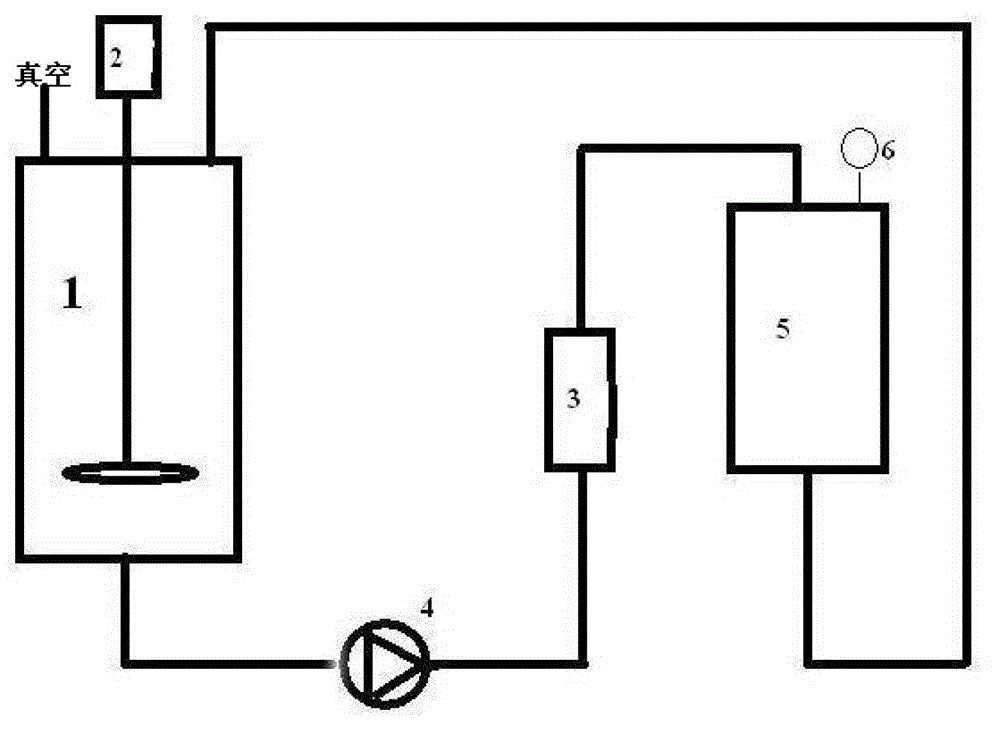
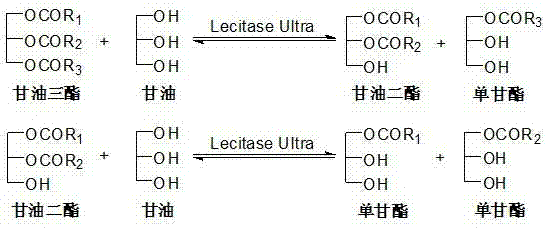
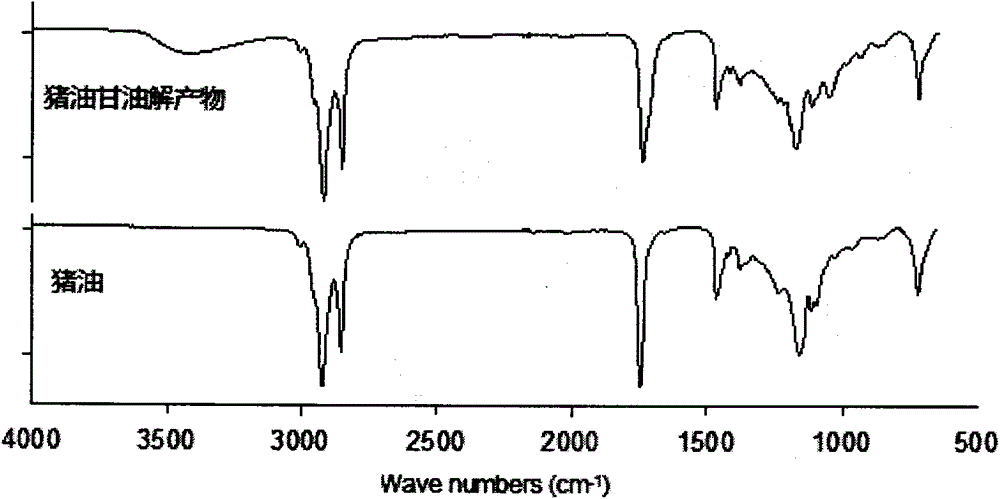
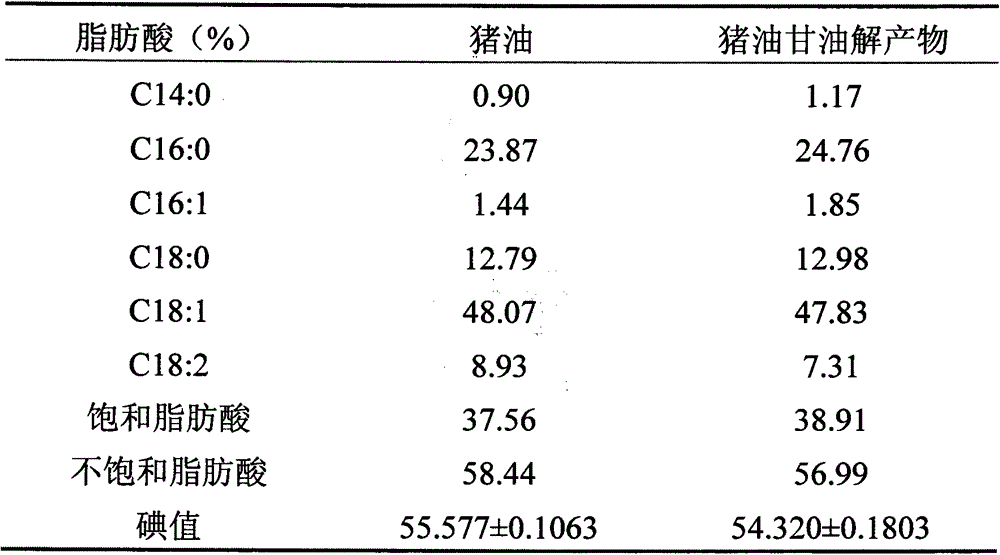
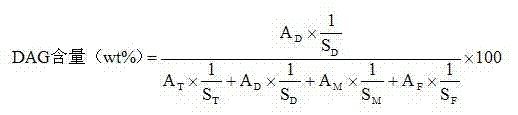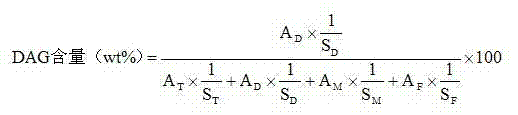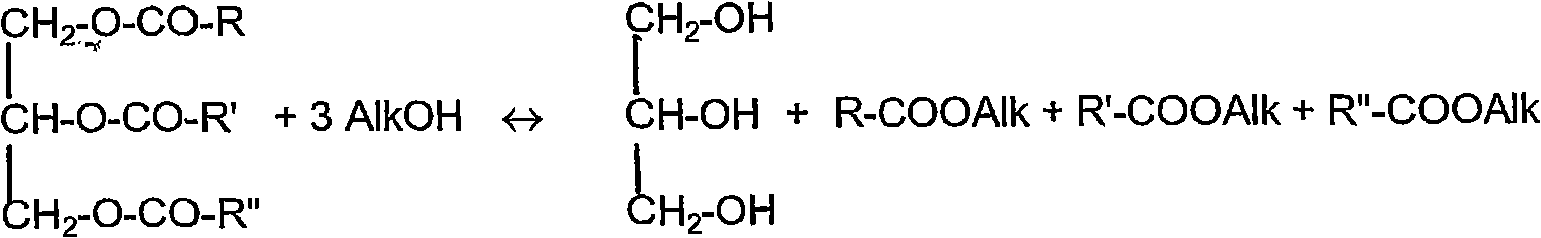Patents
Literature
61 results about "Glycerolysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In organic chemistry glycerolysis refers to any process in which chemical bonds are broken via a reaction with glycerol. The term refers almost exclusively to the transesterification reaction of glycerol with triglycerides (fats/oils) to form mixtures of monoglycerides and diglycerides. These find a variety of uses; as food emulsifiers (e.g. E471), 'low fat' cooking oils (e.g. diacylglycerol oil) and surfactants (such as monolaurin).
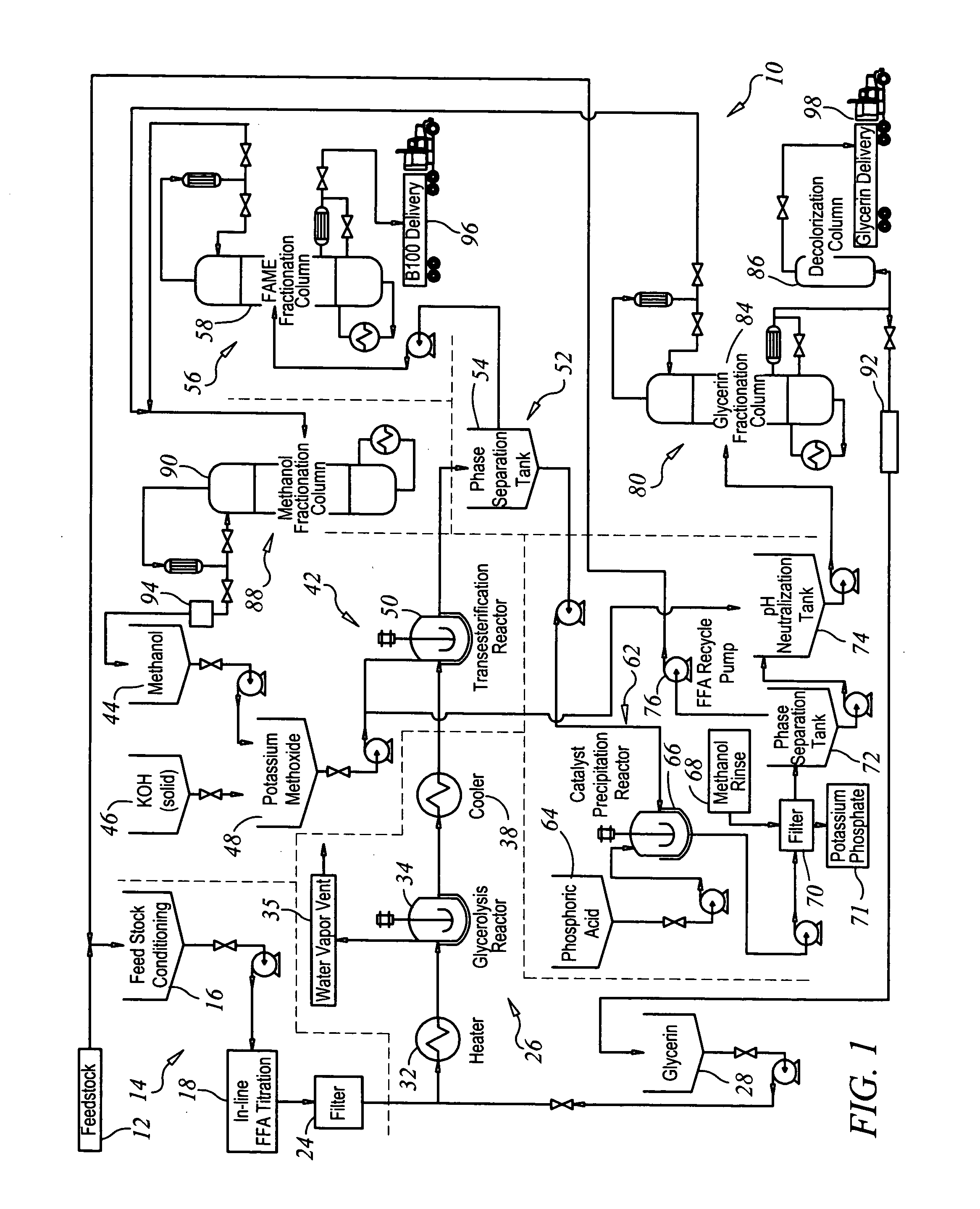
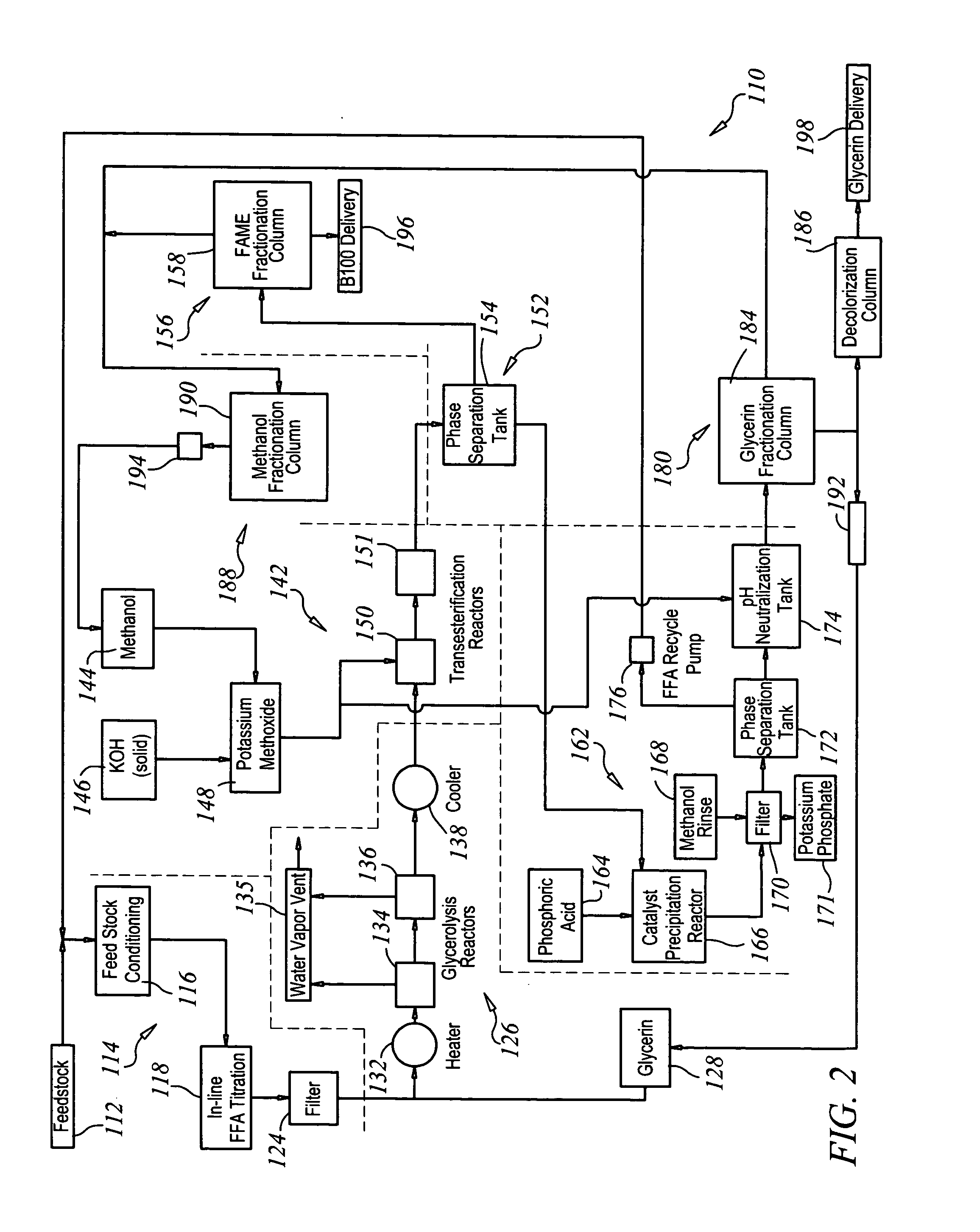
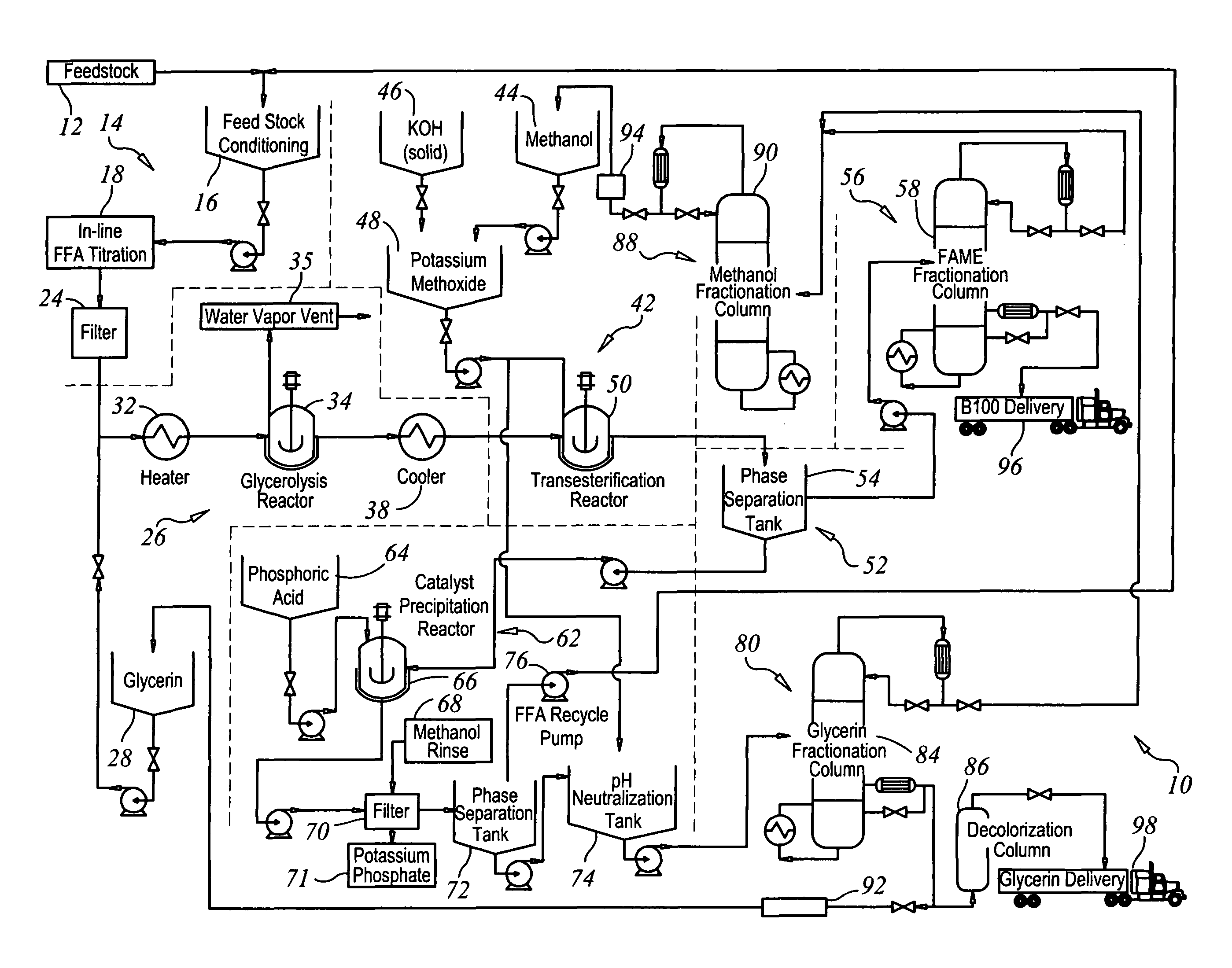
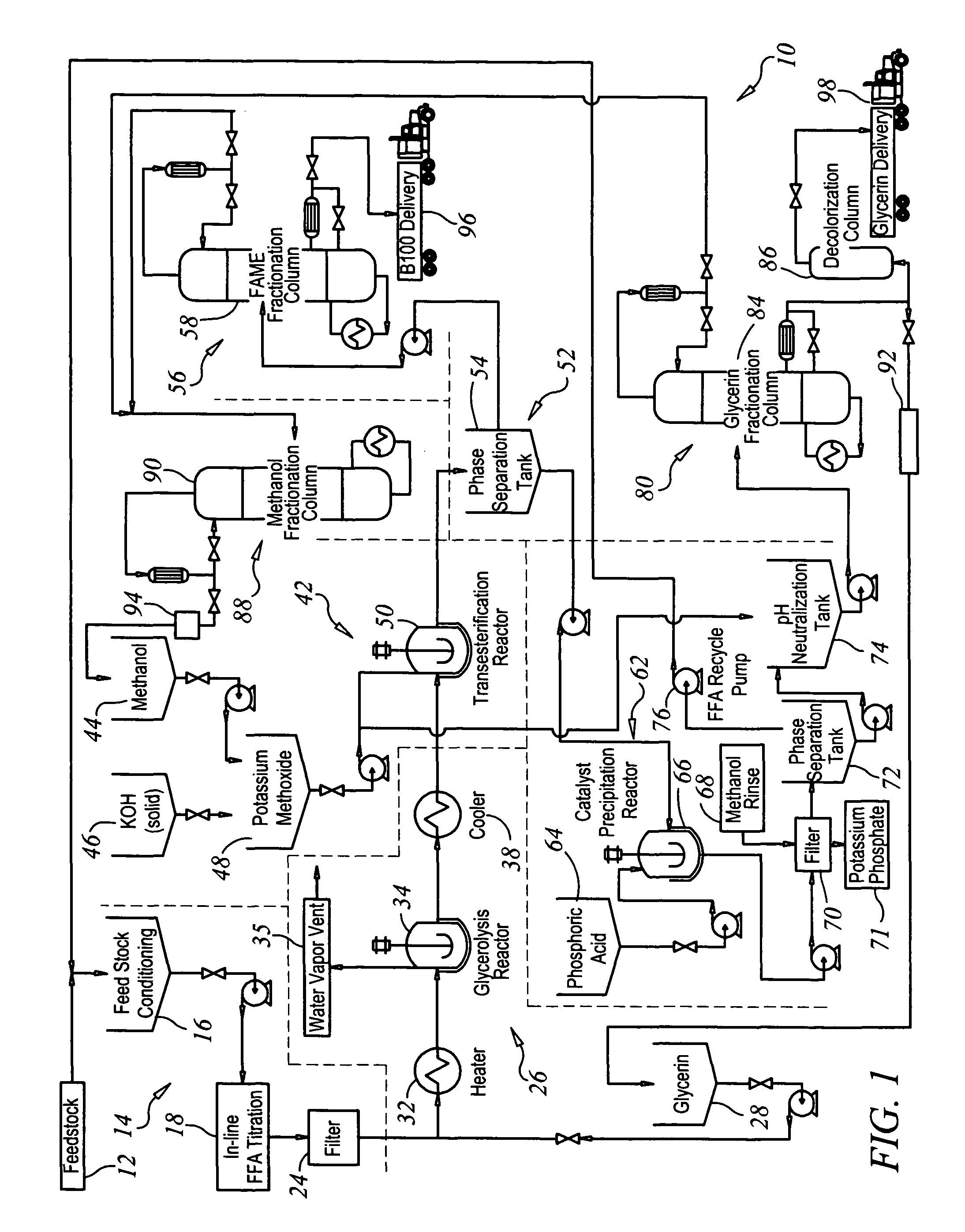
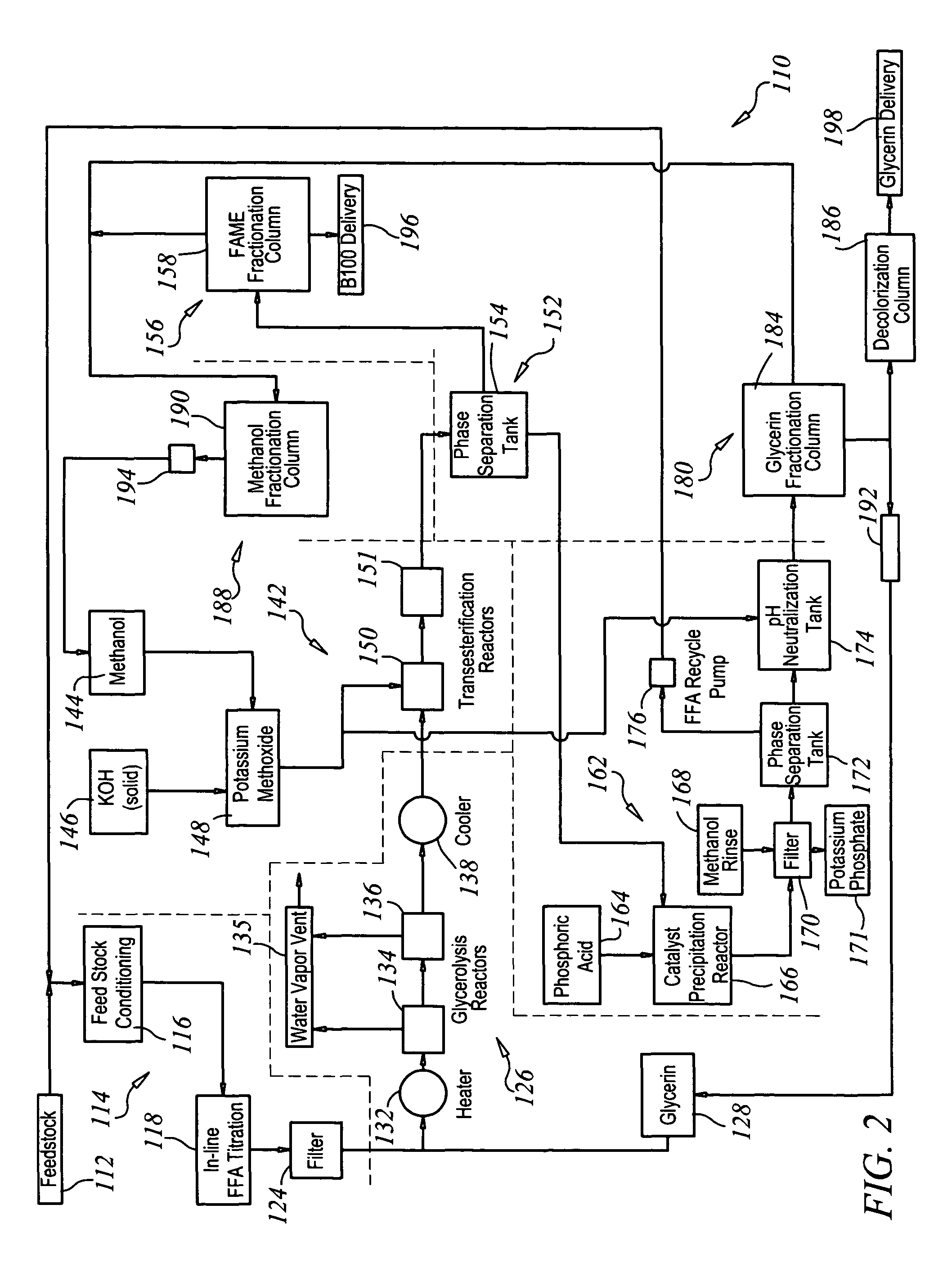
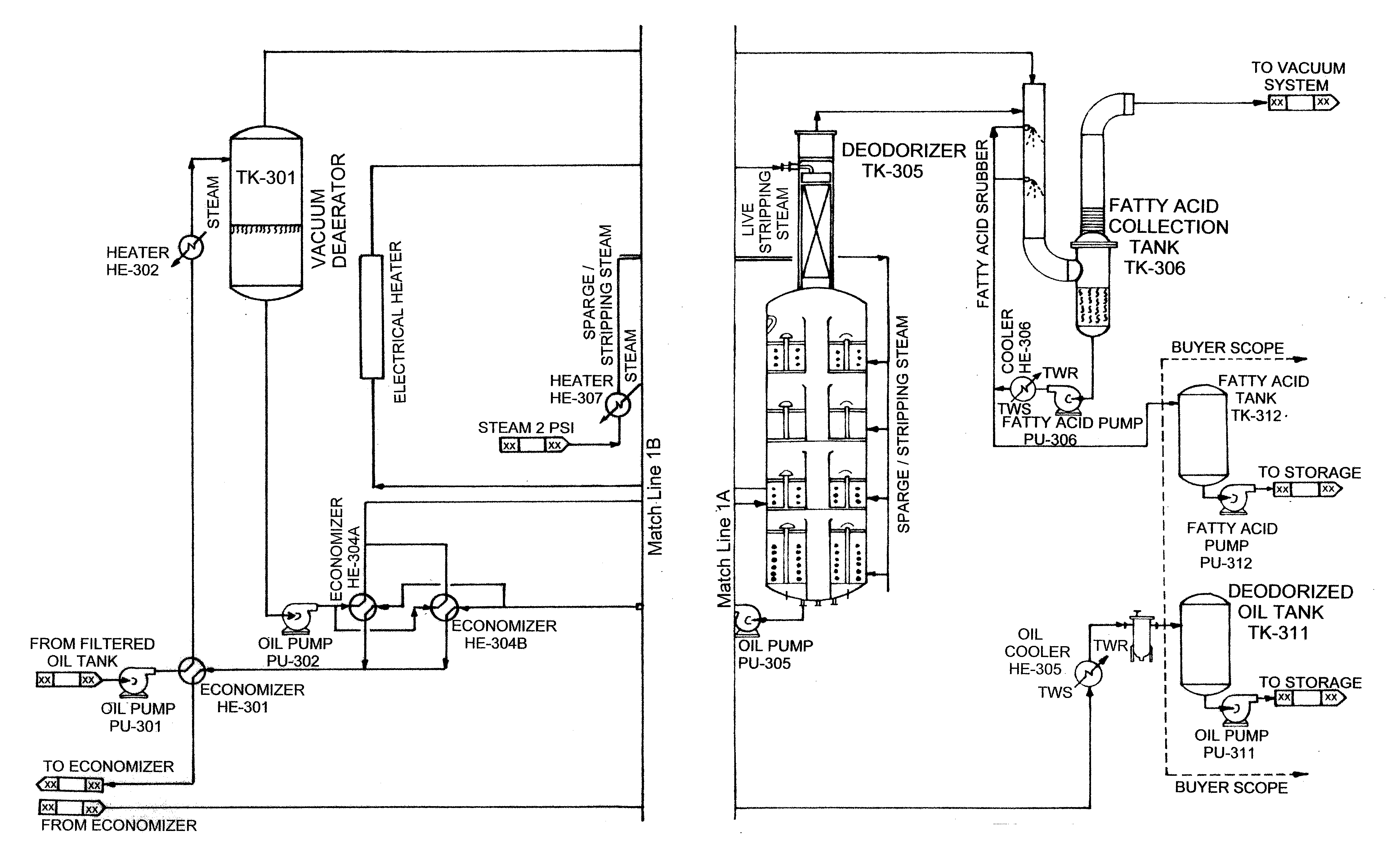
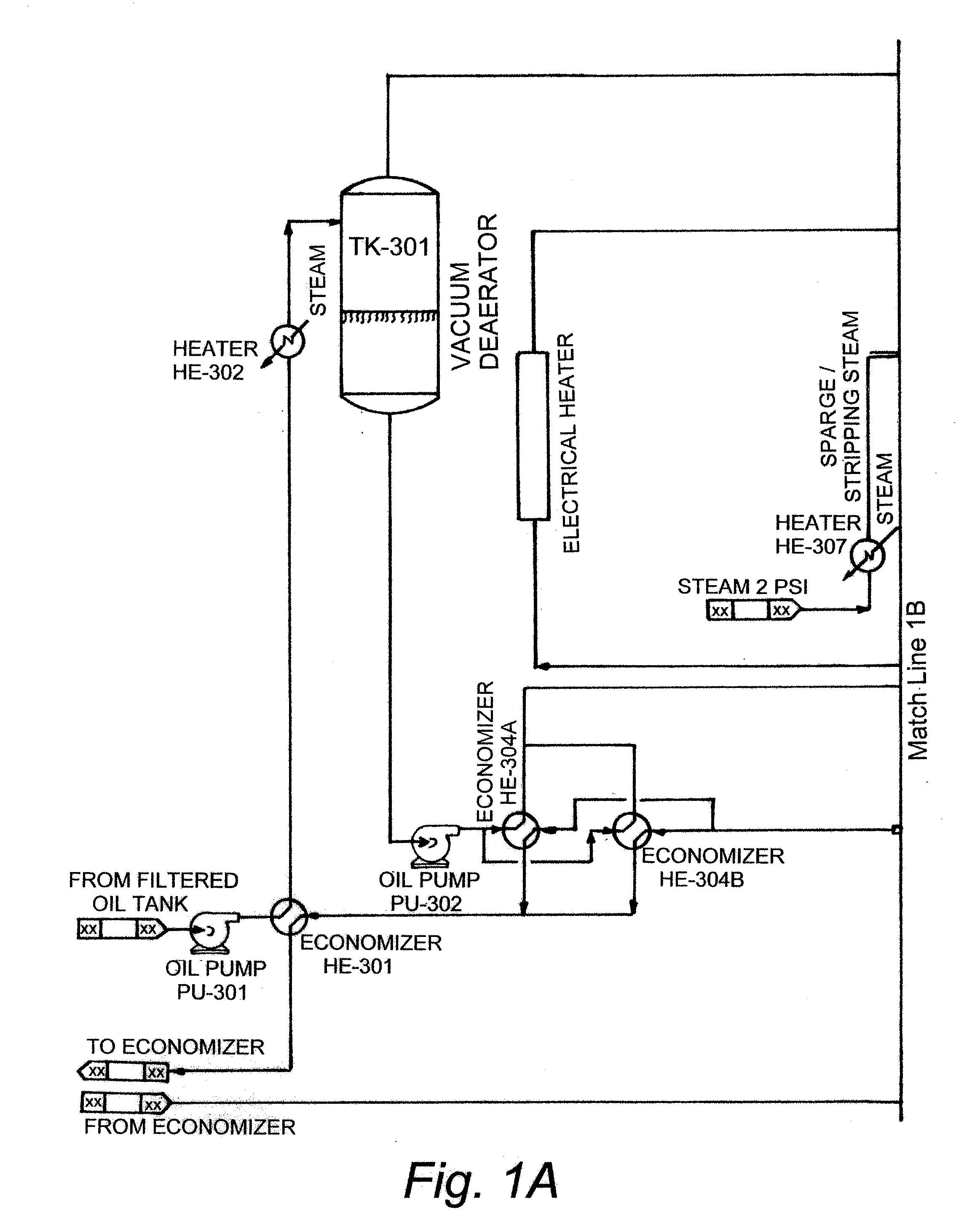
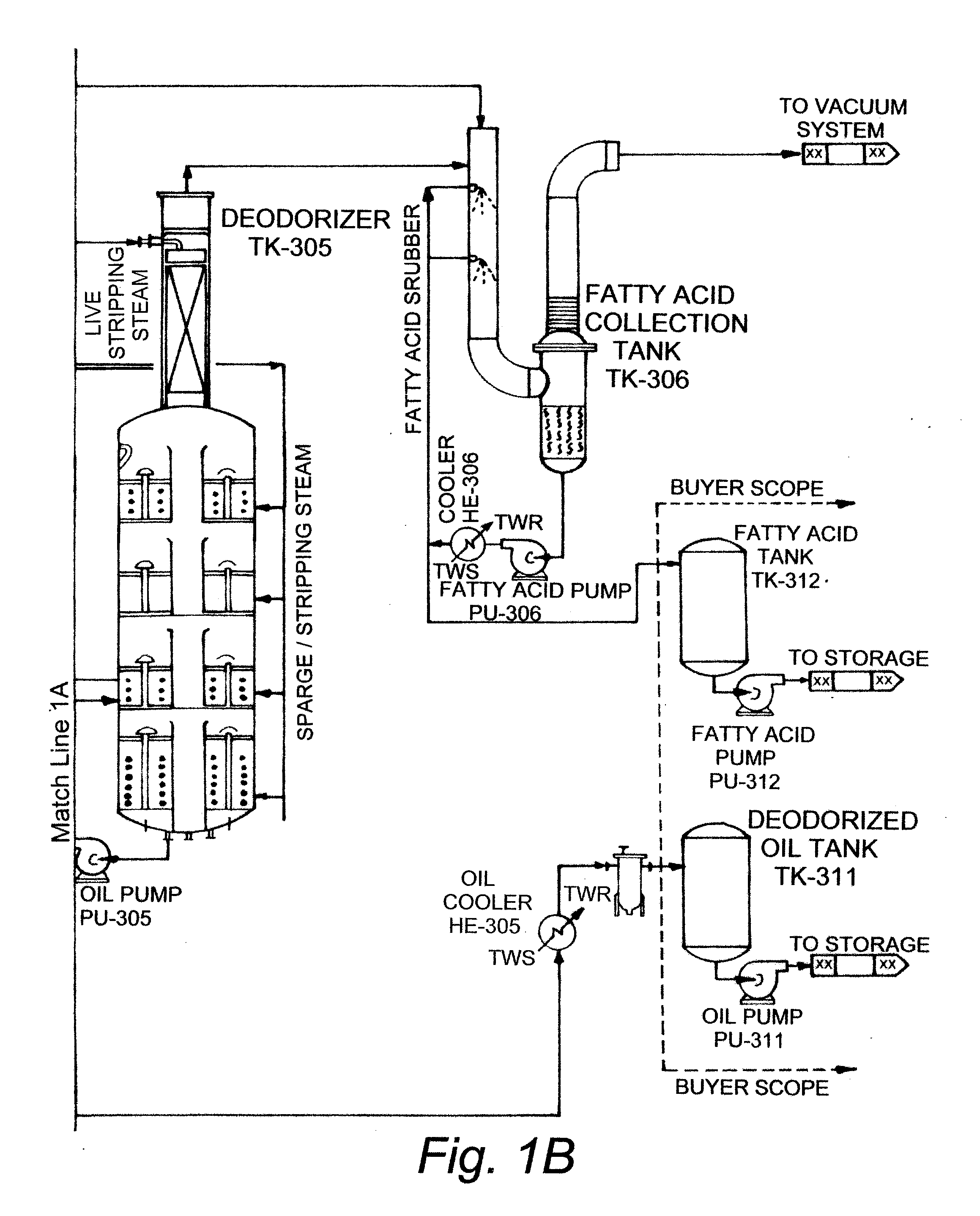
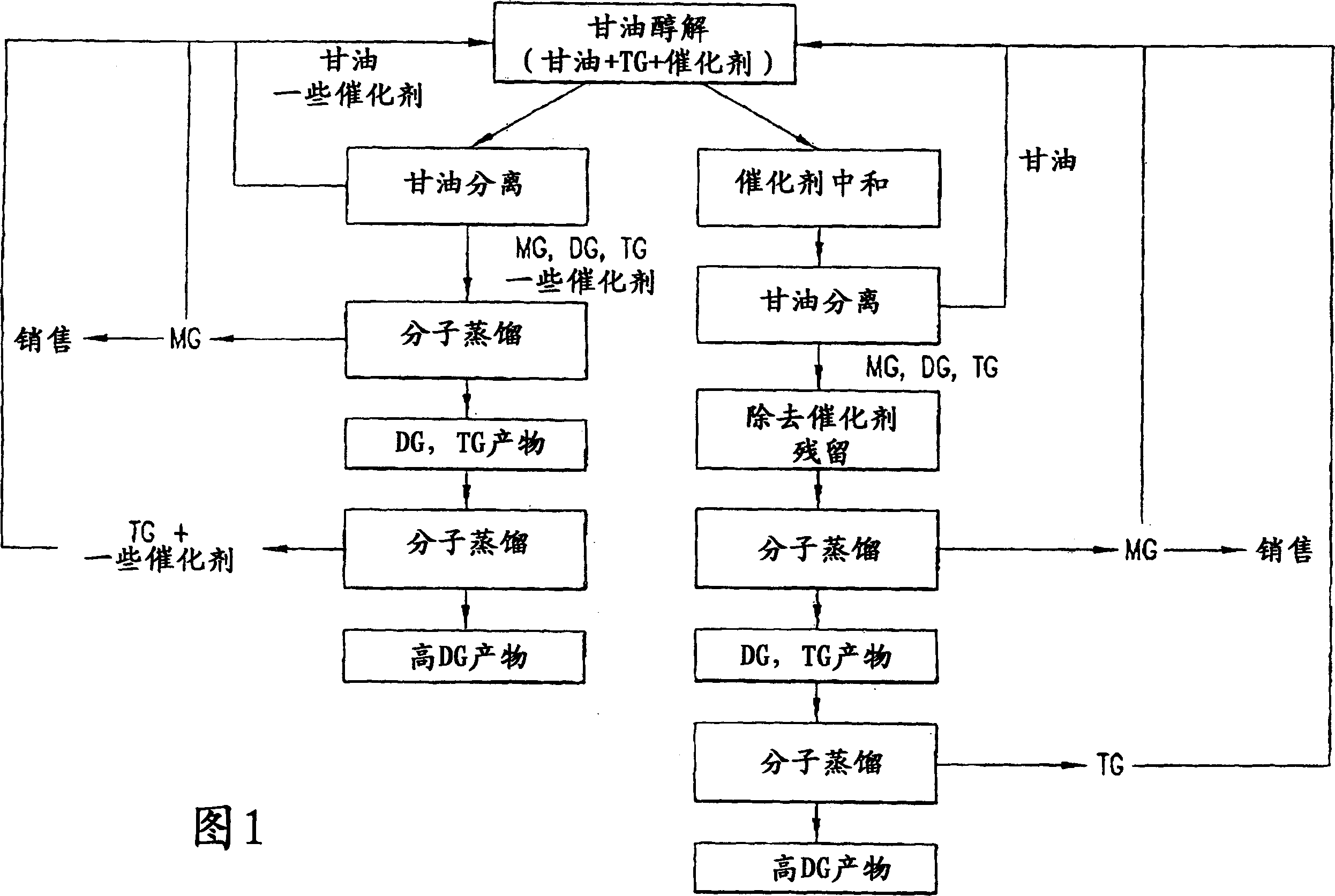
Production of biodiesel and glycerin from high free fatty acid feedstocks
ActiveUS20070277429A1Increase wasteLow costFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationGlycerolGlycerolysis
A system and method for converting a high free fatty acid grease feedstock to biodiesel. The process comprises a glycerolysis reaction to convert free fatty acids to glycerides and a base catalyzed transesterification reaction to produce fatty acid methyl esters and glycerin in the absence of solvents. In preferred embodiments, both glycerin and methanol are recycled. The process can process a feedstock containing up to 100 percent free fatty acid content to produce biodiesel and glycerin with minimal waste generation.
Owner:REG SENECA LLC +1
