pdc drill tool with eccentric oscillating rotation
A technology of eccentric swing and eccentric rotation, which is applied in the direction of drill bits, drilling equipment, earthwork drilling and production, etc., and can solve problems such as inability to break rocks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
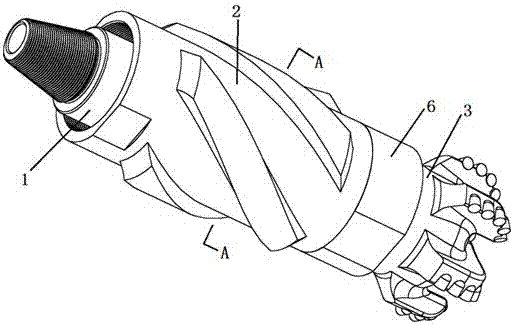
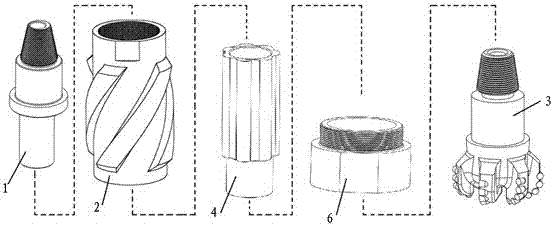
[0050] Such as Figures 1 to 9 As shown, the PDC bit tool of the present invention that can realize eccentric swing rotation is composed of an eccentric shaft 1, an outer shell 2, a PDC bit 3, a cycloidal shaft 4, and a lower joint 6, wherein:
[0051] Such as Figure 5 As shown, one end of the eccentric shaft 1 is provided with a connecting thread 11, and the middle part is provided with a positioning shoulder 13, and the center distance between the geometric center of the eccentric shaft section 12 and the geometric center of the eccentric shaft body is e.
[0052] Such as Image 6 As shown, the upper and lower ends of the outer casing 2 are respectively provided with connecting threads 22 and 23 . Gauge corrugations 21 are arranged on the outer cylindrical surface, and the gauge corrugations 21 can be in a straight structure or in a spiral structure, and the number of them is two or more. An axial shackle surface 25 is arranged on the upper end of the outer shell 2, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Such as Figure 10 As shown, this embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the difference is that passive wear-resistant teeth 211 or active cutting teeth 212 are fixed on the gage flute 21, or passive wear-resistant teeth 211 and active cutting teeth are fixed at the same time. 212.
[0062] Under the ideal drilling conditions of the conventional PDC bit (the "ideal drilling condition" here refers to the working state in which the center of rotation of the bit coincides or nearly coincides with the center of the wellbore trajectory during the process of drilling and breaking the PDC bit), the cutting teeth rotate in one revolution cycle. The cutting amount and cutting load in the drill bit do not change much, so its mechanical stability is good (under ideal drilling conditions, the ratio of lateral unbalanced force to axial force of most PDC drill bits can be controlled within 5% level).
[0063]However, in this embodiment, the PDC bit performs alternatin...
Embodiment 3
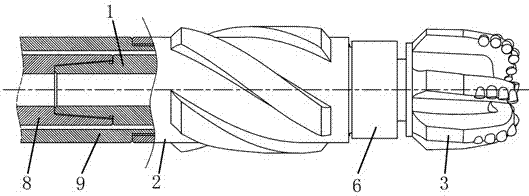
[0066] Such as Figure 11 As shown, this embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 2, and the difference is that a lower joint 6 is provided between the PDC drill bit 3 and the cycloidal shaft 4, and the lower joint 6 is connected to the outer shell 2, and in the An eccentric bearing 7 is installed between the PDC drill bit 3 and the lower joint 6 . The eccentric bearing 7 can be a needle roller eccentric bearing, a sliding bearing, a cylindrical roller bearing, a double-row tapered roller bearing, or a self-aligning roller bearing.
[0067] Since in this embodiment, the PDC drill bit 3 is a cantilever structure in the state of track-changing eccentric rotary motion, its structural rigidity and mechanical stability are lower than those of conventional PDC drill bits. Introducing the eccentric bearing 7 in this embodiment can make the "eccentric wheel-PDC bit" mechanism into a double support structure, thereby improving the structural rigidity and mechanical stability of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com