Aquaporin based thin film composite membranes
An aquaporin and composite membrane technology, applied in the field of manufacturing the thin film composite membrane, can solve problems such as obstacles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Embodiment 1. prepare liposome and proteoliposome
[0062] Materials and methods used for preparation
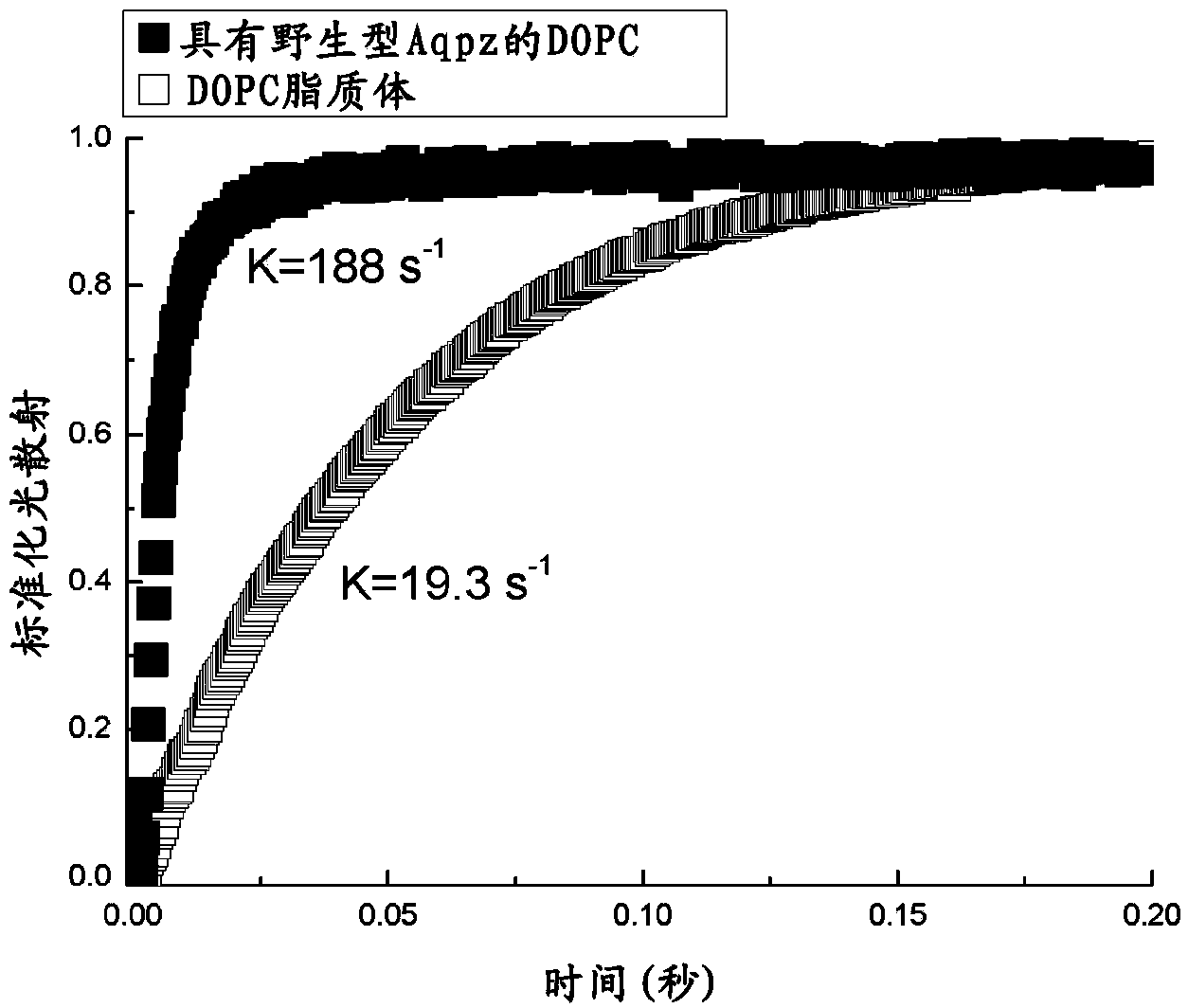
[0063] Unless mentioned otherwise, ultrapure water with a resistivity of 18.2 MΩcm from a Milli-Q ultrapure water system (Milli-pore Singapore Pte Ltd) was used to prepare the reagents in this study. Analytical grade NaCl, KCl, KH with a purity greater than 99% 2 PO 4 , MgCl 2 , MgSO 4 and Na 2 SO 4 Available from Merck (Germany). Sucrose (ultrapure grade) was obtained from USB Corporation (Cleveland, USA). Chemicals used in aquaporin Z expression and purification (including Ampicilin, Chloramphenicol, IPTG, Tris, β-mercaptoethanol, glycerol, and lysozyme) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich and purchased from ACS (American Chemical Society) grade or SigmaUltra grade. Benzonase was purchased from Merck. Ni-NTA resin was purchased from Bio-Rad. n-Octyl-b-D-glucopyranoside (OG, ultrapure grade, Merck, Germany) was used as a detergent during proteoliposome prepar...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Example 2. Preparation of thin film composite membranes with lipid-AqpZ vesicles and testing in RO devices
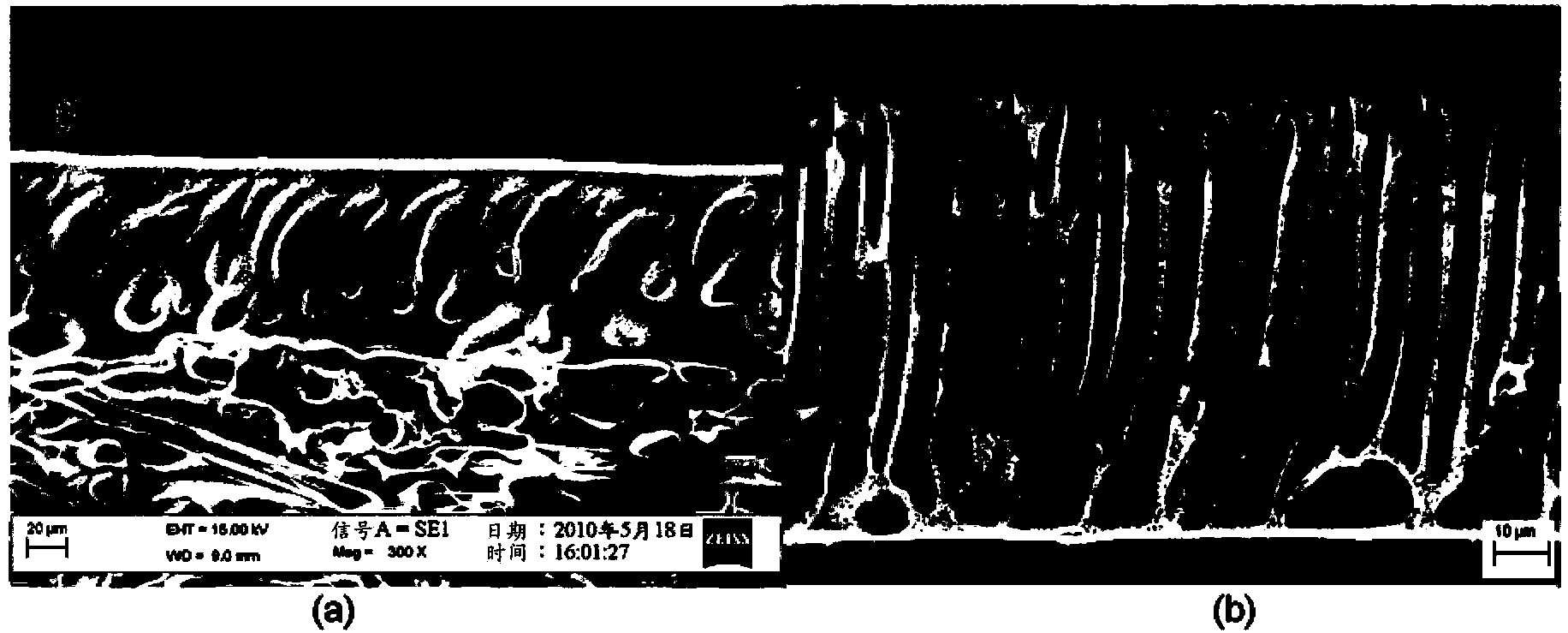