Process for the production of monoglyceride based on the glycerolysis of methyl ester
InactiveUS6127561AAvoid pollutionFatty acid chemical modificationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionMonoglycerideDistillation
The invention discloses a process for the production of monoglycerides by glycerolysis of methyl ester derived from animal or vegetable fat and oils which includes mixing a surplus of 0.1 to 3 moles of glycerols in relation to methyl ester, subjecting the reaction mixture to a reaction temperature between 130 to 160 at a vacuum of 200 to 400 mbar, adding of alkaline catalysts, stopping the reaction by fast cooling of the reaction mixture and the destruction of the alkaline catalyst when the quantity of glycerides has reached a concentration of mono and diglyceride of 40 to 60%, leaving the catalyst in the reaction mixture to catalyse the reaction downstream in a reactor, separating the surplus methyl ester and glycerol by distillation and stopping the reaction by fast cooling of the reaction mixture with reactor and the destruction of the alkaline catalyst when the quantity of glycerides has reached a concentration of 40 to 60% and the ratio of concentrations of mono and diglyceride lies between 3 to 10.
Owner:GLOBAL PALM PROD
Production of biodiesel and glycerin from high free fatty acid feedstocks
ActiveUS7806945B2Increase wasteQuality improvementFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationGlycerolSolvent
A system and method for converting a high free fatty acid grease feedstock to biodiesel. The process comprises a glycerolysis reaction to convert free fatty acids to glycerides and a base catalyzed transesterification reaction to produce fatty acid methyl esters and glycerin in the absence of solvents. In preferred embodiments, both glycerin and methanol are recycled. The process can process a feedstock containing up to 100 percent free fatty acid content to produce biodiesel and glycerin with minimal waste generation.
