Viscosity index improver, method for producing same, and oil composition
A viscosity index improvement and compound technology, applied in the field of viscosity index improvers, can solve problems such as insufficient research on practical physical properties, and achieve the effect of excellent improvement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
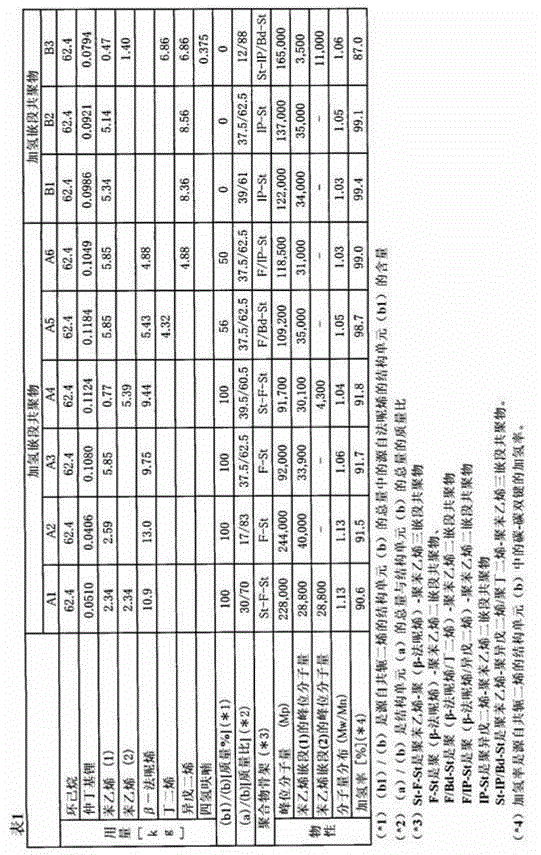
[0132] 62.4 kg of cyclohexane as a solvent and 51.0 g of sec-butyllithium (10.5% by mass cyclohexane solution) as an anionic polymerization initiator were put into a pressure-resistant container subjected to nitrogen replacement and dried, and the temperature was raised to 50°C. After that, 2.34 kg of styrene (1) was added and polymerized for 1 hour, then 10.9 kg of β-farnesene was added and polymerized for 2 hours, and 2.34 kg of styrene (2) was added and polymerized for 1 hour to obtain A reaction solution comprising polystyrene-poly(β-farnesene)-polystyrene triblock copolymer. To this reaction solution, 5% by mass of palladium on carbon (loaded palladium: 5% by mass) was added as a hydrogenation catalyst relative to the block copolymer, and the reaction was carried out for 10 hours under a hydrogen pressure of 2 MPa and 150°C. . After cooling and releasing the pressure, remove the palladium carbon by filtration, concentrate the filtrate, and then carry out vacuum drying to...
Embodiment 2
[0135] 62.4 kg of cyclohexane as a solvent and 40.6 g of sec-butyllithium (10.5% by mass cyclohexane solution) as an anionic polymerization initiator were put into a pressure-resistant container subjected to nitrogen replacement and dried, and the temperature was raised to 50°C. Afterwards, 13.0 kg of β-farnesene was added and polymerized for 2 hours, and then 2.59 kg of styrene was added and polymerized for 1 hour to obtain a poly(β-farnesene)-polystyrene diblock copolymer the reaction solution. To this reaction solution, 5% by mass of palladium on carbon (loaded palladium: 5% by mass) was added as a hydrogenation catalyst relative to the block copolymer, and the reaction was carried out for 10 hours under a hydrogen pressure of 2 MPa and 150°C. . After cooling and releasing the pressure, the palladium carbon was removed by filtration, the filtrate was concentrated, and then vacuum-dried to obtain the hydrogenated product of poly(β-farnesene)-polystyrene diblock copolymer (h...
Embodiment 3
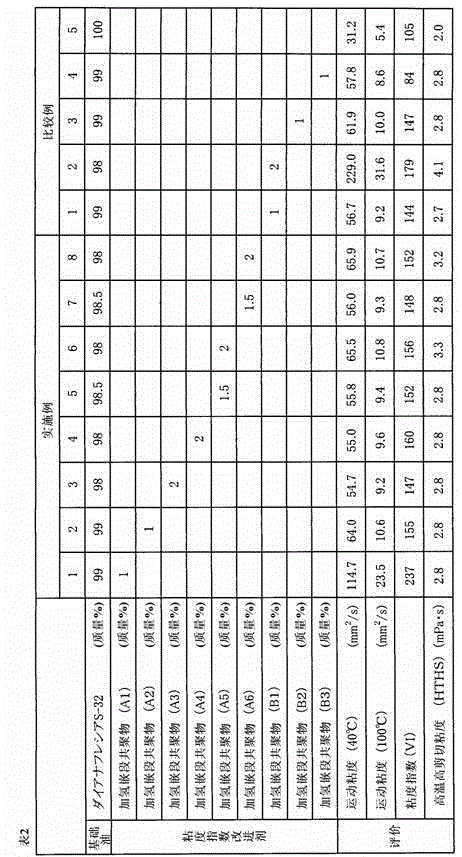
[0138] A hydrogenated block copolymer (A3) and an oil composition were produced in the same manner as in Example 2, except that the compounding described in Table 1 was followed, and the above-mentioned evaluation was performed. The results are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com