[0098] A commercial UF membrane (MWCO, 50,000 Dalton (Dalton)) was used as the substrate, 50 ml of amine aqueous solution 1.5 wt% MPD containing 0.08 mg / g DOPC-AqpZ vesicles was spread on the surface of the UF membrane substrate, and the substrate was held with the aqueous solution Wet for 15 minutes. Subsequently, the aqueous amine solution was removed from the surface, and the substrate was allowed to stand vertically in air for 10 minutes, then the surface was blown with compressed nitrogen gas at 2 bar for 1 minute to remove any possible aggregated vesicles on the surface, and then the substrate was allowed to continue Dry vertically for another 20 minutes. Subsequently, a 0.1 w / v% TMC solution was poured on the surface layer of the saturated substrate and allowed to react for 1 minute. The resulting membranes were stored in Milli-Q water until use. The tf...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Example 3. Preparation and thin film composite membrane with lipid vesicles and tested in RO device
[0100] The two stages of interfacial polymerization and the composition of the reactive monomer solution during the process were similar to Example 2, except that only 0.08 mg / g DOPC vesicles without AqpZ were dissolved in the aqueous amine solution. RO test was carried out as in Example 2. The flux and rejection rate of the thin film composite membrane with DOPC-AqpZ vesicles to 500ppm NaCl (200 psi) are 16.9L / m2.h and 98.5%, respectively. Results from experiments involving comparisons of water flux and solute rejection for thin-film composite membranes incorporating lipid vesicles only or lipid-AqpZ vesicles at increasing pressures up to 200 psi are shown in Figure 7 , which clearly shows that a relatively high water flux can be obtained with the incorporation of DOPC vesicles. However, incorporation of DOPC-AqpZ vesicles significantly improved the water flux of th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com