Owner:REG SENECA LLC +1
Non-hydrogenated vegetable oil based margarine for puff pastry containing an elevated diglyceride emulsifier
ActiveUS20070148313A1Sufficient structureHigh than usual level of diglycerides functionDough treatmentFatty acid esterificationGreek letter betaGlycerol
A mono-, di-, and triglyceride emulsifier is provided that is obtained by the interesterification or glycerolysis of triglycerides with glycerol. The diglyceride portion w / w is at least about 65% to about 80%, and most preferably from about 70% to about 80%. The high diglyceride emulsifier is useful in preparing a margarine from a selected quantity a non-hydrogenated vegetable oil and from an amount of saturated fat for use in puff pastry products. The puff pastry is trans fat free and a less than usual percentage of saturated fats. A preferred structured puffpastry margarine is prepared by mixing on a weight to weight basis about 14 parts of the high diglyceride emulsifier that is in predominantly stable beta crystal form, from about 14 to 27 parts of a non-hydrogenated vegetable oil, and from about 40 to about 52 parts of a saturated fat.
Owner:CARAVAN INGREDIENTS
Process of converting low and high free fatty acid containing oils into no free fatty acid containing oils
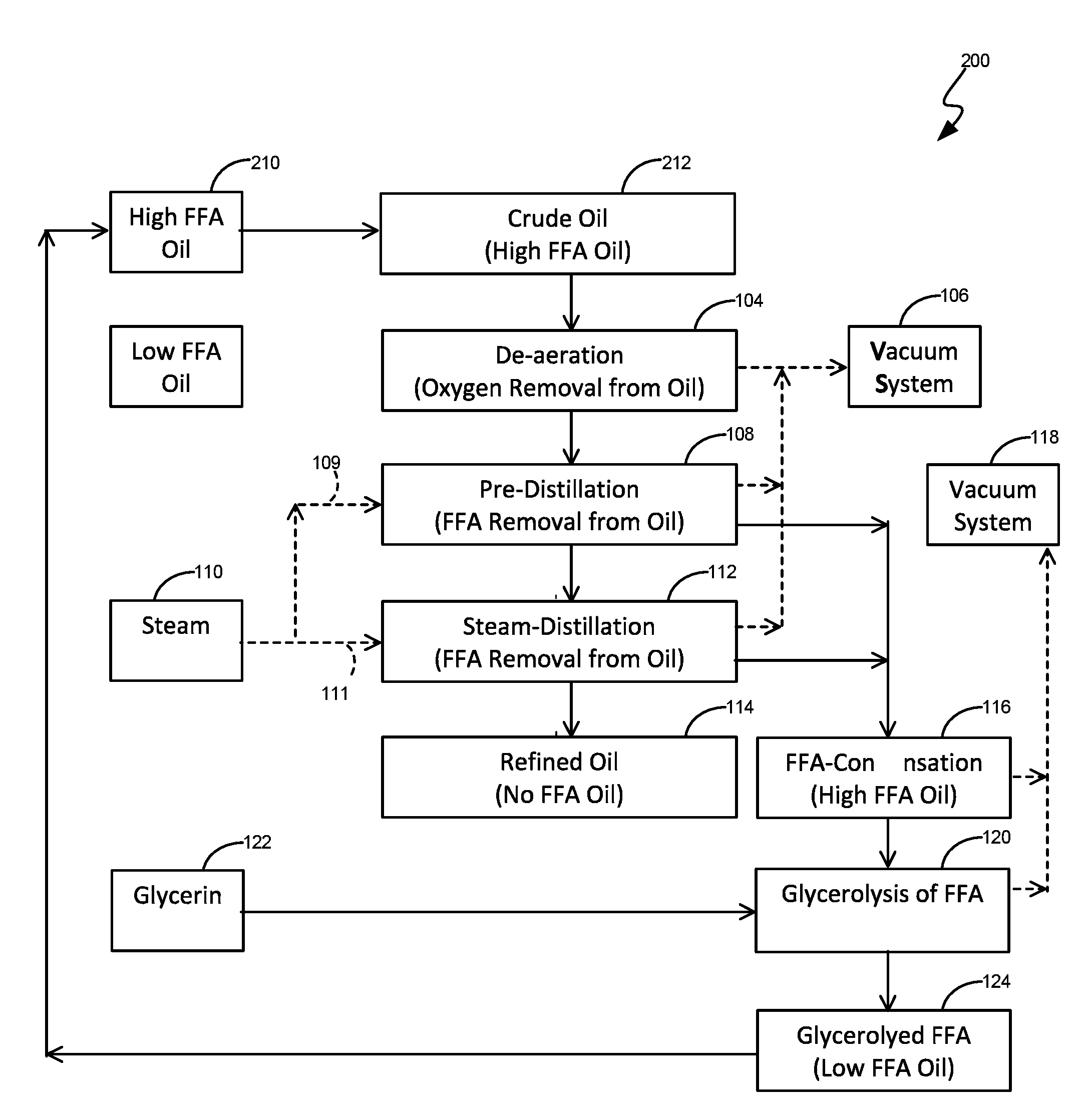
InactiveUS20140221675A1Improve consistencyPrevent excessive inputFatty acid esterificationFatty acids production/refiningSteam distillationGlycerolysis
A system and method for the conversion of high free fatty acid (HFFA) containing oils defined as oils containing 20-100% free fatty acids (FFA) and low free fatty acid (LFFA) containing oils defined as oils containing 1-20% free fatty acids (FFA) into oil with less than 0.5% FFA (defined as NFFA oil) includes a combination of partial glycerolysis of HFFA oils to produce LFFA oils and subsequent stripping of LFFA oils to produce NFFA oils via steam distillation.
