A Method to Improve the Working Distance of Distributed Spontaneous Raman Scattering Temperature Sensor
A spontaneous Raman scattering and temperature sensor technology, applied in thermometers, thermometers with physical/chemical changes, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as test distance drop, limit the maximum optical power of injected light, and light source power weakening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
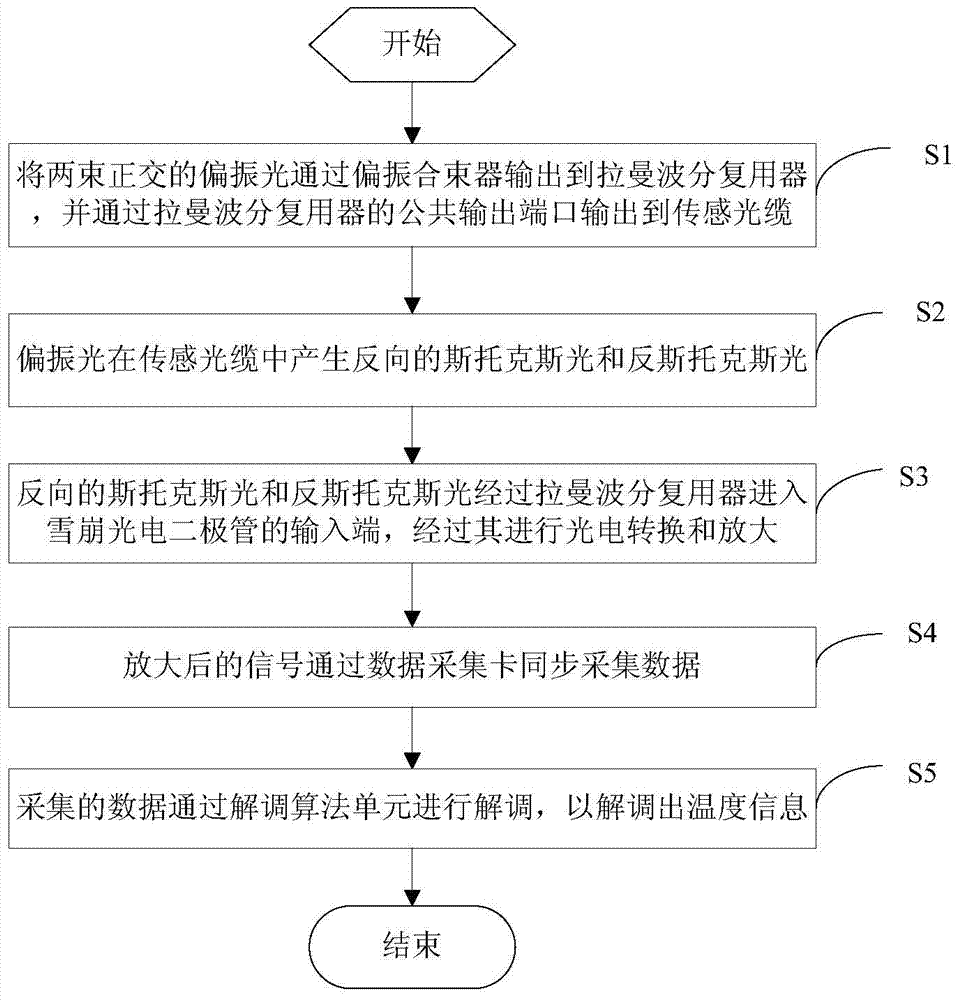
[0024] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
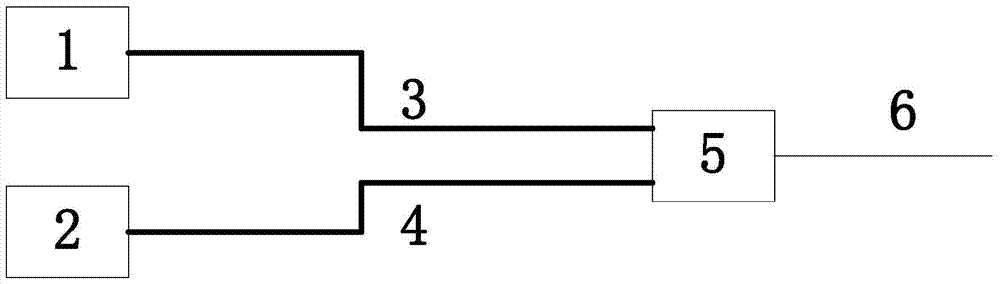
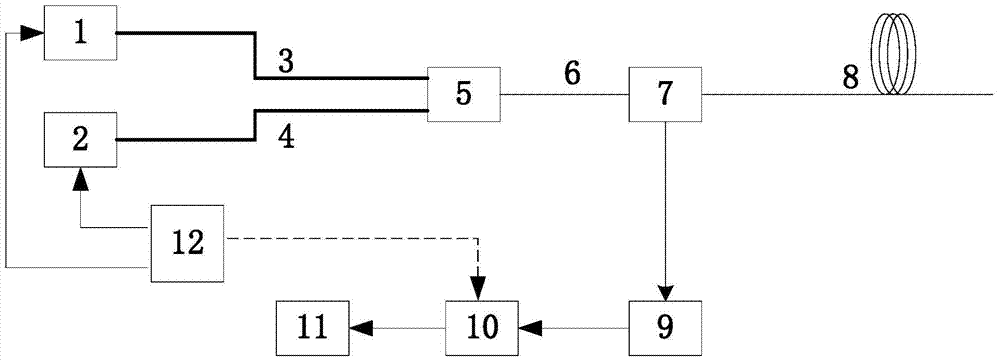
[0025] The whole system can be divided into two parts, such as figure 1 parts shown and figure 2 The next two blocks. figure 1 It shows a design diagram of a light source that improves the working distance of a distributed spontaneous Raman scattering temperature sensor in an embodiment of the present invention. For the convenience of description, only the parts related to the embodiment of the present invention are shown, and the details are as follows:
[0026] The light source part of the whole system includes a first laser (polarization maintaining fiber output) 1, outputting linearly polari...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com