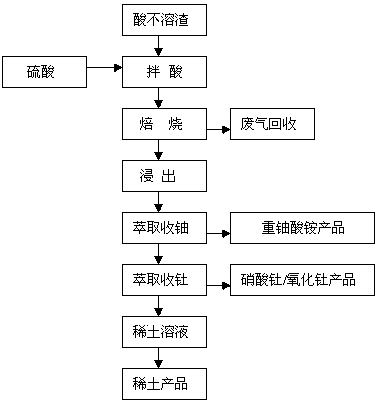
Method for recovering thorium, uranium and rare earth from monazite smelting acid-insoluble slag
A monazite and acid-insoluble technology is applied in the field of recovering thorium, uranium and rare earth from the acid-insoluble slag of monazite smelting, which can solve the problems of large investment in equipment, low recovery rate, difficulty in reflecting social and economic benefits, and achieve Low consumption, environmental friendliness, obvious social and economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] (1) Mix 1000g of monazite smelting acid insoluble slag (including rare earth (REO): 12%, thorium: 2.5%, uranium: 0.3%) with 1200g (98% by volume) concentrated sulfuric acid and place in an air atmosphere at 250°C Roast at constant temperature for 3 hours to form soluble salts of rare earth, thorium, uranium and other valuable elements, that is, to form roasted slag; (2), after leaching the roasted slag with water at room temperature, control the acidity of the solution to 1mol / L, filter, and filter the filtrate with N,N- Dipropyl-1-propanamine extraction agent extracts uranium, and the weight percentage of N,N-dipropyl-1-propanamine and filtrate used is 18%; Then use ammonium bicarbonate back extraction to obtain ammonium diuranate product, used bicarbonate The weight ratio of ammonium to filtrate is 50%. The analysis shows that the thorium and rare earth in the ammonium diuranate product are less than 0.01%, and the thorium and rare earth are hardly extracted and remain...
Embodiment 2
[0028] (1) Mix 1200g of monazite smelting acid-insoluble slag (of which rare earth (REO): 13%, thorium: 2.8%, uranium: 0.4%) and 1600g (98% by volume) concentrated sulfuric acid and put them in an air atmosphere at 300°C Roast at constant temperature for 4 hours to form soluble salts of rare earth, thorium, uranium and other valuable elements, that is, to form roasted slag; (2), after leaching the roasted slag with water at room temperature, control the acidity of the solution to 1.5mol / L, filter, and use trioctane as the filtrate Ammonium diuranate product is obtained by back extraction with ammonium bicarbonate, and the weight ratio of ammonium bicarbonate and filtrate used is 52% , the analysis found that thorium and rare earths in the ammonium diuranate product were less than 0.01%, thorium and rare earths were hardly extracted, and remained in the solution; (3), the solution after extracting uranium was extracted with diethylamine extractant, and the diethylamine used was ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com