Owner:TECH INT INC
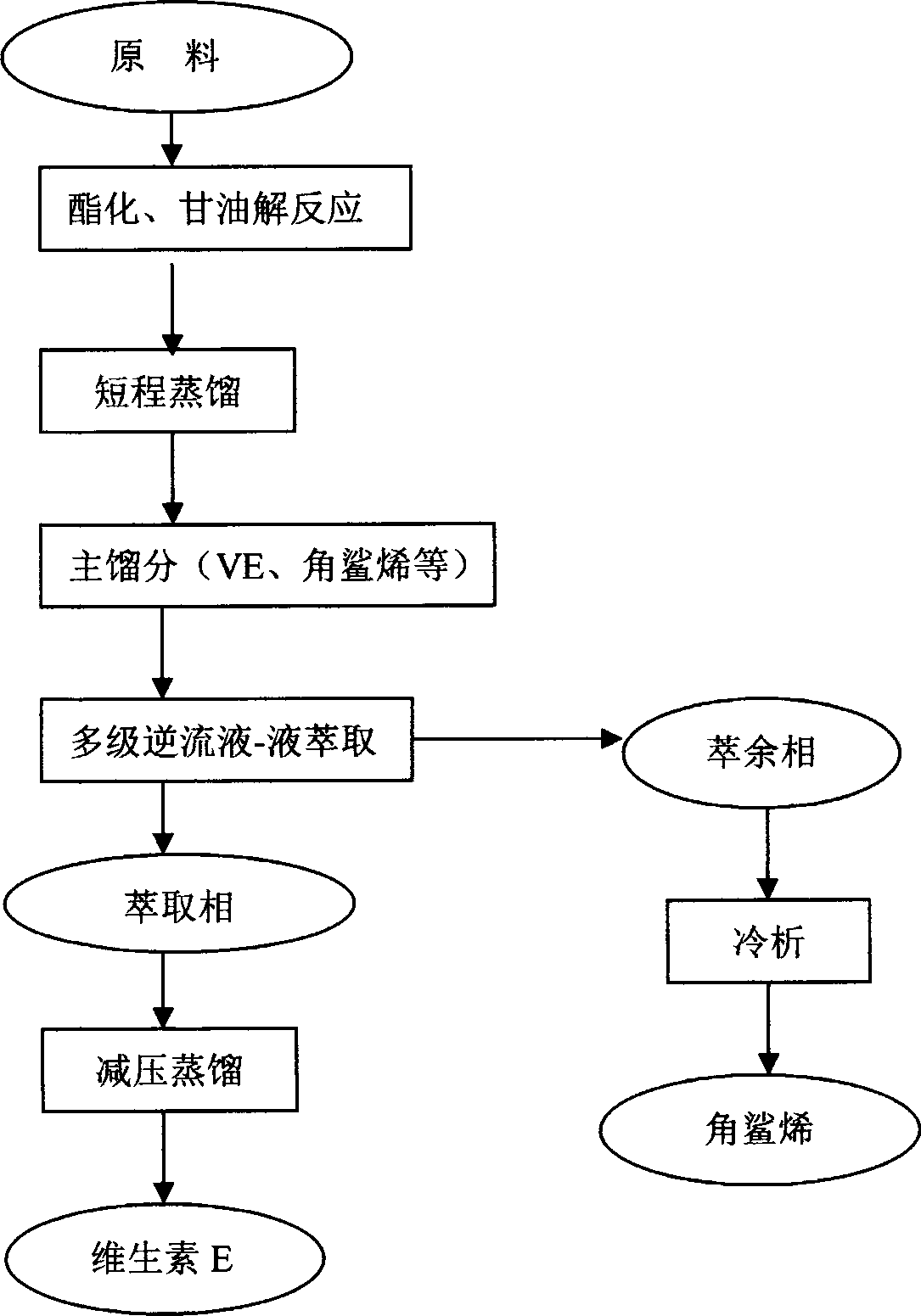
Novel technology for extracting vitamin E and squalene by employing multi-stage counter-current liquid-liquid extraction method
The invention discloses a novel technology for extracting vitamin E and plant squalene from a deodorizer distillate (DD oil) of vegetable oil by employing a multi-stage counter-current liquid-liquid extraction method. The technology comprises the following steps: firstly, converting a free fatty acid in the DD oil into fatty acid methyl ester by a common esterification method, then converting the fatty acid methyl ester into glyceride by glycerolysis reaction; distilling out the vitamin E, squalene and the like with relatively low boiling point by using short-path distillation, and reserving the glyceride, steryl ester and the like with high boiling points at the kettle bottom; and finally, separating out the vitamin E and the squalene by using the multi-stage counter-current liquid-liquid extraction method.
Owner:TIANJIN V HEALTECH CO LTD
Chemical process for the production of 1,3-diglyceride oils
InactiveCN1585814AFatty acid esterificationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAlkaline earth metalTriglyceride
A method for producing 1,3-diglyceride oils from triglyceride containing oils is disclosed. The method uses alkali metal salts or alkali earth metal salts of mono-carboxylic or di-carboxylic acids to drive glycerolysis under conditions such that commercial, food-quality 1,3-diglyceride oils are produced.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
A method for producing diglycerides with high acid value rice bran oil
The invention discloses a method for producing diglyceride with rice bran oil of high acid value. The method adopts rice bran oil of high acid value as the substrate material and glycerin as the acyl acceptor, and employs lipase for the glycerolysis of rice bran oil of high acid value through enzymatic reaction and the synthesis of diglyceride through esterification in a non-solvent system. The method comprises the steps of: (1) subjecting crude rice bran oil of high acid value to a hydrated degumming process so as to obtain degummed rice bran oil of high acid value; (2) adding glycerin into the degummed rice bran oil of high acid value, thus obtaining a mixture of diglyceride; (3) separating the mixture of diglyceride, thus obtaining diglyceride. In the invention, the preparation processis shortened, the unit operation process of separating the solvent from the system is nonexistent, and the energy consumption is saved. The method of the invention makes fully use of the free fatty acid in the system to reduce the acid value of the system, and the loss of nutrient components from the rice bran oil of high acid value under an enzymatic mild reaction condition is reduced.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Non-hydrogenated vegetable oil based shortening containing an elevated diglyceride emulsifier composition
ActiveUS20070148312A1Desirable consistencyFunction increaseFatty acid esterificationEdible oils/fats with aqeous phaseTriglycerideGlycerol
A mono-, di-, and triglyceride emulsifier composition is provided that is obtained by the interesterification or glycerolysis of triglycerides with glycerol. The diglyceride portion w / w is at least about 65% to about 80%, and most preferably from about 70% to about 80% (HiDi). The high diglyceride emulsifier is useful in preparing a trans free shortening from anon-hydrogenated vegetable oil for use in bakery goods, which then have a significantly lower saturated fat content and a substantially higher polyunsaturated level than heretofore available when a conventional mono- and diglyceride emulsifier is used in the goods. A preferred shortening that is predominantly in stable beta prime crystalline form is prepared by mixing on a weight to weight basis from about 10% to about 30%, and preferably about 15% to 20%, of the HiDi composition, with the remainder being non-hydrogenated soybean oil.
Owner:CARAVAN INGREDIENTS
Preparation method of diglyceride-enriched functional oil
InactiveCN102199634AIncrease contentVigorousChemical industryOn/in organic carrierVegetable oilDiglyceride
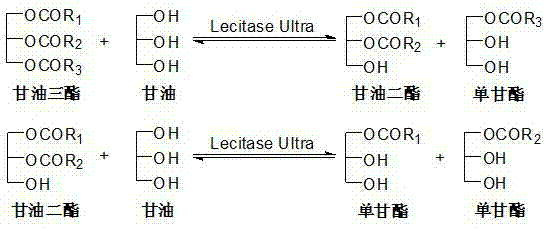
The invention relates to a preparation method of diglyceride-enriched functional oil. The method comprises following steps of: (1) immobilizing Lecitase Ultra; (2), carrying out a glycerolysis reaction on vegetable oil under the catalysis of immobilized Lecitase Ultra; and (3) carrying out product separation. The Lecitase Ultra used in the preparation method disclosed by the invention has low price which is only 5-10 percent of the price of lipase; and resin DA-201 for Lecitase Ultra immobilization has low cost. The immobilized Lecitase Ultra has good catalysis effect, high diglyceride content, less byproducts and recycling performance of the immobilized Lecitase Ultra; and therefore the diglyceride-enriched functional oil prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention has lower cost and favorable application prospect in the industry.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing diglyceride through continuous glycerolysis by enzyme method
The invention relates to a method for preparing diglyceride through continuous enzymatic glycerolysis, which pertains to the technical field of gease modification. In the invention, glycerin, raw oil material and low-boiling single-phase organic solvent are fully mixed, and then continuous glycerolysis is carried out through a fixed bed reactor filled with immobilized lipase, and the products are distilled for removing the organic solvent to obtain the high-content diglyceride mixture. The invention greatly reduces the viscosity of the reaction system, improves the intersolubility of reaction materials, and protects the enzyme, thus improving the reaction efficiency and prolonging the service life of the enzyme.
Owner:无锡中粮工程科技有限公司
Method of glycerolysis reaction for preparing partial glyceride
ActiveCN103060394AImprove thermal stabilityEasy to recycleOn/in organic carrierFermentationGlycerolGlycerolysis
The invention discloses a method of glycerolysis reaction for preparing partial glyceride, and belongs to the technical field of oil modification. The method comprises a first step of immobilization of Lipase T1, a second step of glycerolysis reaction of immobilized lipase catalysis oil, and a third step of separating products. The Lipase T1 is high in thermostability, after being immobilized through hydrophobicity macroreticular resin, the Lipase T1 can catalyze glycerolysis to be reacted under no-water environment in range of 75-95 DEG C. No by-product is produced, content of the partial glyceride is high in the products, immobilized enzyme can be recycled, and therefore the method of the glycerolysis reaction for preparing the partial glyceride has good application prospect in industries.
Owner:YHSN TECH LTD
Method for extracting squalene from grease
ActiveCN106748615AEfficient enrichmentAvoid the downside of yield reductionDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsSterolMonoglyceride
The invention discloses a method for extracting squalene from grease. The method comprises the following steps of using glycerin and lipase to perform glycerolysis on the grease; converting most of triglyceride in the grease into monoglyceride and diglyceride; utilizing a cyclodextrin inclusion technique to extract the squalene, so as to avoid the complicated operation of the one-step column chromatography or saponification extraction method, greatly reduce the usage amount of organic solvent, and avoid the defects of high cost and low efficiency in the supercritical extraction and high-efficiency counter-current chromatography. The method has the advantages that the amount of impurities is small, the squalene and residual sterol are adsorbed and separated by an alumina column, and the purpose of further purifying the squalene is realized.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HANFANG PHARMA
Non-hydrogenated vegetable oil based shortening containing an elevated diglyceride emulsifier composition
ActiveUS7691428B2Without the attendant negative effects on cardiovascular healthDesirable consistencyFatty acid esterificationEdible oils/fats with aqeous phaseSaturated LevelTriglyceride
A mono-, di-, and triglyceride emulsifier composition is provided that is obtained by the interesterification or glycerolysis of triglycerides with glycerol. The diglyceride portion w / w is at least about 65% to about 80%, and most preferably from about 70% to about 80% (HiDi). The high diglyceride emulsifier is useful in preparing a trans free shortening from a non-hydrogenated vegetable oil for use in bakery goods, which then have a significantly lower saturated fat content and a substantially higher polyunsaturated level than heretofore available when a conventional mono- and diglyceride emulsifier is used in the goods. A preferred shortening that is predominantly in stable beta prime crystalline form is prepared by mixing on a weight to weight basis from about 10% to about 30%, and preferably about 15% to 20%, of the HiDi composition, with the remainder being non-hydrogenated soybean oil.
