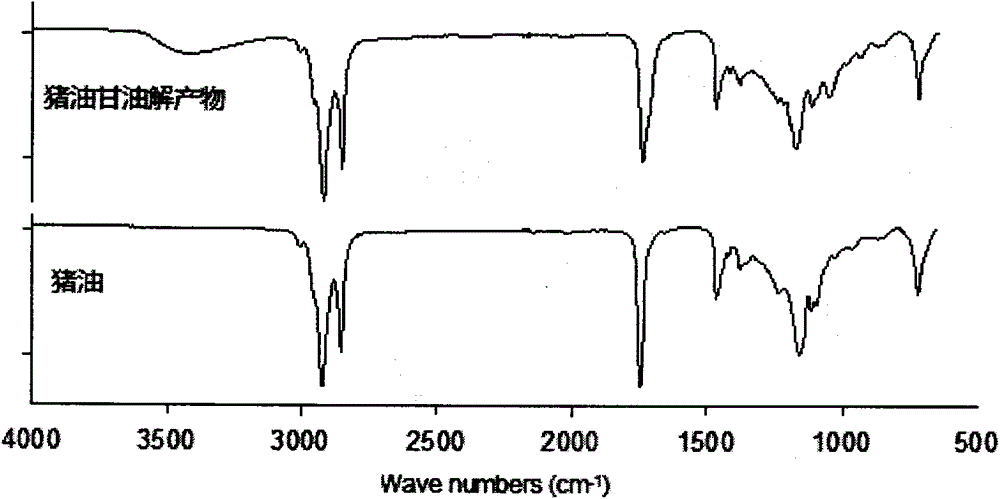
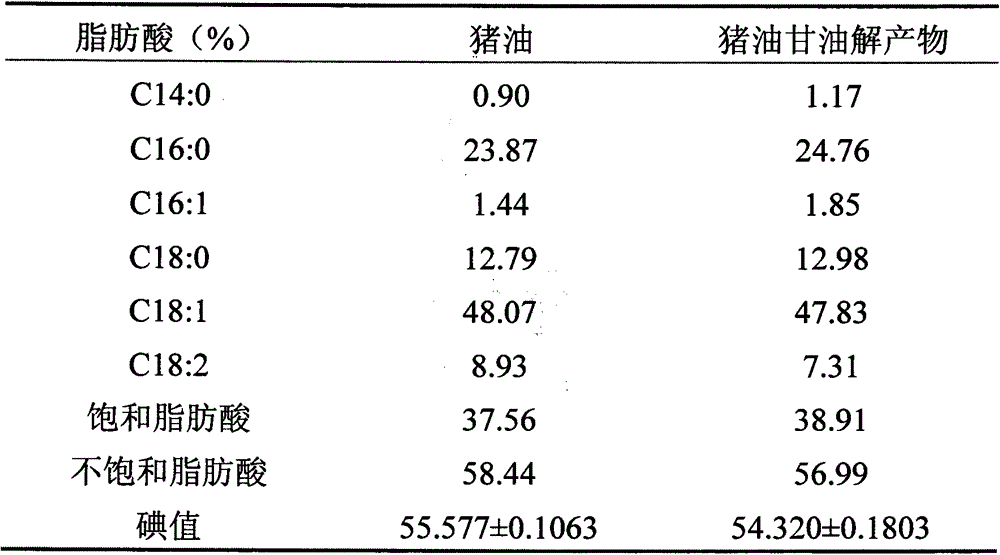
Gradual cooling auxiliary enzymatic method for glycerolysis preparation of lard diglyceride
A technology of gradual cooling and diglyceride, which is applied in the field of gradual cooling to assist the preparation of diglyceride, which can solve the problems of difficult absorption, high heat, and high melting point, and achieve the effect of easy separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Mix lard and glycerin with a molar ratio of 1:1 in a round bottom flask, dehydrate for 30min under the conditions of vacuum degree -50.0kpa and heating temperature of 82°C, transfer the dehydrated mixture to the Erlenmeyer flask, add Lipozyme RM IM with 10% oil weight was reacted at a magnetic stirring speed of 400r / min. The initial reaction temperature was 65°C. After 2 hours of reaction, the temperature was adjusted to 55°C, reacted for 2 hours, and then adjusted to 40°C for 6 hours. After the reaction, the lipase was removed by filtration to obtain a glycerol hydrolyzate of lard. The content of DAG in the product was analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography to be 41.81%, and the content of 1,3-DAG was 26.52%.
Embodiment 2
[0019] Mix lard and glycerin with a molar ratio of 1:1 in a round bottom flask, dehydrate for 30 minutes under the conditions of vacuum degree -50kpa and heating temperature of 82°C, transfer the dehydrated mixture to a conical flask, add oil 14% Lipozyme RM IM was reacted at a magnetic stirring speed of 400r / min. The initial reaction temperature was 65°C. After 2 hours of reaction, the temperature was adjusted to 55°C, reacted for 2 hours, and then adjusted to 40°C for 6 hours. After the reaction, the lipase was removed by filtration to obtain a glycerol hydrolyzate of lard. The content of DAG in the product was analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography to be 54.04%, and the content of 1,3-DAG was 39.68%.
Embodiment 3
[0021] Mix lard and glycerin with a molar ratio of 2:1 in a round bottom flask, dehydrate for 30 minutes under the conditions of vacuum degree -50kpa and heating temperature of 82°C, transfer the dehydrated mixture to a conical flask, add oil 14% Lipozyme RM IM was reacted at a magnetic stirring speed of 400r / min. The initial reaction temperature was 65°C. After 2 hours of reaction, the temperature was adjusted to 55°C, reacted for 2 hours, and then adjusted to 40°C for 6 hours. After the reaction, the lipase was removed by filtration to obtain a glycerol hydrolyzate of lard. The content of DAG in the product was analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography to be 51.27%, and the content of 1,3-DAG was 38.28%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com