Low-carbon microalloyed free-cutting steel
A free-cutting steel and alloying technology, which is applied to the steel grades of high-end automotive small parts and low-carbon microalloyed free-cutting steels. and other problems to achieve the effect of excellent cutting performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention is described in detail below:
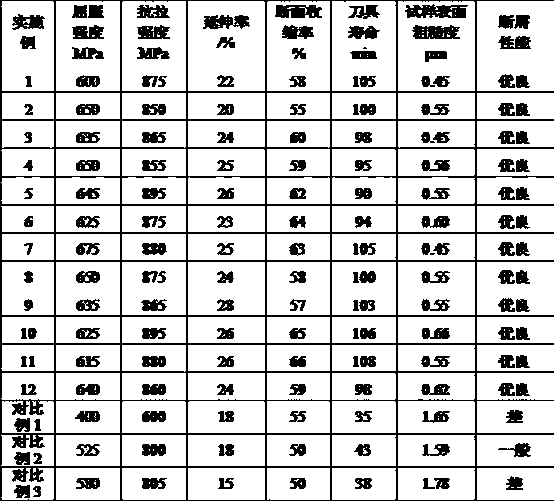
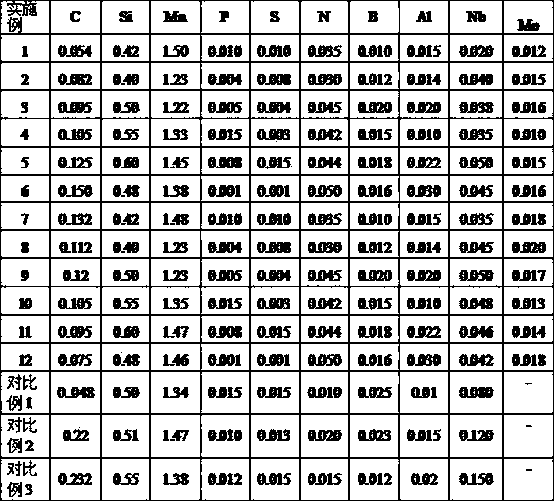
[0025] Table 1 is the value list of each embodiment of the present invention and comparative examples;
[0026] Table 2 is a list of mechanical properties and cutting properties of each embodiment of the present invention and comparative examples.
[0027] Each embodiment of the present invention is produced according to the following conventional processes:
[0028] Electric furnace (converter) → refining (LF, VD, RH) → continuous casting → (heating) rolling;
[0029]Among them, the heating temperature of the billet is controlled at 1150-1250°C, and the holding time is 100-150min; the starting temperature of rough rolling is 1100-1200°C; the finishing rolling temperature is 850-900°C; Water cooling, the cooling rate is 50-120°C / min; after being bundled, it is put into the pit and slowly cooled to room temperature. The process parameters of each embodiment are arbitrarily selected within the stated range.
[0030...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com