Owner:CARAVAN INGREDIENTS
Process for converting low and high free fatty acid containing oils into no free fatty acid containing oils and associated systems and devices
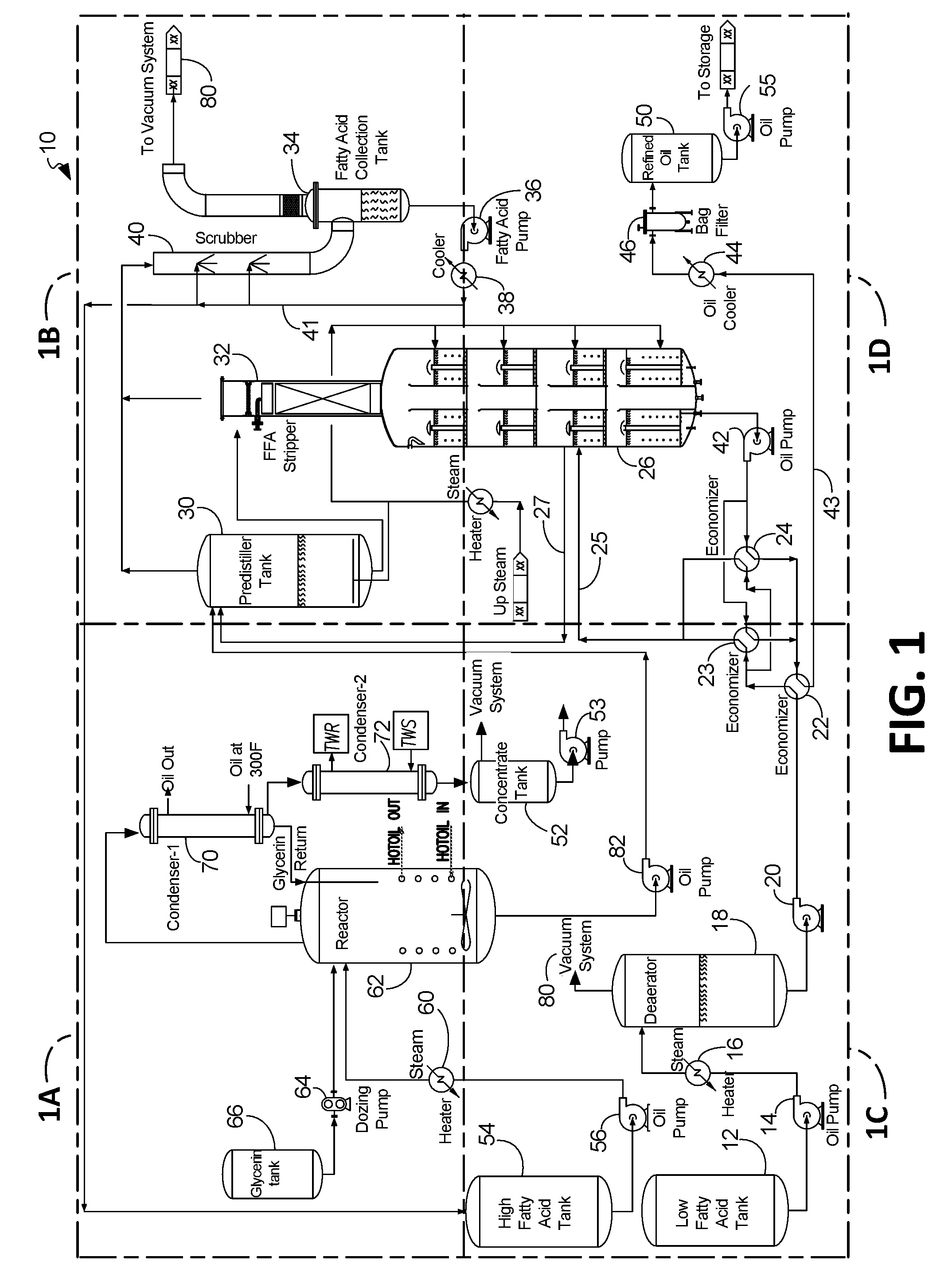
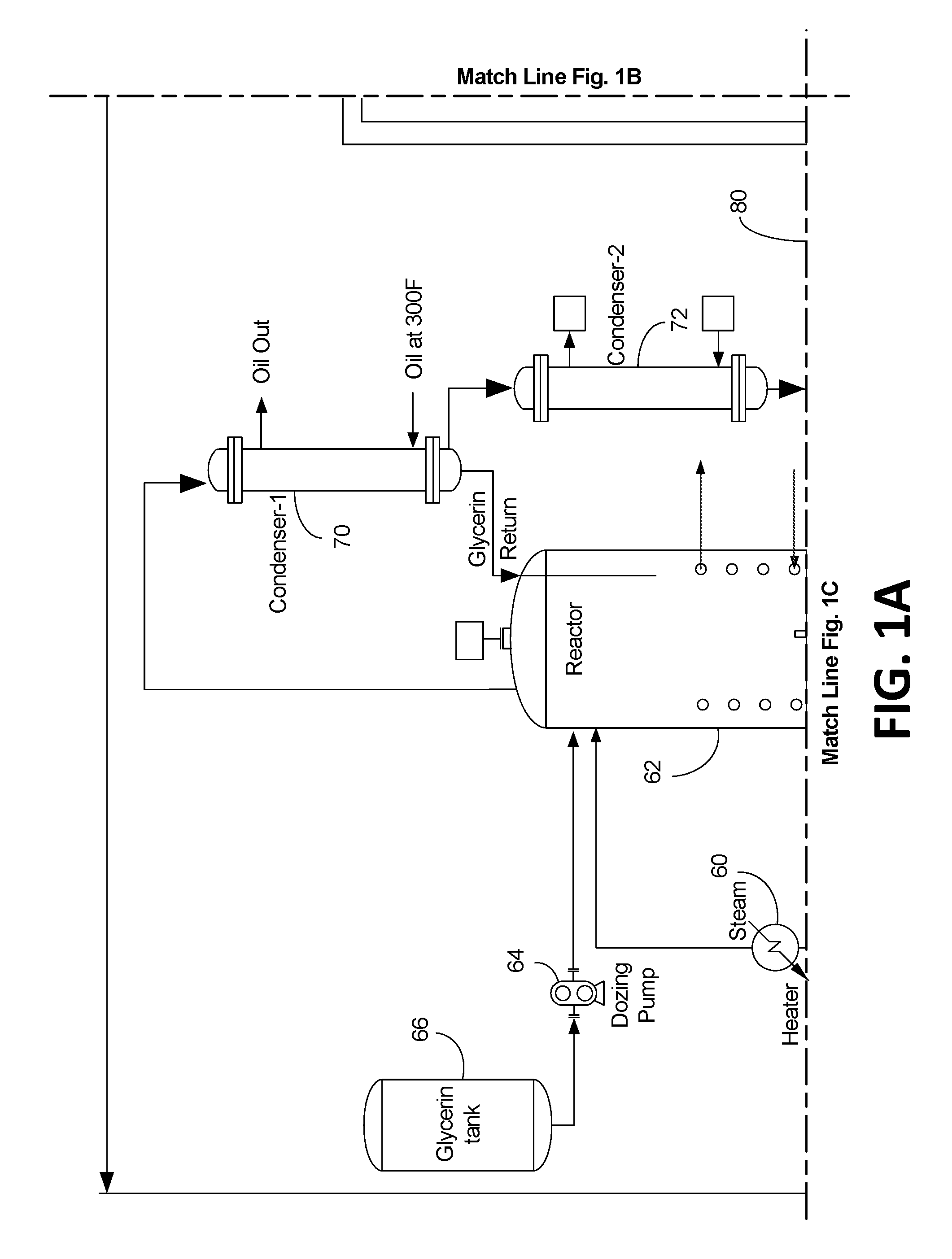
InactiveUS20160152924A1Reduce energy consumptionReduce waste consumptionFatty acid esterificationFatty acids production/refiningGlycerolSteam distillation
The disclosed apparatus, systems and methods relate to the conversion of high free fatty acid (“HFFA”) containing oils defined as oils containing 20-100% free fatty acids (“FFA”) and low free fatty acid (“LFFA”) containing oils defined as oils containing 1-20% free fatty acids (FFA) into oil with less than about 0.5-1% FFA. If the feedstock is HFFA oil, the process includes a combination of partial glycerolysis of HFFA oils to produce LFFA oils and subsequent stripping of LFFA oils to produce NFFA oils via steam distillation. If the feedstock is LFFA oil, the process includes stripping of LFFA oils to produce NFFA oils via steam distillation and subjecting FFA to partial glycerolysis to convert FFA to oil.
Owner:TECHNOCHEM
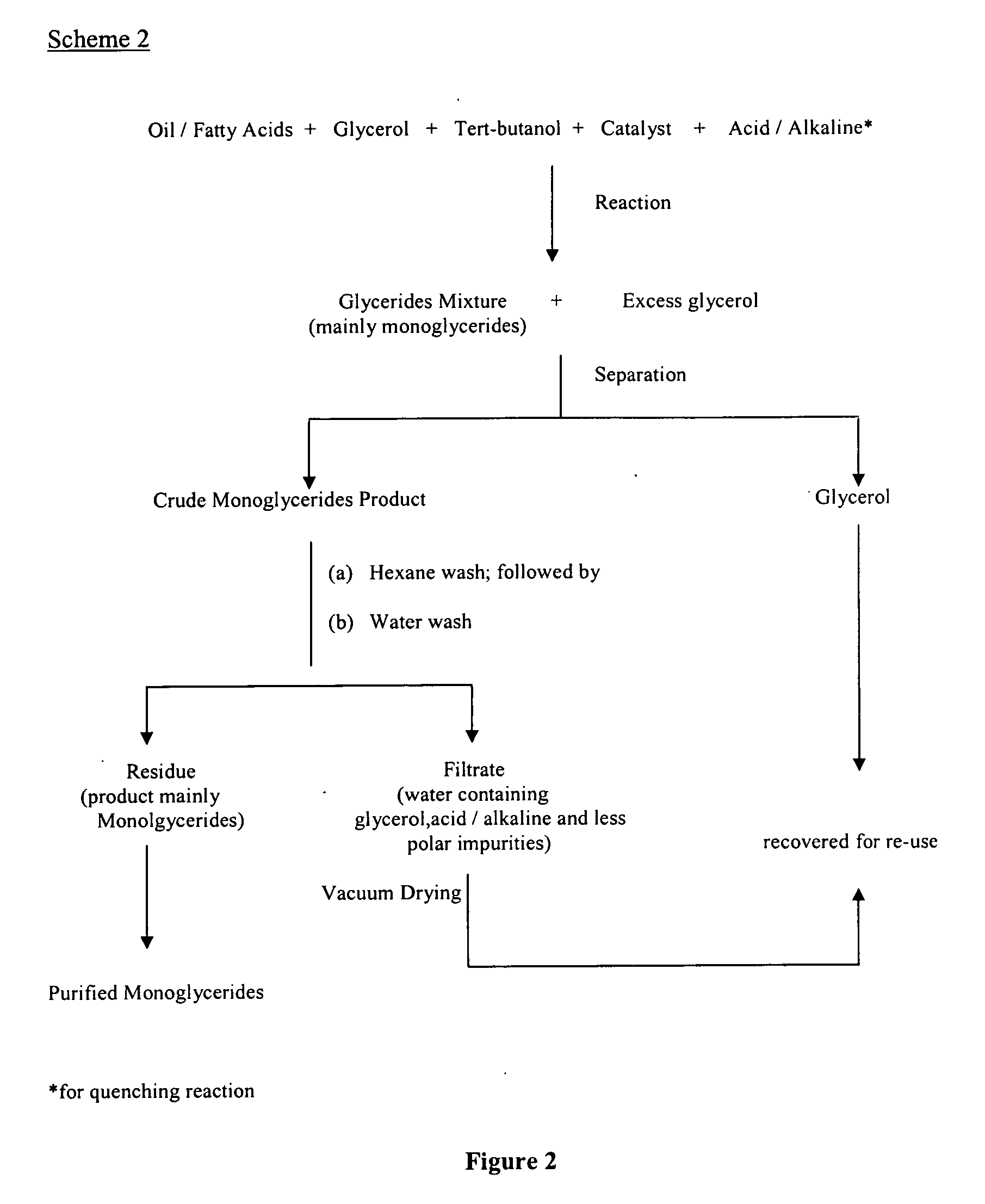
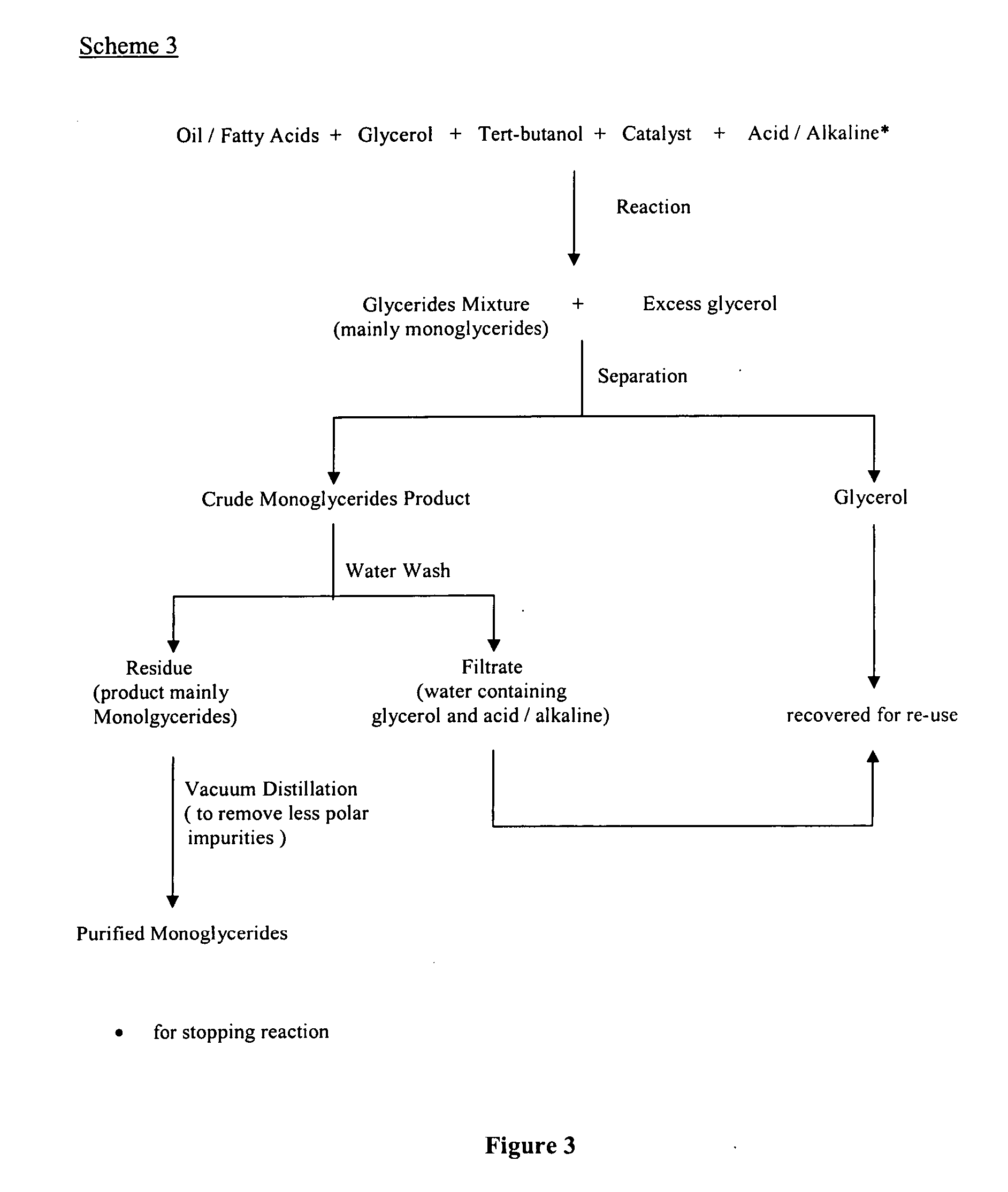
High purity palm monoglycerides
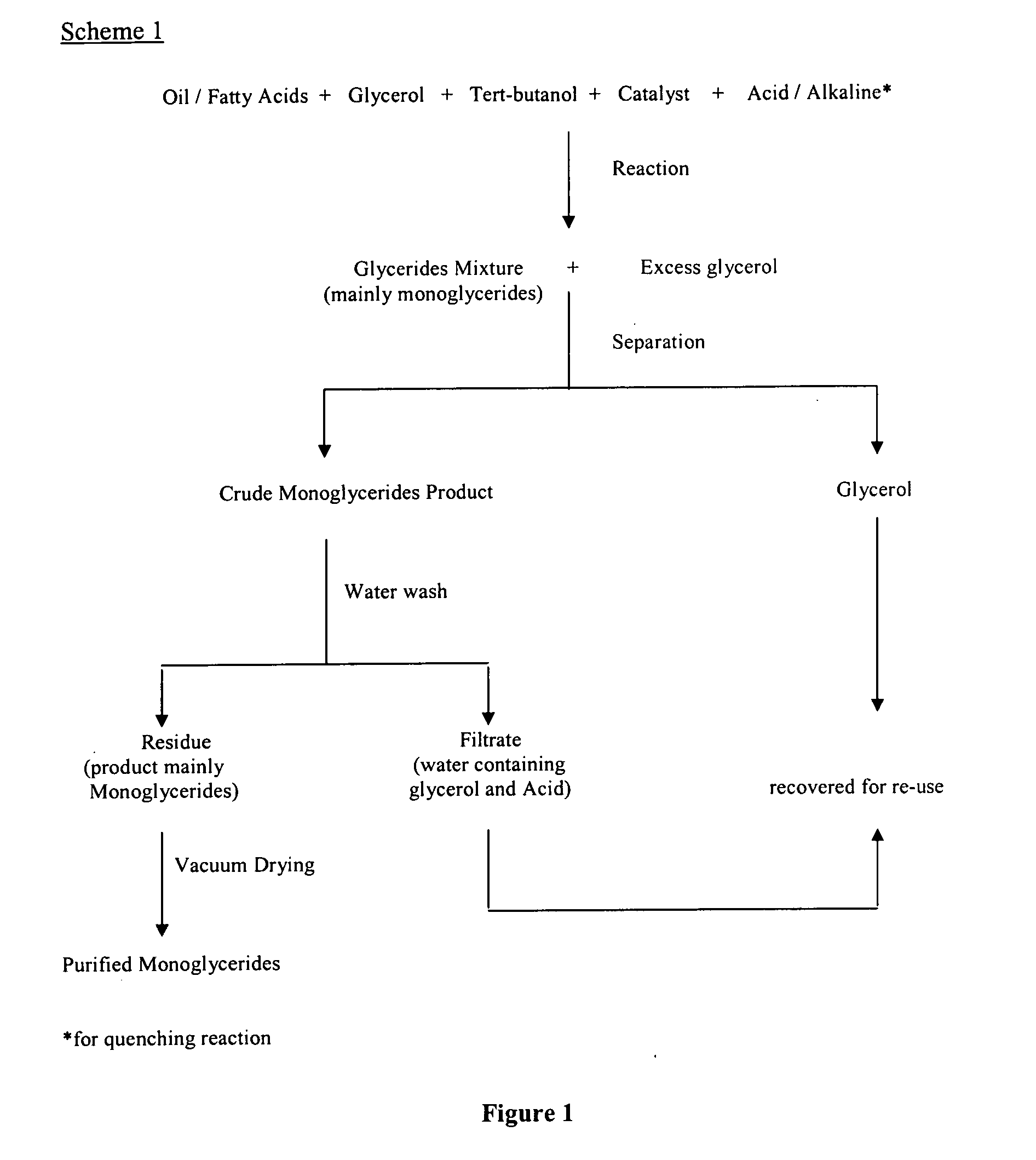
InactiveUS20060128979A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationMonoglycerideGlycerol
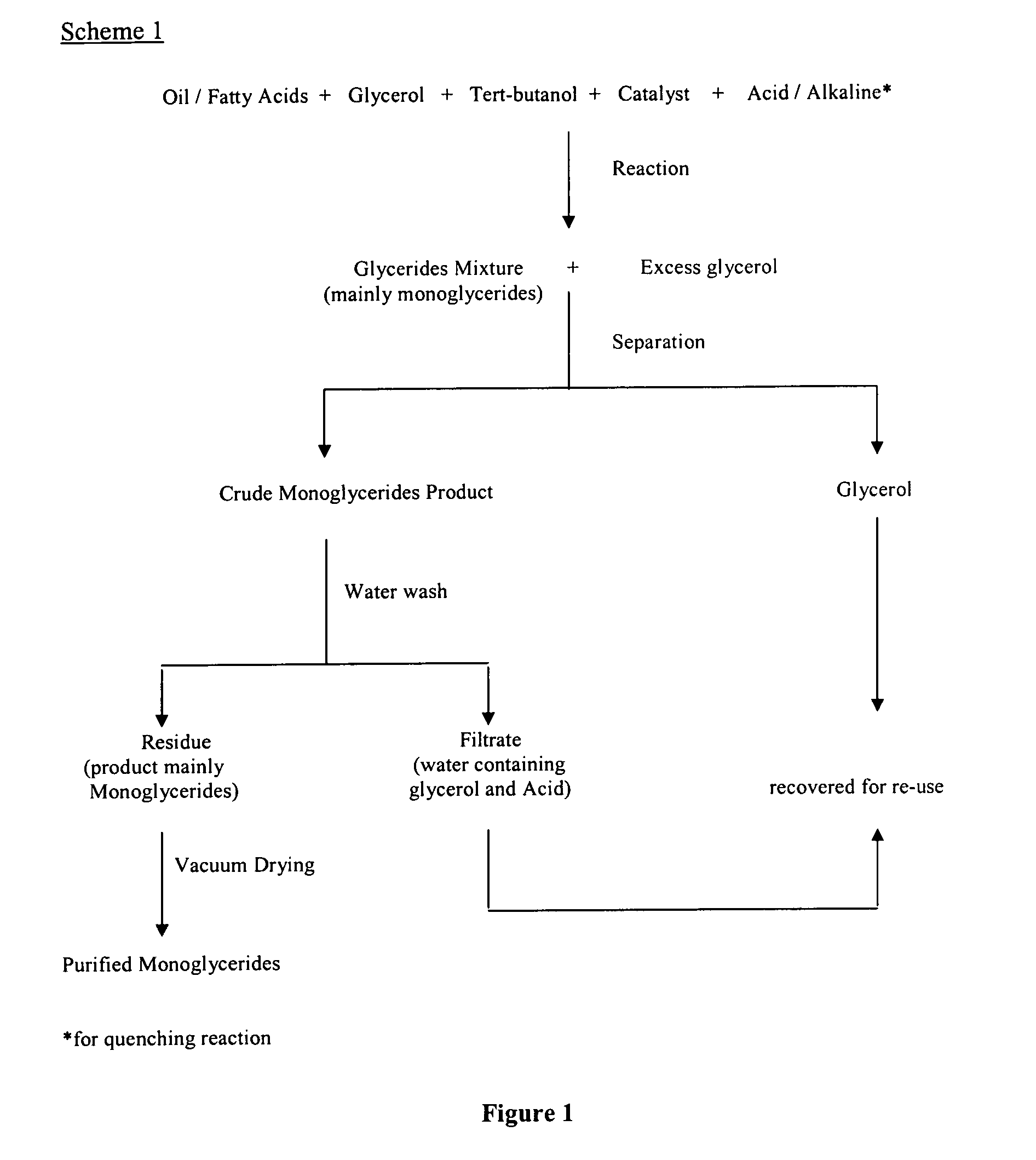
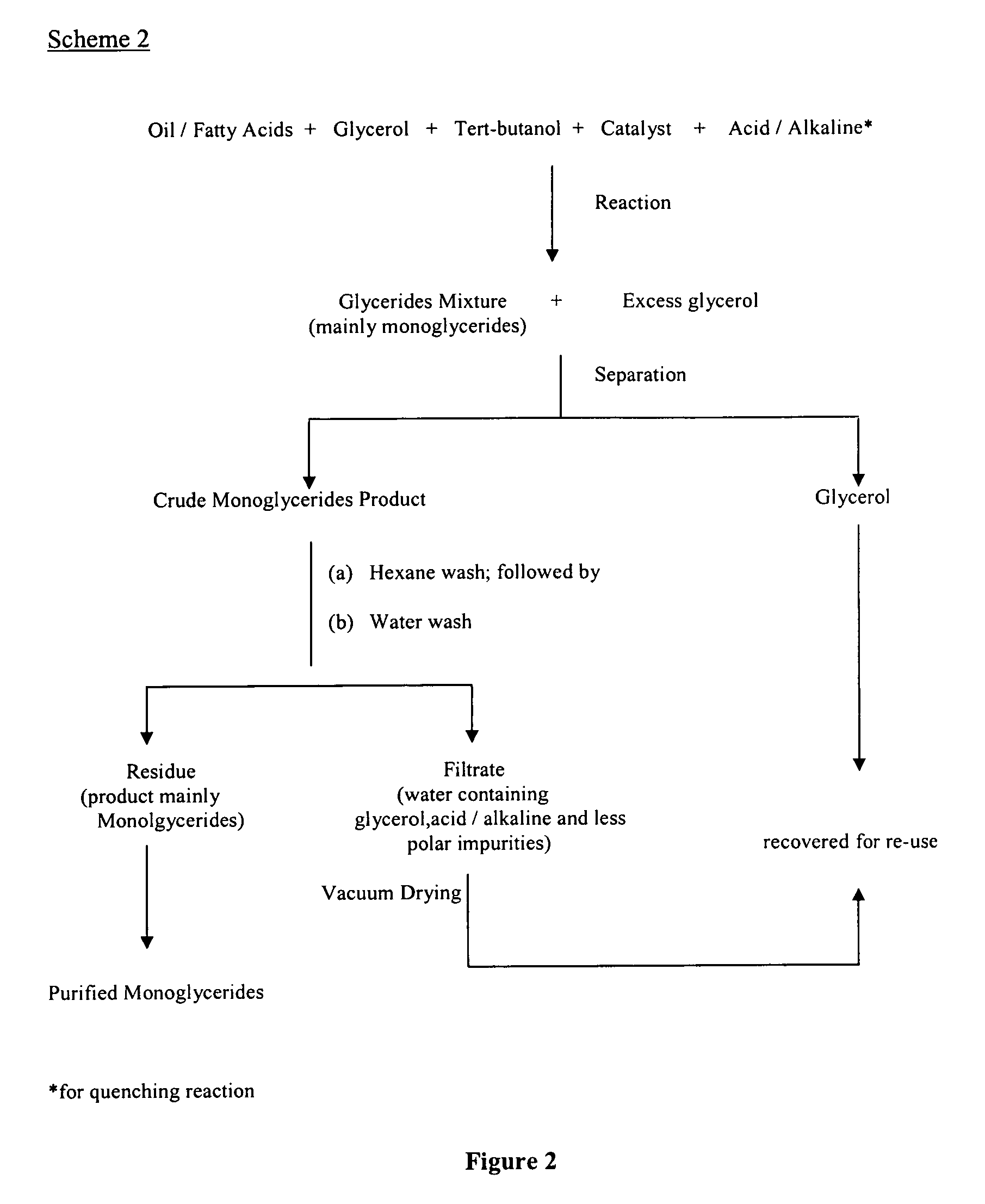
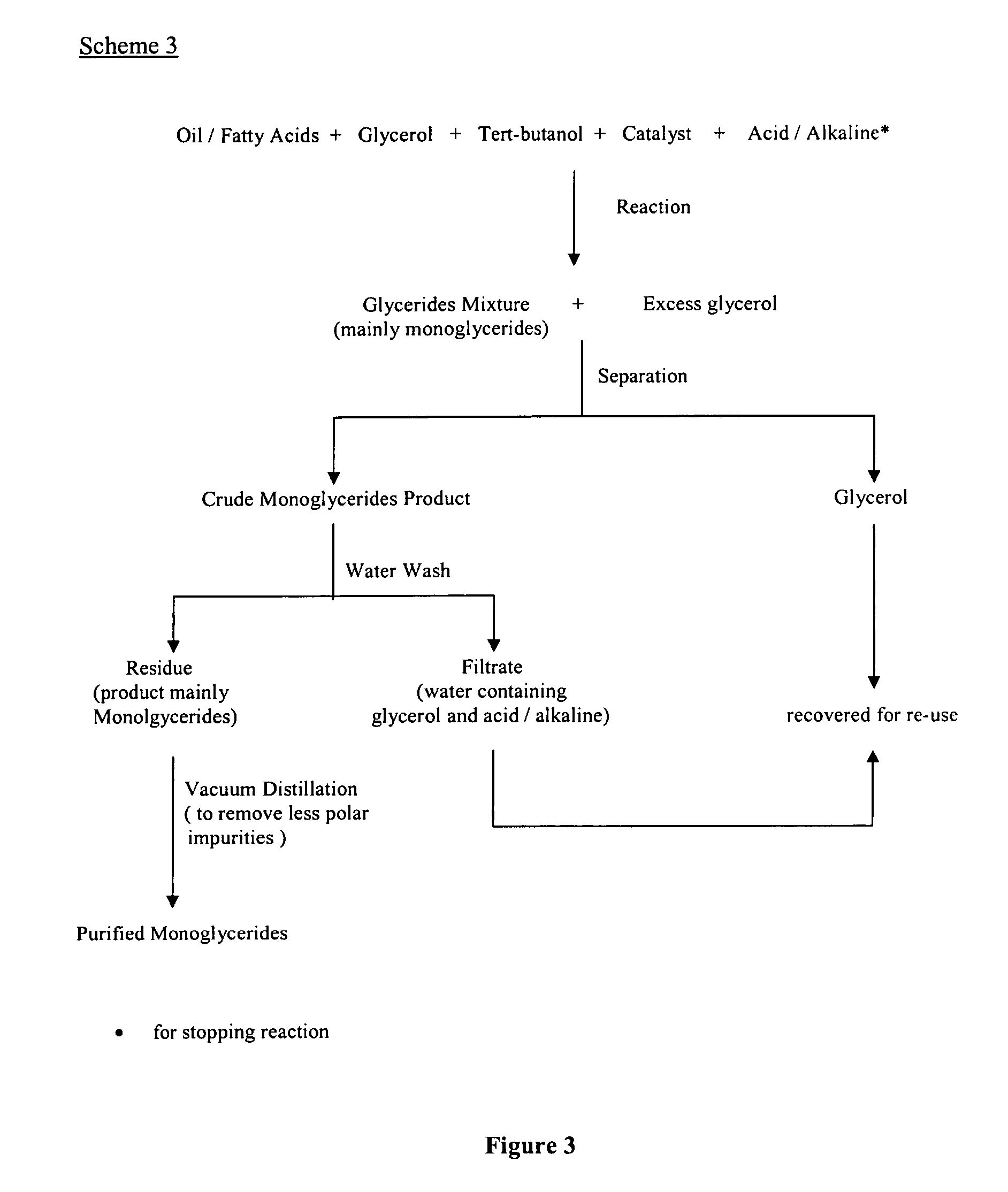
The present invention relates to a process for producing high purity monoglycerides from edible oils / fats and fatty acids through glycerolysis, in particular but not exclusively to the production of monoglycerides from palm oil and palm oil products. This is achieved by providing a process for the production of monoglycerides of fatty acids or fats and oils, comprising the steps of reacting fatty acids or fats and oils with excess glycerol in the presence of an acidic or alkaline catalyst; substantially separating the crude reaction product from the other reaction components; removing unwanted reaction components from the crude reaction product by washing; drying the reaction product.
