared in step (2) into the reactor , react with diphenyl ether for 3 hours at a temperature of 90°C, a pressure of 5KPa, and a stirring rate of 300 r / min, and then keep the pressure and stirring conditions constant and react at a temperature of 60°C for 2 hours.
[0036] (4) Feed chlorine gas into the reaction kettle again, react at a temperature of 50°C and a pressure of 0.15MPa, stop feeding chlorine gas when the oxidation-reduction potential suddenly rises, and then continue to react at a tempera...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com