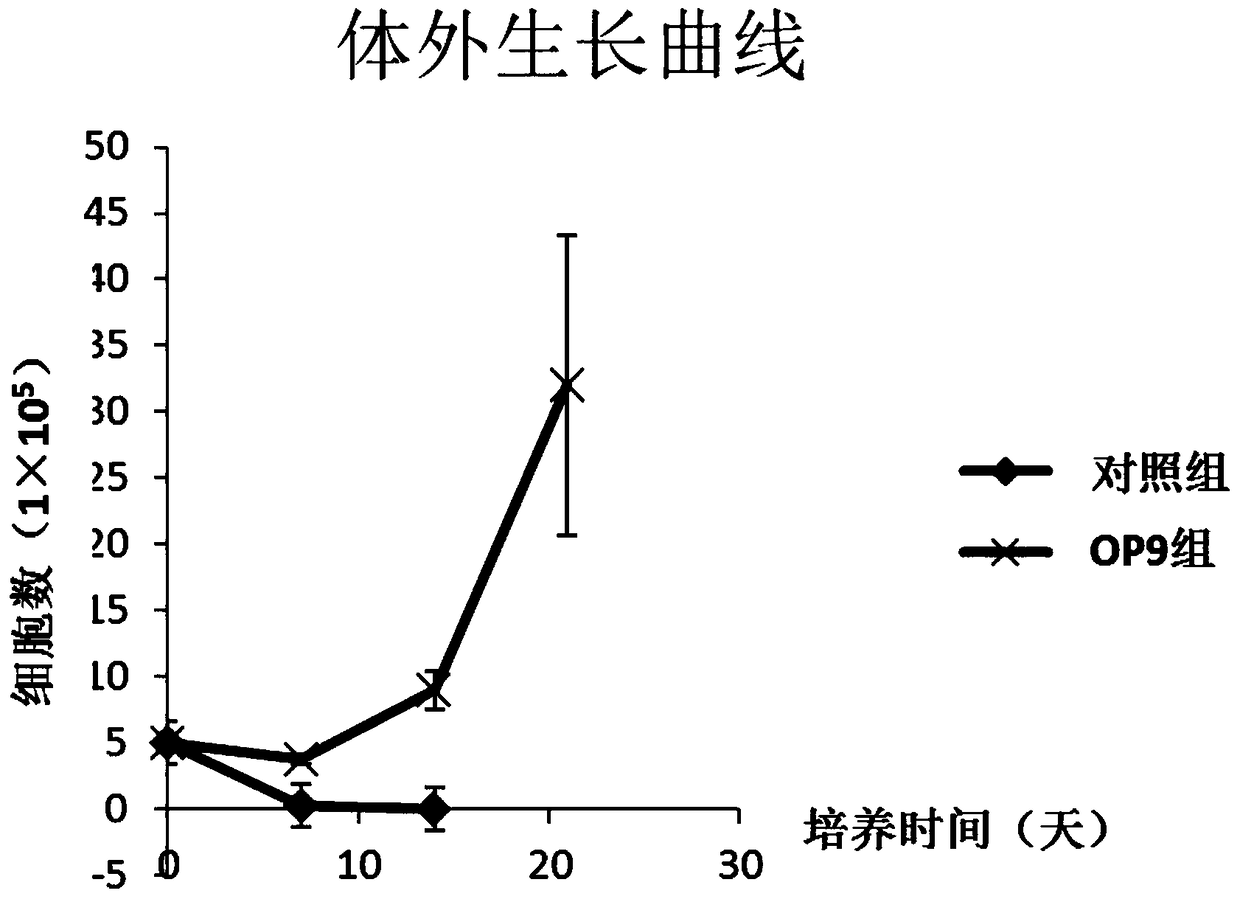
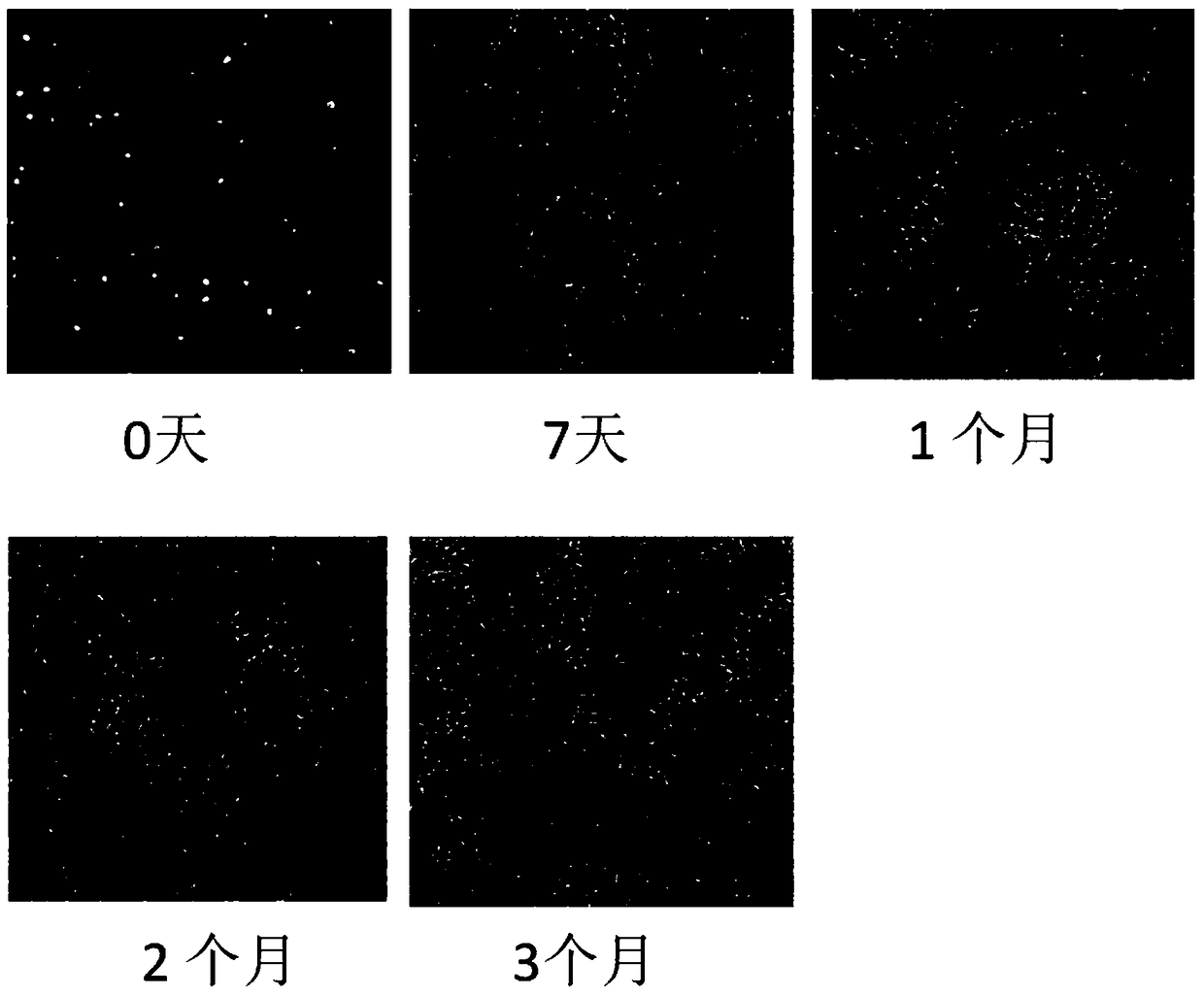
A kind of in vitro culture method of primary B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells
A technology for in vitro culture of leukemia cells, applied in the field of in vitro culture of primary B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells, can solve the problems of long time-consuming, high cost, and low success rate of culture, and achieve the effect of facilitating promotion and high success rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] 1. Culture of OP9 cell line
[0031] OP9 medium: αMEM medium (HyClone, Thermo Scientific, MA, USA), 20% fetal bovine serum (Gibco, Life Technologies, NY, USA), 2mM L-glutamine, 100U / ml penicillin, and 100ug / ml streptomycin.
[0032] Cell passage (adhesion):
[0033] 1) Cells are cultured and maintained in a T75 culture dish. First, use a Pasteur pipette to suck out the culture medium, and wash it once with 2ml PBS;
[0034] 2) Add 2.0-3.0mL 0.25% (w / v) trypsin-0.53mM EDTA solution and incubate for 5-15 minutes until the cell layer is observed to float and disperse under the microscope;
[0035] Note: To avoid cell clumps, do not shake the flask while waiting for the cells to detach. Cells are difficult to separate and can be placed at 37°C to facilitate trypsin catalysis.
[0036] 3) Add 6.0-8.0mL of medium, and gently blow off the cells with a Pasteur pipette;
[0037] 4) Transfer the cell suspension to a 15mL centrifuge tube with a Pasteur pipette, centrifuge at 1...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2: the processing of B-ALL sample
[0047] 1) Mix the bone marrow sample of the B-ALL patient with normal saline in equal proportions;