Owner:LEMBAGA MINYAK SAWIT MALAYSIA
Preparation method for epoxidized plant oil
ActiveCN104894175ASimple separation processEasy to operateChemical recyclingFermentationGlycerolOil phase
The invention discloses a preparation method for the epoxidized plant oil, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) subjecting the plant oil and hydrogen peroxide to epoxidation reaction with partial glyceride lipase as a catalyst and glycerol as a reaction promoter; (2) separating reaction products to recover the oil phase and obtain the epoxidized plant oil. The above process is free of any side reaction, such as hydrolysis, glycerolysis and the like. Meanwhile, the product of the method is single and the production process is easy to control. The catalyst can be recycled. Therefore, the method is good in industrial application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Peanut butter having a non-hydrogenated vegetable oil based high diglyceride emulsifier
InactiveUS20070148314A1Avoid separationEffective structureFatty acid esterificationFood preparationTriglycerideGlycerol
A mono-, di-, and triglyceride stabilizer is provided that is especially adapted for stabilizing nut butters such as peanut butter to prevent separation of the oil portion of the butter from the solids portion while retaining the glossy appearance of the product. The stabilizer is obtained by interesterification or glycerolysis of triglycerides with glycerol. The diglyceride portion w / w of the stabilizer is greater than 60%, and most preferably about 65%. Preferably about 1% to about 4% w / w of the stabilizer is added to the nut butter.
