Space laser interferometer gravitational wave detector design based on TRIZ and method thereof
A technology of laser interference and gravitational waves, which is applied in the field of precision measurement and can solve the problem of not directly detecting gravitational waves.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
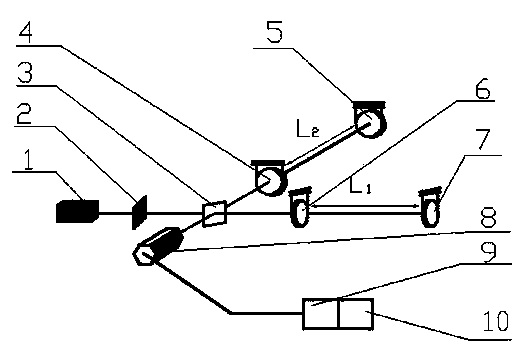
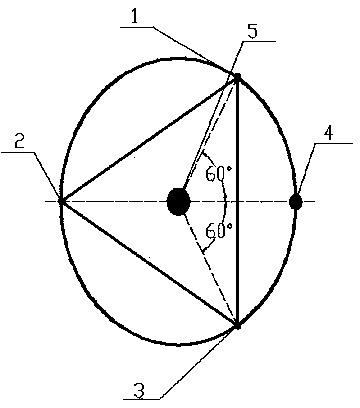
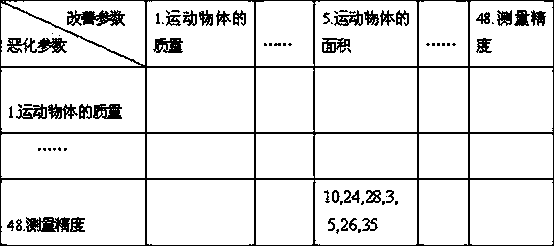
[0014] The patent of the present invention discloses the technical evolution route of researching optical interferometer by using TRIZ and optical interference principle. According to the high frequency band (10Hz-10kHz) is the most sensitive frequency band of the laser interferometer for detecting gravitational waves on the ground; the middle frequency band (0.1Hz-10Hz) is the short arm length (10 3 -10 5 km) the most sensitive frequency band of the space gravitational wave detection laser interferometer; the low frequency band (10 -4 Hz-10 -1 Hz) is the arm length of the laser interferometer for detecting gravitational waves in deep space (10 6 -10 9 km) the most sensitive frequency band. We analyze ground-based laser interferometer gravitational wave detectors, such as figure 1 As shown, it is found that the adaptability of the instrument system to detect low- and medium-frequency gravitational waves is poor. According to the 2008 TRIZ contradiction matrix table, the "...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com