[0048] 2) In a new 15mL centrifuge tube, add one-half of the diluted blood volume in lymphatic separation fluid (Lymphoprep, StemCell Technologies);
[0049] 3) Slowly superimpose the diluted blood on the layered liquid surface along the wall of the centrifuge tube, keeping the liquid surface clear;
[0050] 4) Gently put the bone marrow sample mixture centrifuge tube into the centrifuge, and centrifuge at 800g / min for 20min;
[0051] 5) Gently take out the centrifuge tube, layer the bone marrow sample mixture, use a Pasteur pipette to carefully absorb the cells in the middle cloud layer and place them in a new 15mL centrifuge tube;
[0052] 6) Wash twice with serum-free αMEM medium or PBS, and resuspend the isolated cells in medium as spare sample cells;
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3: Co-cultivation of primary B-ALL
[0054] B-ALL medium: IMDM medium (HyClone, Thermo Scientific, MA, USA), 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco, Life Technologies, NY, USA), 2mM L-glutamine 100U / ml penicillin, and 100ug / ml streptomycin;
[0055] 1) After diluting the spare sample cells and adding appropriate B-ALL medium for dilution, perform cell counting;
[0056] 2) Dilute the backup sample cells to 1×10 according to the cell counting results 6 / mL;
[0057] 3) Aspirate the OP9 cell culture medium planted in the 24-well plate, and wash it once with B-ALL medium;
[0058] 4) Put 1×10 in 2) 6 / mL sample cells were added to the 24-well plate of 3), and 500ul was added to each well;
[0059] 5) After seeding the plate, shake the cells gently to make them evenly spread on the OP9 stromal cells and fully contact with them;
[0060] 6) Placed at 37°C, humidity 95%, 5% CO 2 cultured in an incubator.
[0061] Note: co-cultivation consumes the medium very quickly, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com