Owner:CARAVAN INGREDIENTS
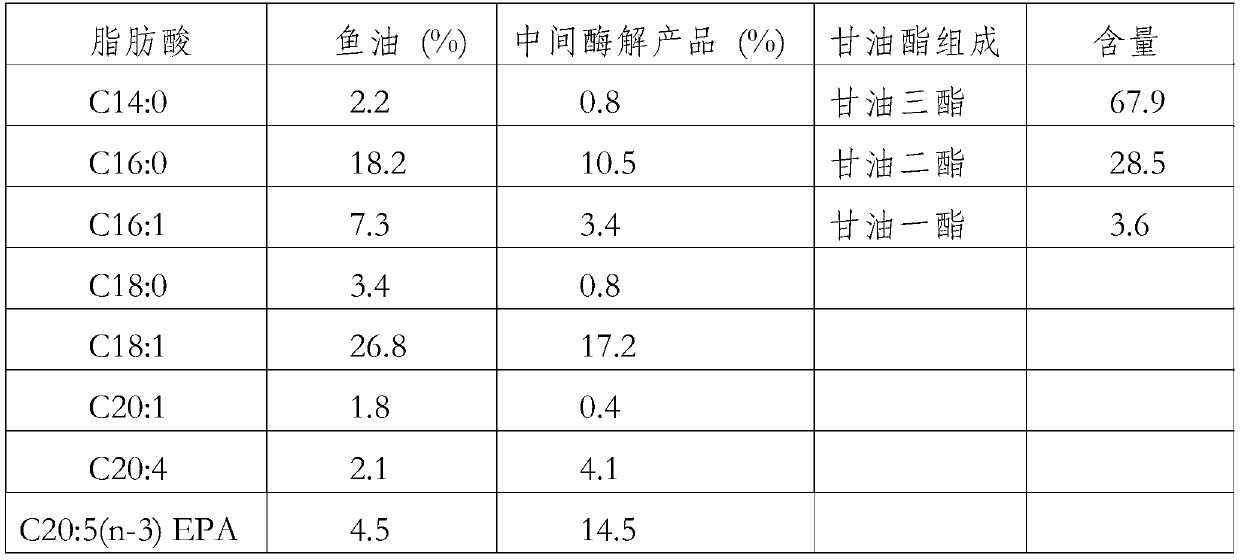
Method for preparing glyceride rich in fish oil and n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid by virtue of enzyme method and product of method
The invention discloses a method for preparing glyceride rich in fish oil and n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid by virtue of an enzyme method and a product of the method. The method comprisesthe following steps: carrying out enzymatic alcoholysis reaction, so as to obtain an intermediate enzymolysis product rich in n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid; adding the intermediate enzymolysis product and glycerin into an intermittent reactor in a molar ratio of 1 to (3-6), adding 3wt%-12wt% of lipase, and carrying out reaction at a temperature of 30-70 DEG C and a stirring velocity of300rpm-800rpm for 6-12 hours, so as to obtain a monoglyceride product; and adding the intermediate enzymolysis product and the glycerin into the intermittent reactor in a molar ratio of 1 to (0.5-2),adding 4wt%-14wt% of lipase, and carrying out reaction at a temperature of 30-70 DEG C and a stirring velocity of 300rpm-800rpm for 6-12 hours, so as to obtain a diglyceride product. The monoglyceride product or diglyceride product rich in n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid is prepared through combination of enzymic-method alcoholysis enrichment and enzymic-method glycerolysis, the processoperation is simple, and the content of n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid in the obtained diglyceride product or monoglyceride product is high.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Conjugated fatty acid containing monoglycerides and process for producing them
InactiveUS7220873B2High degree of esterificationFatty acid esterificationFatty acids production/refiningIodo fatty acidMonoglyceride
This invention provides monoglycerides containing a conjugated fatty acid, and a process for producing the above described conjugated fatty acid containing monoglycerides in which all kinds of lipases can be used as catalysts.This invention relate to monoglycerides containing a conjugated fatty acid (preferably in an amount of 50% or more of fatty acids).This invention also relates to a process for producing the conjugated fatty acid containing monoglycerides, in which the conjugated fatty acid containing a free fatty acid and glycerol are subjected to the reaction of esterification, or of esterification and glycerolysis in the presence of lipase as a catalyst.
Owner:OSAKA MUNICIPAL TECHN RES INST +1
Preparation method of diglyceride-enriched functional oil
InactiveCN102199634BVigorousEasy to recycle and reuseChemical recyclingOn/in organic carrierVegetable oilPhospholipase
The invention relates to a preparation method of diglyceride-enriched functional oil. The method comprises following steps of: (1) immobilizing Lecitase Ultra; (2), carrying out a glycerolysis reaction on vegetable oil under the catalysis of immobilized Lecitase Ultra; and (3) carrying out product separation. The Lecitase Ultra used in the preparation method disclosed by the invention has low price which is only 5-10 percent of the price of lipase; and resin DA-201 for Lecitase Ultra immobilization has low cost. The immobilized Lecitase Ultra has good catalysis effect, high diglyceride content, less byproducts and recycling performance of the immobilized Lecitase Ultra; and therefore the diglyceride-enriched functional oil prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention has lower cost and favorable application prospect in the industry.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing diglyceride by enzymatically catalyzing glycerol by supercritical CO2 system
InactiveCN101948885ALow viscosityImprove solubilityFermentationBulk chemical productionGlycerolCombined method
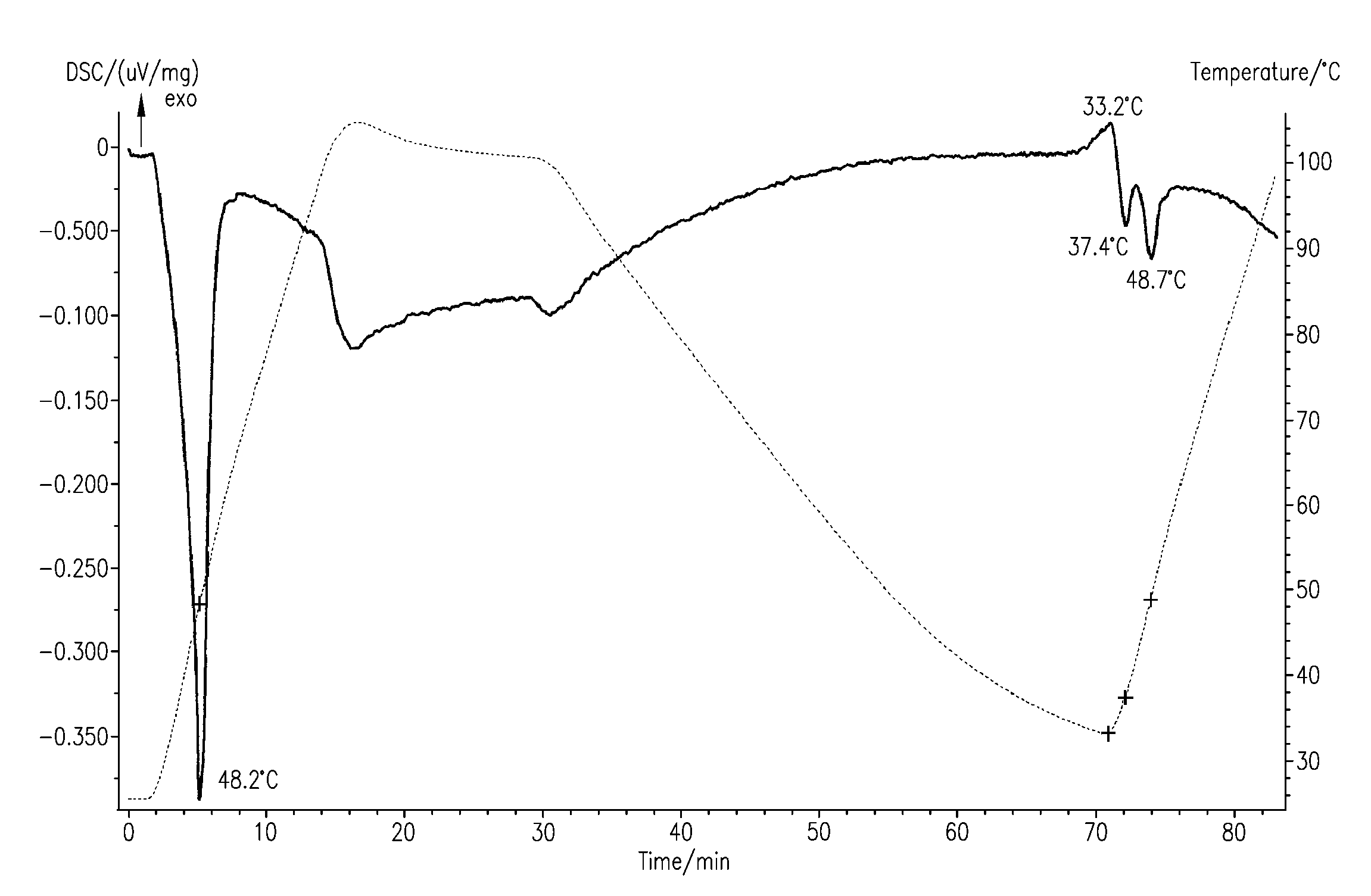
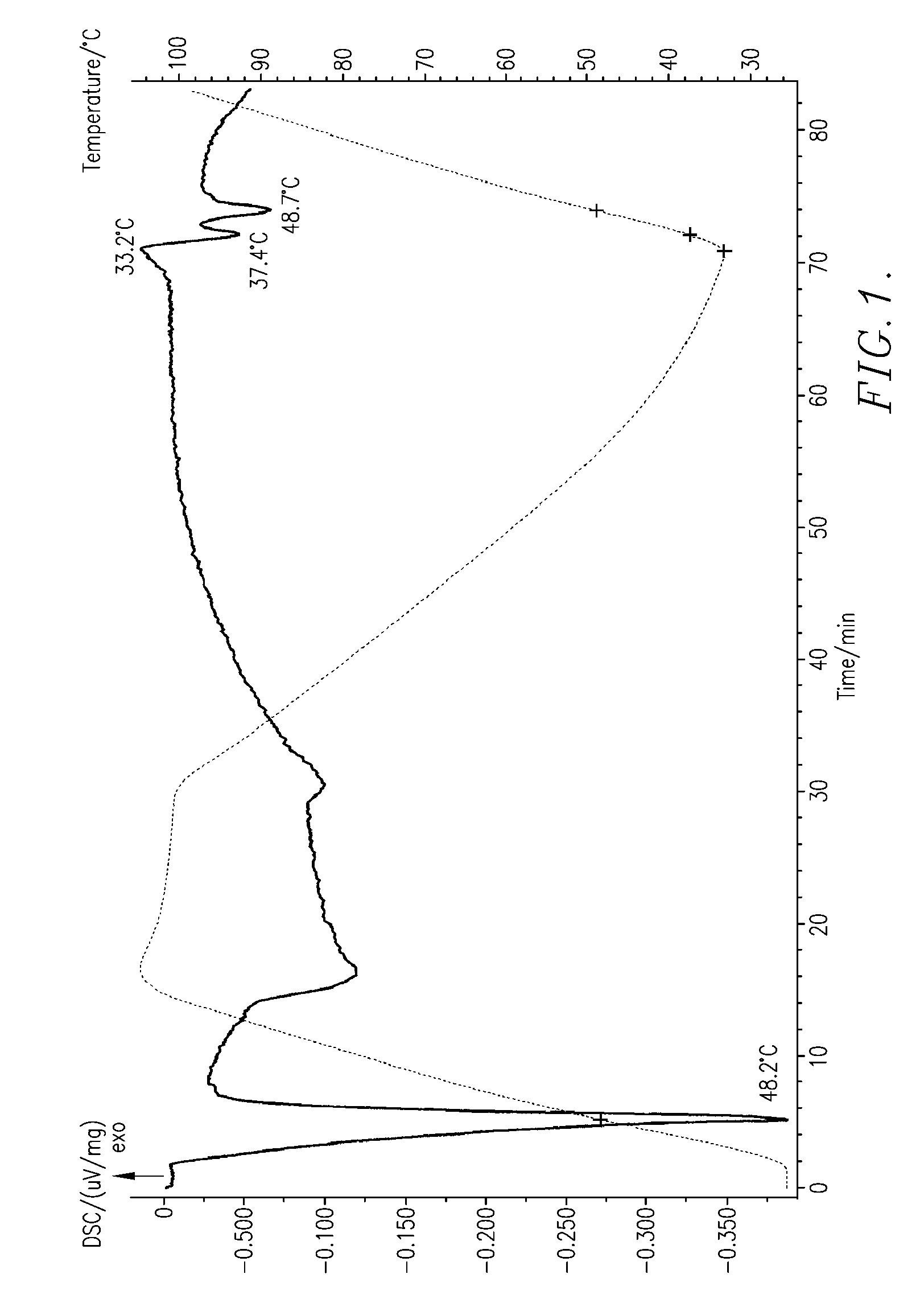
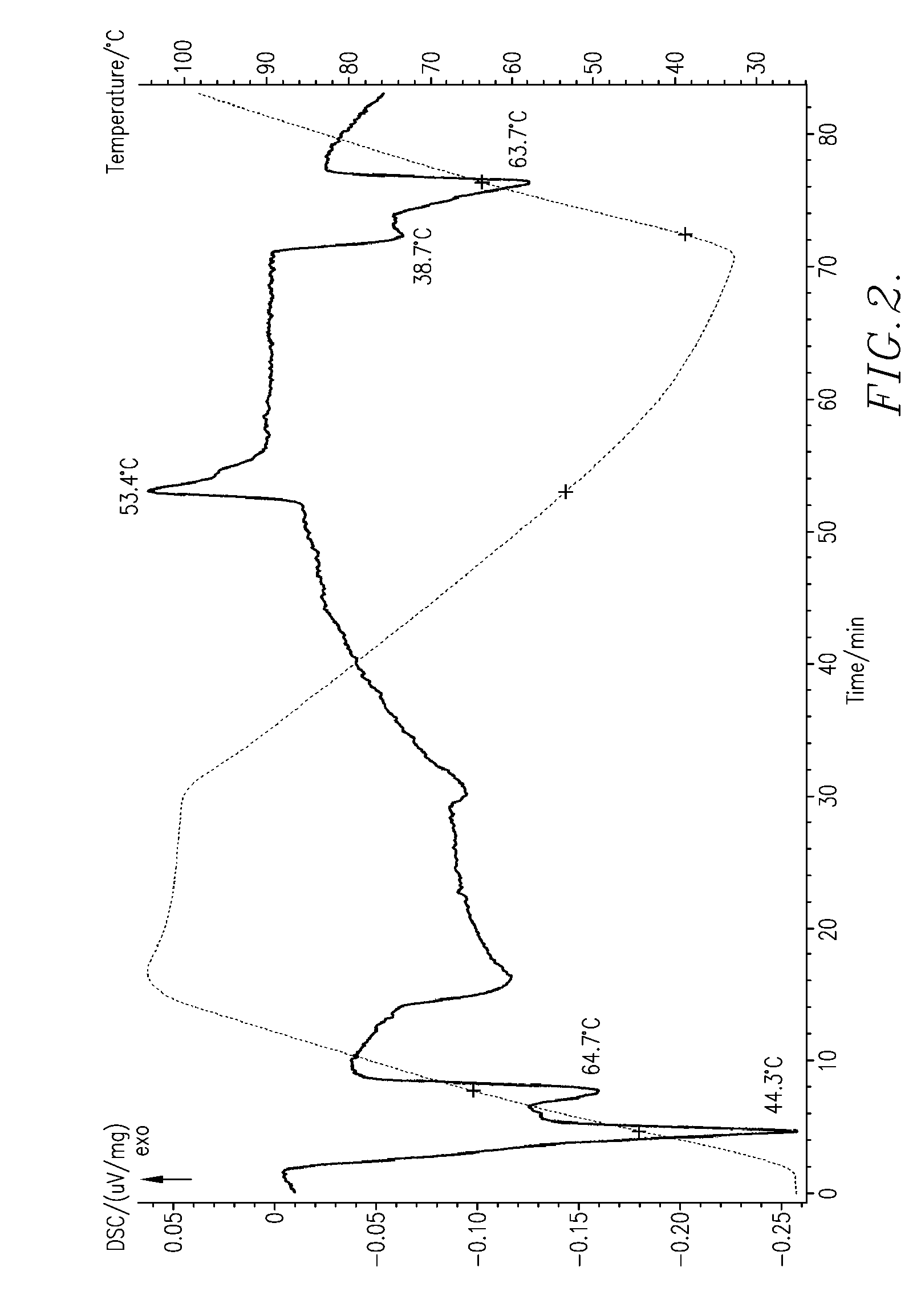
The invention discloses a method for preparing diglyceride by enzymatically catalyzing glycerol by a supercritical CO2 system. Diglyceride (Diglyceride, DAG) is a natural ingredient of oil, has the content of about 5 percent, is an ingredient with stronger function in natrual oil and can be divided into two kinds of 1, 2-DAG and 1, 3-DAG according to different combination positions of acyl and glycerol hyroxyl, wherein the active function of the 1, 3-DAG is better. In recent years, by taking the natural oil as a raw material, the method for preparing the DAG comprises a glycerolysis method, a hydrolysis method, a hydrolysis-esterification combined method and the like. At present, the glycerolysis method is mainly adopted, but has low reaction yield and has little 1, 3-DAG content. In a supercritical state, a CO2 fluid simultaneously plays the roles of a solvent and a catalyst and can efficiently avoid the phenomena of catalyst positioning, inactivation and the like. In addition, moreimportantly, the CO2 fluid can prevent glycerolysis reverse reaction in the reaction environment. The diglyceride content in a product generated through the method is 70.2 percent, wherein the content of the 1, 3-DAG can reach 48.8 percent.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
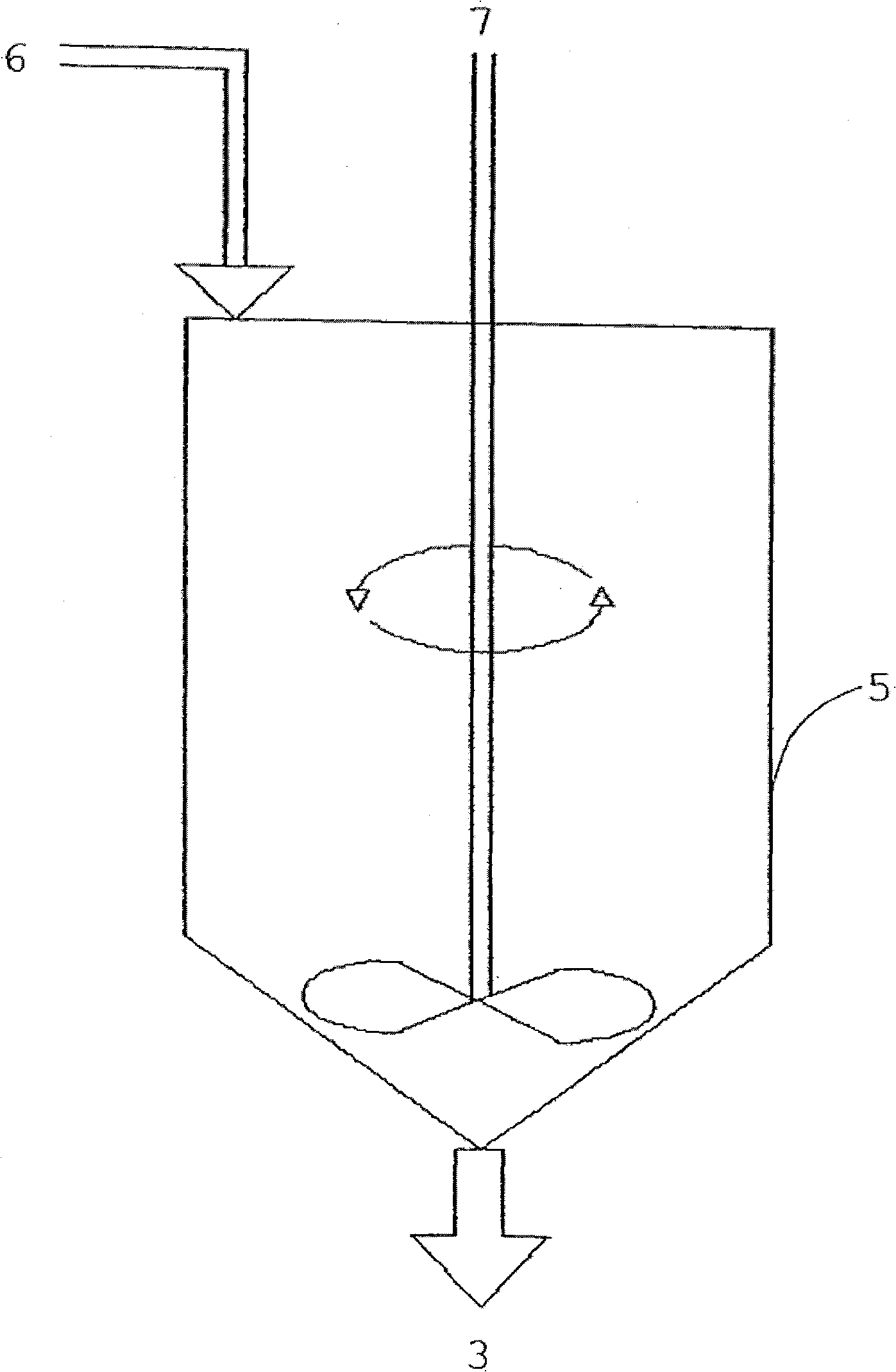
Gradual cooling auxiliary enzymatic method for glycerolysis preparation of lard diglyceride
A gradual cooling auxiliary enzymatic method for glycerolysis preparation of lard diglyceride belongs to the field of deep processing of lard. The method comprises the steps as follows: 1, removing water from raw materials of lard and glycerin in a molar ratio of 1-3:1 under vacuum and heating conditions; 2, adding a catalyst 1,3 specific lipase LipozymeRM IM in the weight 6-16% of the lard, and gradually cooling with magnetic stirring, reacting at 60-70 DEG C for 2-4 h, reacting at 50-60 DEG C for 2-4 h, reacting at 35-50 DEG C for 4-20 h; and 3, after the reaction, taking out the sample, and filtering to remove the lipase, so as to obtain the lard diglyceride. The invention uses lard as the raw material and employs the gradual cooling auxiliary enzymatic method for glycerolysis preparation of lard diglyceride, so as to make full utilization of the cheap lard resource; at the same time, the invention has the advantages of no organic solvent residual and easy separation of product and enzyme, and lays foundation for constructing processing technology of healthful diacylglycerol oil.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
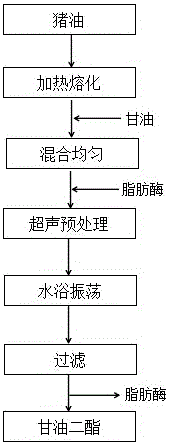
Method for preparing diglyceride through lard glycerolysis catalysis by power ultrasonic pretreatment enzyme method
