A method for visually characterizing the spatial distribution and content of moisture in cement-based materials
A cement-based material, spatial distribution technology, applied in the direction of using radiation for material analysis, can solve problems such as the difficulty of cement-based materials, and achieve the effect of accurately predicting changes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1C
[0033] Embodiment 1 CT imaging experiment
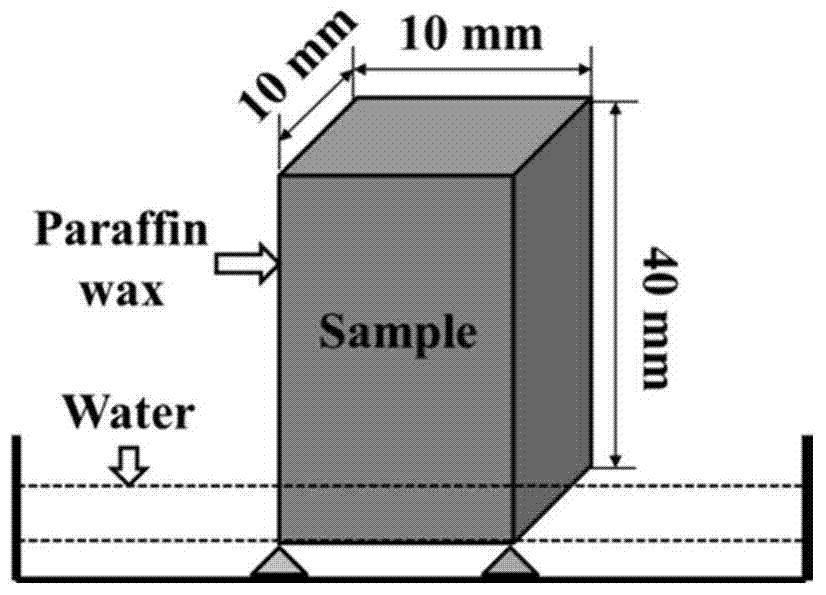
[0034] Step 1: Firstly, the cement slurry is prepared by using ordinary Portland cement. After the sample is formed for 24 hours, the formwork is removed and placed in a standard curing room with a humidity of 95% and a temperature of 20°C for 1 year, and then the specimen is cut into 10mm×10mm× prisms of 40 mm in diameter, and dried in an oven at 105° C. to constant weight to obtain the sample.
[0035] Step 2: Then use paraffin to seal all the end faces and sides of the sample except the water-immersed surface to prevent moisture from intruding into the inside of the sample from the side, then put the sample into a flat-bottomed plastic container, and support the water-immersed surface with a small block.
[0036] Step 3: Place the flat-bottomed plastic container containing the sample on the X-CT imaging device table, inject water into the flat-bottomed plastic container so that the liquid level is 2mm higher than the sample immers...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2 typical capillary water absorption CT image
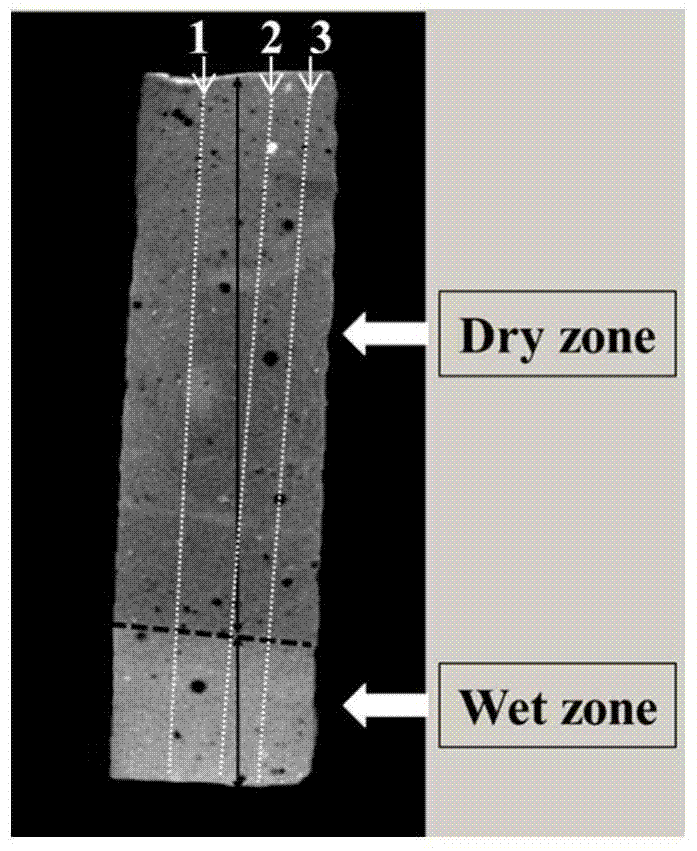
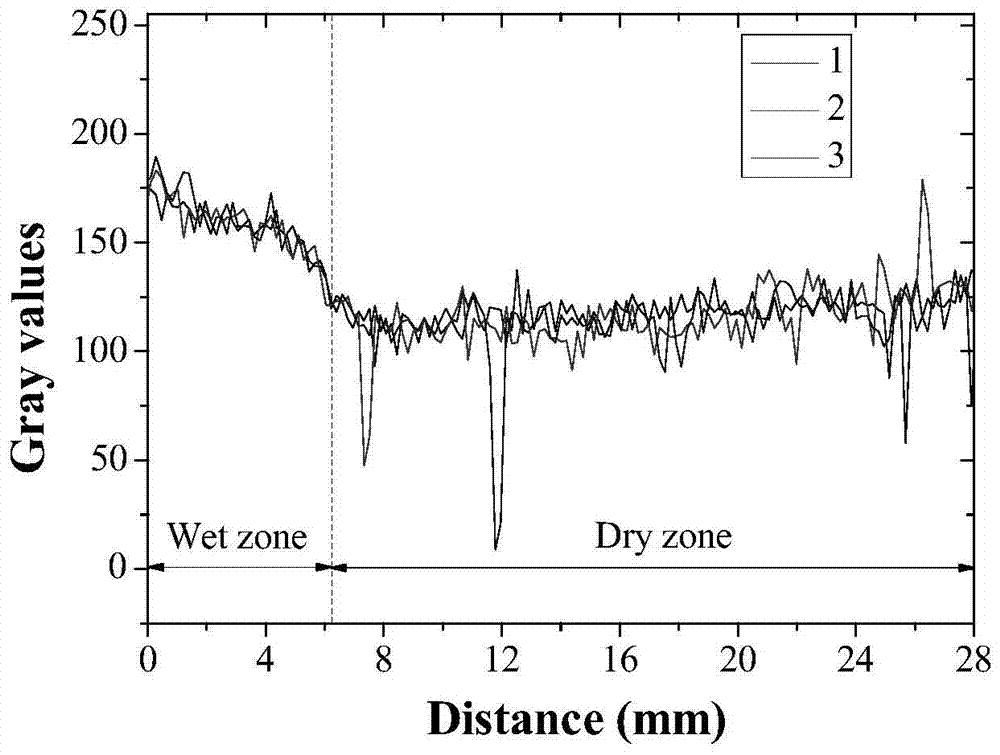
