Method and system for dynamically distributing resources in microcontroller unit MCU
A micro control unit and dynamic allocation technology, applied in the MCU field, can solve problems such as chip discarding, high SRAM, chip waste, etc., and achieve the effects of improving performance, effective utilization, and miniaturization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
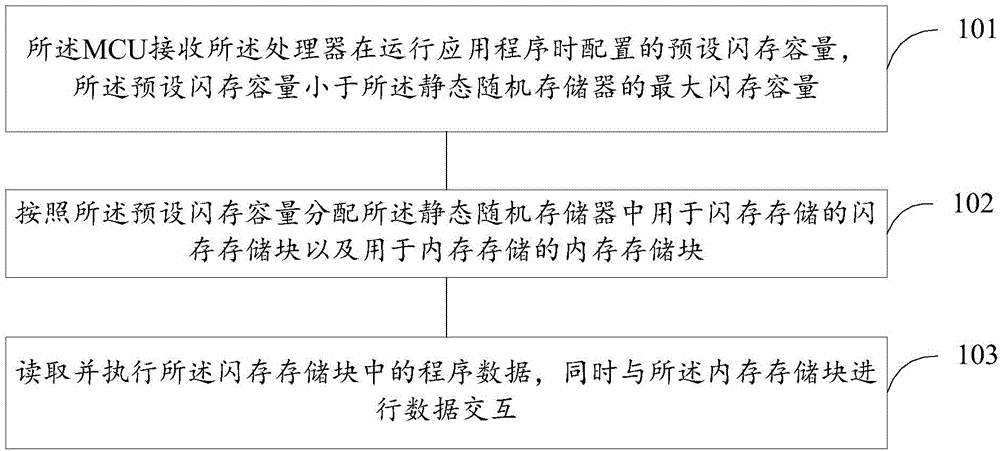
[0065] refer to figure 1 , which shows a flow chart of a method for dynamically allocating resources in a micro control unit MCU according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, the MCU includes a processor and a SRAM, and the SRAM includes a plurality of storage blocks, the method Can include the following steps:
[0066] Step 101. The MCU receives a preset flash memory capacity configured by the processor when running an application program, and the preset flash memory capacity is smaller than the maximum flash memory capacity of the SRAM.
[0067] In the embodiment of the present invention, the MCU includes a processor (CPU) for processing application programs, and a static memory SRAM. The static memory includes a plurality of storage blocks, which can be used to store data in flash memory or internal memory. In the embodiment of the present invention, the application program can carry the preset flash memory capacity, and the user can configure and determine the flash...
Embodiment 2
[0076] refer to figure 2 , shows a flowchart of a method for reading system configuration information of an MCU according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0077] In the embodiment of the present invention, the MCU includes a processor and a SRAM, and the SRAM includes a plurality of storage blocks.
[0078] The method may include the steps of:
[0079] Step 201. After the MCU is powered on and reset, the MCU reads the bad block information from the control information storage.
[0080] Step 202: Mark the bad block of the SRAM as unusable, and reorganize the location of the non-bad block storage blocks according to the bad block information.
[0081] Different from the previous embodiment, in this embodiment, the MCU further includes a control information storage, and the control information storage stores bad block information of the SRAM.
[0082] The control information memory adopts OTP (One Time Programmable, one-time programmable) storage method. Usually, a...
Embodiment 3
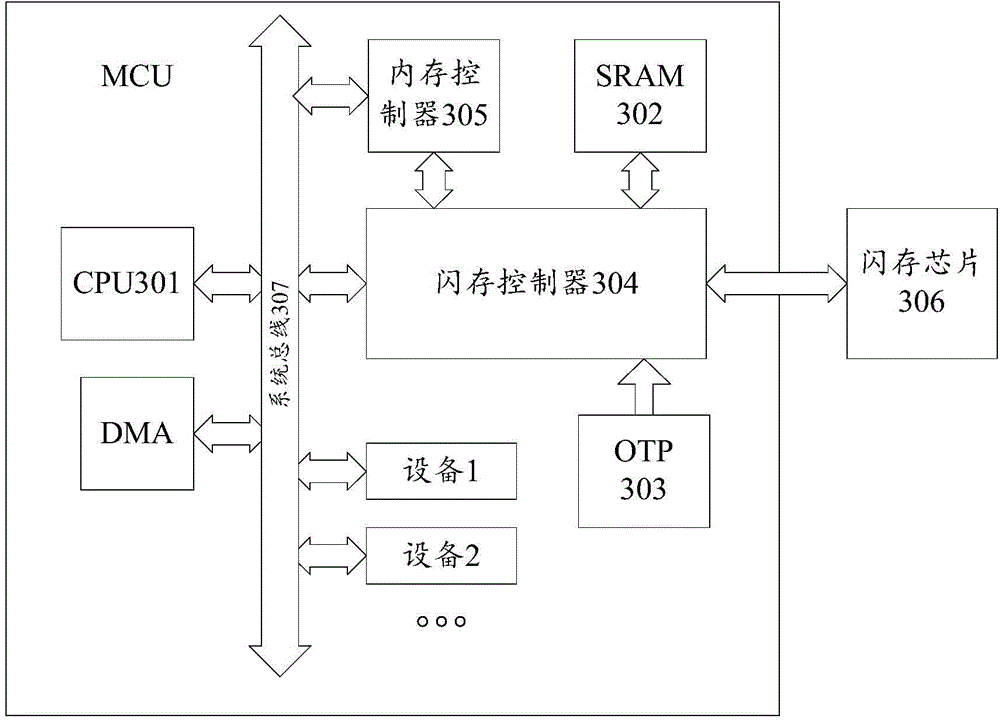
[0105] First, introduce the overall structure of the MCU in the embodiment of the present invention, as image 3 As shown, the MCU may include a CPU 301 , an SRAM 302 , an OTP 303 , a flash memory controller 304 , a memory controller 305 , a flash memory chip 306 and a system bus 307 . They are described as follows:
[0106] CPU301: CPU handles program data, and program data can be read from flash memory.
[0107] SRAM302: SRAM is a standard IP. In the present invention, the memory data and the data in the flash memory chip are stored, and the data will be lost after power off. The reading and writing speed is fast, and it can be read and written in real time.
[0108] OTP303: OTP is a storage type, which means one-time programmable. Usually, the product configuration information is programmed once during the product testing phase, and the data will not be lost when the power is turned off.
[0109] Flash memory controller 304: the function of the flash memory controller is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com