The invention discloses a method for preparing diglyceride through lard glycerolysis catalysis by a power ultrasound pretreatment enzyme method. The method comprises the steps that 1, a certain quantity of lard is placed in a water bath kettle to be completely melted and is then mixed with glycerinum in a conical flask; 2, immobilized lipase Lipozyme RMIM is added into a lard and glycerinum mixture; then, the mixture is put in a constant temperature water bath for ultrasonic pretreatment, and is then transferred into a water bath constant temperature oscillator for reaction; 3, the lipase is removed from the reaction mixture through filtering, and grease containing diglyceride is prepared. The method has the advantages that the low-cost animal product processing by-product of lard is well utilized; the by-product value is improved; high speed and high efficiency are realized; no solvent residue exists; the product can be easily separated from enzyme; a method for fast and efficiently preparing healthy functional diglyceride is provided.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Transesterification of vegetable oils
ActiveCN101952403ARapid responseEasy to separateFatty acid esterificationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionAlcoholVegetable oil
A method for producing diesel grade fuel of plant origin by transesterifying a refined vegetable oil with a charge of a C1-C4 alcohol in the presence of a catalyst and at least 0.2 parts by volume, related to unit volume of refined vegetable oil, of an aliphatic hydrocarbon solvent with a boiling point of -42 DEG C to 200 DEG C, comprises mixing the oil, alcohol, catalyst and solvent in a single reaction vessel under homogeneous conditions which promote transesterif ication to 95-98% completion and which suppress reverse glycerolysis, without stopping transesterif ication to remove by- product polar glycerol, and without subjecting the oil / fuel mixture to a further transesterif ication step with a fresh charge of alcohol and catalyst.
Owner:QS BIODIESEL
High purity palm monoglycerides
InactiveUS7531677B2Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationMonoglycerideGlycerol
The present invention relates to a process for producing high purity monoglycerides from edible oils / fats and fatty acids through glycerolysis, in particular but not exclusively to the production of monoglycerides from palm oil and palm oil products. This is achieved by providing a process for the production of monoglycerides of fatty acids or fats and oils, comprising the steps of reacting fatty acids or fats and oils with excess glycerol in the presence of an acidic or alkaline catalyst; substantially separating the crude reaction product from the other reaction components; removing unwanted reaction components from the crude reaction product by washing; drying the reaction product.
Owner:LEMBAGA MINYAK SAWIT MALAYSIA
Cocoa butter substitute prepared by camellia oil glycerolysis and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a cocoa butter substitute prepared by camellia oil glycerolysis. The cocoa butter substitute includes 88-92% by mass of diacylglycerol. The invention also provides a method for preparation of the cocoa butter substitute by camellia oil glycerolysis. The method includes the steps of: mixing camellia oil having a triglyceride mass content of greater than 95% with glycerin; adding 1, 3 position specific enzyme into the obtained mixture to carry out glycerolysis reaction; then distilling the reactants to remove glycerin, fatty acid, monoglyceride and triglyceride so as to obtain crude camellia oil diacylglycerol; and then subjecting the obtained crude camellia oil diacylglycerol to fractionation to separate a solid phase. The camellia oil diacylglycerol cocoa butter substitute provided by the invention has very similar properties to natural cocoa butter, and has the same taste.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & ENG
Fermentation production culture medium and culture method for aspergillus niger capable of selective synthesis of 1,3-diglyceride
InactiveCN103484507AMild conditionsEasy to controlMicroorganism based processesFermentationDipotassium hydrogen phosphateGlycerol
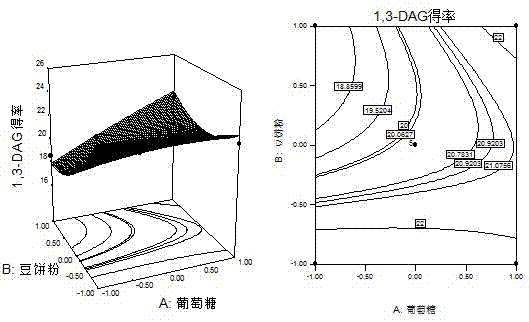
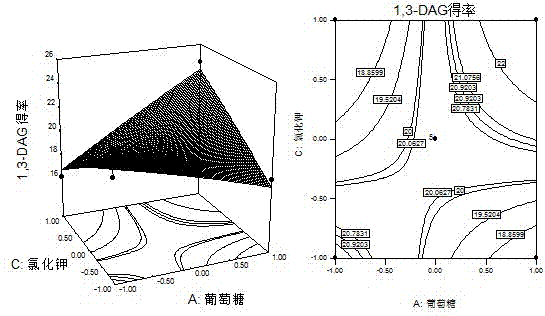
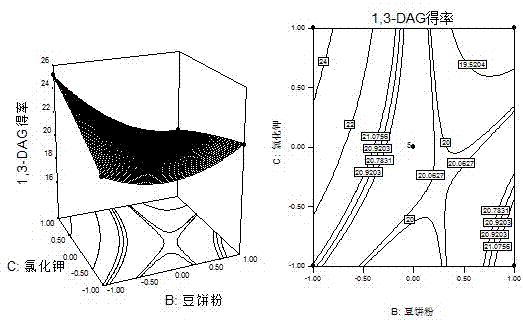
The invention discloses a fermentation production culture medium for aspergillus niger capable of selective synthesis of 1,3-diglyceride. The medium is characterized by comprising the following components, by mass, 1.030% of glucose, 1.785% of soybean cake powder, 0.0441% of potassium chloride, 0.044% of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 0.044% of calcium chloride, 0.044% of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate and 0.044% of zinc sulfate, with the balance being water. The medium provided by the invention enables lipase to have greatly improved capability in catalysis of a glycerolysis reaction of glycerin and triglyceride and allows maximum yield of 1,3-diglyceride to reach 26.887%, increased by 2.7 times compared with yield before optimization. The proportion of 1,3-diglyceride in diglyceride is increased by 88.253%, increased by 1.26 times compared with the proportion before optimization.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
A kind of preparation method of epoxy vegetable oil
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing diglyceride through industrial molecular distillation and reducing 3-chloropropanol ester in diglyceride
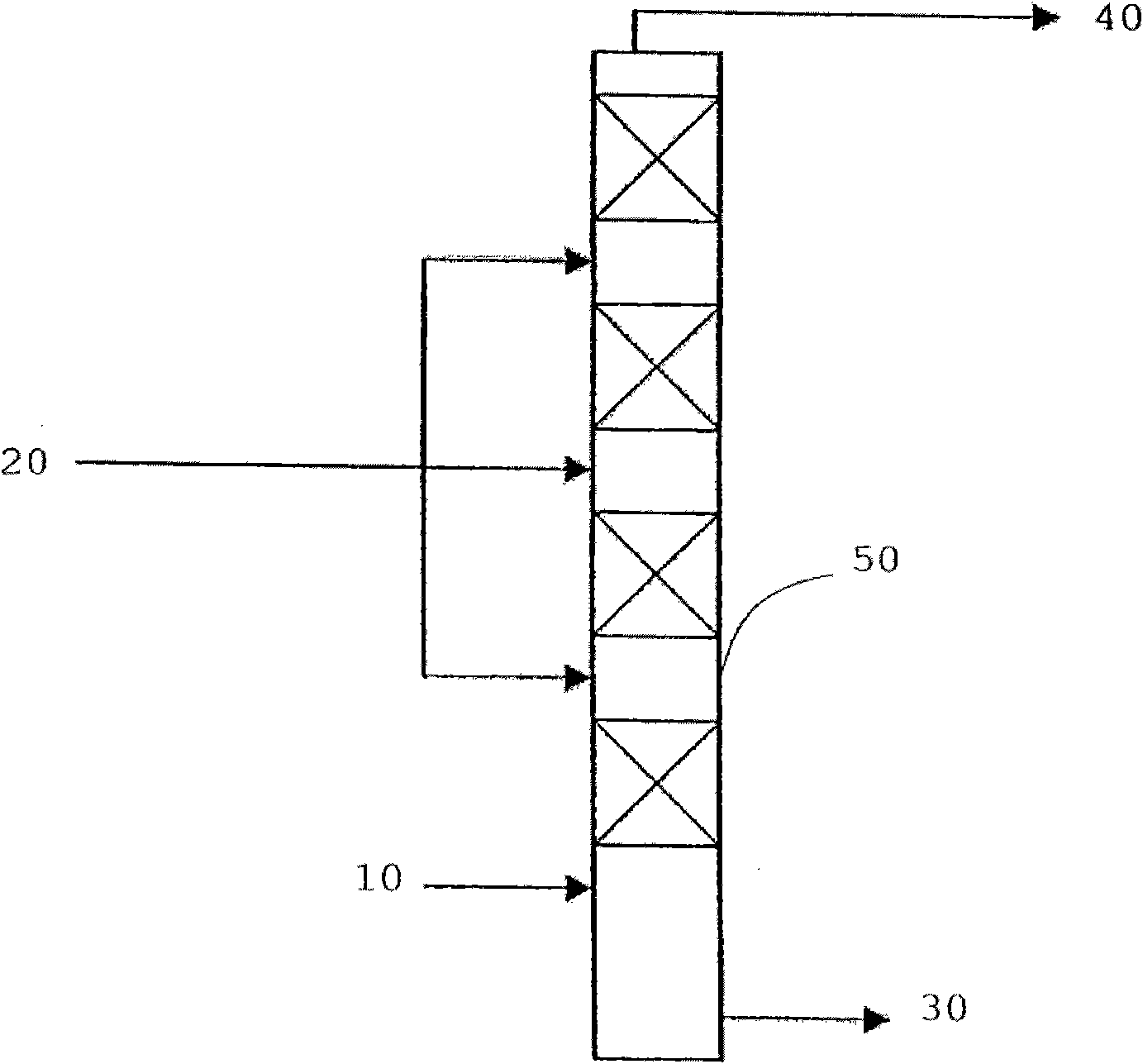
The invention relates to a method for preparing diglyceride through industrial molecular distillation and reducing 3-chloropropanol ester in diglyceride. The method comprises the following main steps: subjecting palm oil, cottonseed oil or vegetable fat to enzymatic glycerolysis so as to obtain diglyceride-rich mixed lipid which is used as a raw material, continuously conveying the raw material to a deaerator via a feed pump and removing air carried by the raw material; heating the degassed raw material to 135 to 160 DEG C, allowing the heated raw material to enter a film evaporator, adjusting the rotating speed of the film evaporator to 150 to 180 r / min and absolute pressure to be 1 mbar or so, and separating out lower-boiling-point components in the raw material; and adjusting the temperature of a heating medium to 230 to 280 DEG C, heating the raw material to 180 to 215 DEG C, uniformly pumping the raw material into a scraped-film type short-path distiller, adjusting the rotating speed of the scraped-film type short-path distiller to 220 to 300 r / min and absolute pressure to be 0.001 to 0.1 mbar or so, and collecting separated light-phase and heavy phase components. In industrial molecular distillation for preparation of a diglyceride product, the flow of the raw material is controlled to be 15 to 25 L / h; and the obtained diglyceride product with purity of 80% or more has to undergo molecular distillation twice.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com