[0039] Taking the water-cement ratio of 0.35 cement paste as an example after absorbing water for 20 minutes, the typical CT imaging of capillary water absorption experiment is as follows: figure 2 As shown, the sample can be divided into two regions according to the location of water absorption: the wet region and the dry region, and the brightness of the bottom wet region is greater than that of the upper dry region. In addition, the height of the bright area on the left side of the cement paste is higher than that on the right side. This is because the cement-based composite material is a heterogeneous material, and the size and volume distribution of the capillary pores are not uniform, resulting in a slow rate of water intrusion into the material. difference.
[0040] In order to accurately characterize the intrusion depth of water in the slurry, three straight lines were randomly selected on the 2D CT im...
Embodiment 3
[0041] The influence of embodiment 3 ground slag dosage
[0042] Figure 4 CT images for in situ observation of water intrusion into cement paste with 0% and 10% fine slag content at different times. With the increase of capillary water absorption time, under the action of capillary adsorption force, the water continuously climbs from the bottom of the sample to the top. Before 60 minutes, the water can quickly invade into the inside of the sample in a short time. When the water absorption time increases from 60 minutes to 270 minutes The capillary water absorption rate is lower than before. It can be seen that the capillary water absorption process of cement paste is rapid in the early stage and slow in the later stage. In addition, it can be observed from the images that the water front does not remain at a fixed position. The water intrusion depth is deeper at the left and right ends of the slurry in the early stage, and the water front is located in the middle of the slu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com