Method for analyzing bitterness intensity of leaves of tea tree
An analysis method and technology of bitterness and astringency, applied in the direction of electrochemical variables of materials, etc., can solve the problems of avoiding subjectivity, limited evaluation objects, and difficulty in direct comparison of specific taste intensity, achieving the effect of quantitative operation and avoiding errors.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
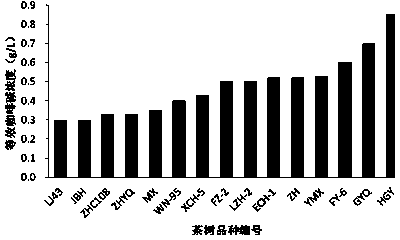
[0033] Comparison of the intensity of bitterness and astringency of fresh leaves of 15 tea tree varieties, the specific steps are as follows
[0034] (1) Caffeine (purity ≥ 95%) is used as a bitter standard substance, based on its detection threshold of 0.097g / L (Susanne Scharbert et al., 2005), and the actual content range of 2%-4% in tea (Ina Kazuo et al., 2007) and the concentration range of caffeine in normal tea soup, prepared 6 standard solutions with gradient concentrations, the concentrations were 0.1 g / L, 0.2 g / L, 0.3 g / L, 0.5 g / L, 0.8 g / L, 1 g / L ; EGCG (purity ≥ 95%) was used as astringent standard substance, based on its detection threshold of 0.087g / L (Thomas Hoffmann et al., 2006), the actual content range of 6.1%-11.61% in tea (Lapczynski et al., 2000) and normal For the concentration range of EGCG in tea soup, six standard solutions with gradient concentrations were prepared, the concentrations were 0 g / L, 0.25 g / L, 0.5 g / L, 0.75 g / L, 1 g / L, and 1.25 g / L. Use t...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The comparison of the intensity of bitterness and astringency of tea tree leaves with different greening degrees, the specific steps are as follows:
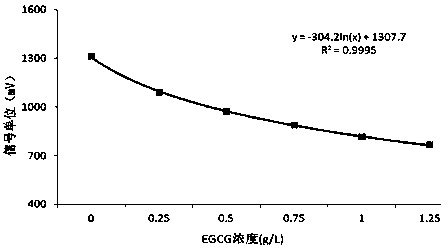
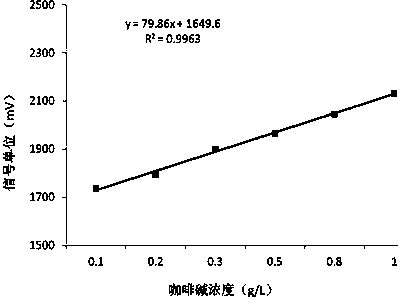
[0040] (1) Prepare different concentrations of EGCG solutions (0g / L, 0.25g / L, 0.5 g / L, 0.75 g / L, 1 g / L, 1.25 g / L) and caffeine solutions (0.1 g / L, 0.2 g / L, 0.3g / L, 0.5 g / L, 0.8 g / L, 1 g / L), establish a function equation: where, where bitterness: y = 79.86x + 1649.6, y is the signal value (mV), x is Concentration of caffeine solution (g / L); astringency: y = -304.2ln(x) + 1307.7, y is the signal value (mV), x is the concentration of EGCG solution (g / L).
[0041] (2) Take 800g of fresh tea tree leaves (coded as ECH-1) to carry out the spreading test, and the spreading thickness is 0.5cm. From 0h to 36h, samples were taken every 4h, a total of 10 samples were taken. The first sampling weight is 1.2g, and the remaining sampling weights are calculated according to the following function and weighed.
[0042]
[0043] In ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The comparison of the intensity of bitterness and astringency of tea tree leaves with different degrees of fermentation, the specific steps are as follows:
[0051] (1) Prepare different concentrations of EGCG solutions (0g / L, 0.25g / L, 0.5 g / L, 0.75 g / L, 1 g / L, 1.25 g / L) and caffeine solutions (0.1 g / L, 0.2 g / L, 0.3g / L, 0.5 g / L, 0.8 g / L, 1 g / L), establish a function equation: where, where bitterness: y = 79.86x + 1649.6, y is the signal value (mV), x is Concentration of caffeine solution (g / L); astringency: y = -304.2ln(x) + 1307.7, y is the signal value (mV), x is the concentration of EGCG solution (g / L).
[0052] (2) 1100g fresh leaves of tea tree variety (coded as ECH-1), spread green for 14h, knead for 10min and then ferment. During the fermentation process, sampling was done every 2h from 0h to 14h, and a total of 9 samples were taken. The first sampling weight is 1.2g, and the remaining sampling weights are calculated according to the following function and weig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com