High modulus fiber reinforced polymer composite
A fiber-reinforced, polymer-based technology, applied in the field of high-modulus fiber-reinforced polymer composites, can solve the problems of no improvement in the adhesion of resin fibers and no record of carbon fiber adhesion levels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-8 and comparative example 1-4
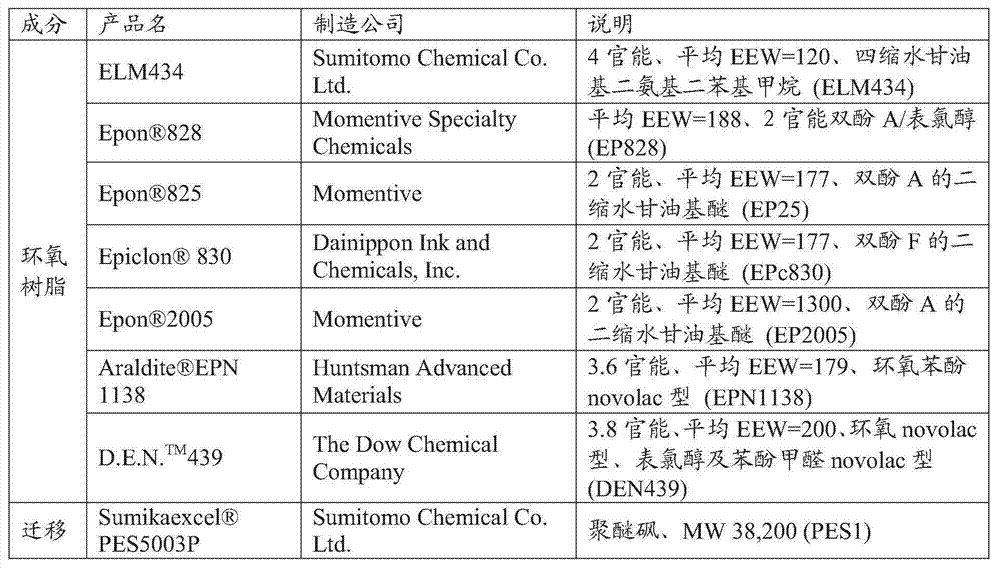
[0100] Examples 1-8 and Comparative Examples 1-4 (where Comparative Examples 1-4 are each a control of an existing state-of-the-art system) show the effect of high resin modulus and adhesion on the properties of high modulus carbon fiber composites . High modulus carbon fibers MX and M40J with different surface chemistries were used.
[0101] Appropriate amounts of the thermosetting resin and additives in the adhesive composition shown in Table 1 were charged into a mixer preheated at 100°C. After loading, the temperature was heated to 160°C while stirring the mixture and held for one hour. Afterwards, the mixture was cooled to 65°C, and curing agent and accelerator were added. The final resin mixture was stirred for an additional hour, then removed and some of it was stored in the refrigerator.
[0102] Some of the hot mixture was degassed in a planetary mixer rotating at 1500 rpm for a total of 20 minutes, then poured into a 0.25 thick Coated metal molds. The resin was...
Embodiment 9-13、 comparative example 5-6
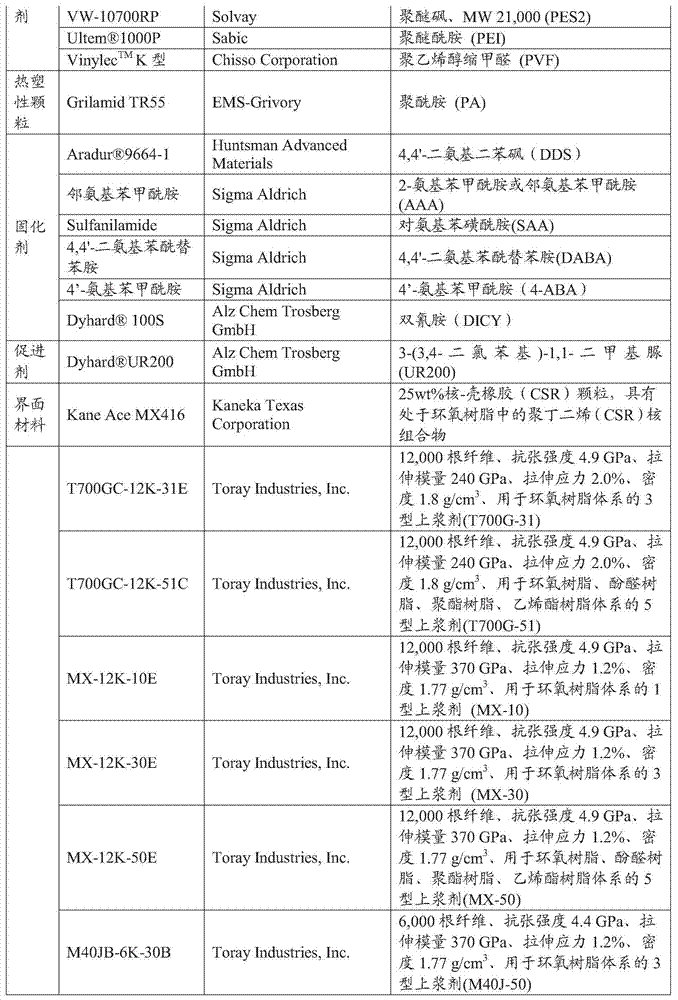
[0108] In these Examples and Comparative Examples, it was investigated whether the adhesion of the adhesive composition to the high modulus carbon fiber could be further improved by including an interface material in the investigated system. Mechanical tests on the resin, prepreg, and composite material were performed using the same procedure as in the aforementioned Examples and Comparative Examples.
[0109] The interface material CSR was incorporated into Examples 1 and 5, and Examples 9-10 were implemented. In these cases, a reinforcing interfacial phase is formed. Because of the presence of the interfacial phase, the failure mode shifted from mixed mode (Examples 1, 5) to cohesive failure (Examples 9-10) at the interfacial phase, indicating a better bond between resin and fiber. Comparing with each system (Comparative Examples 5-6), it can be found that, in addition to the effects already observed, the interfacial phase (presumably comprising at least the interfacial mat...
Embodiment 14-18、 comparative example 7-8
[0111] Mechanical tests on the resin, prepreg, and composite material were performed using the same procedure as in the aforementioned Examples and Comparative Examples.
[0112] In order to confirm that the effect of AAA is superior to that of DDS or DICY in Comparative Examples 7-8 (control), adjustments were made in Examples 14-18. Standard modulus carbon fiber T700G-31 was used. As in the previous example using high modulus fibers, a substantial improvement in ILSS and compression was also observed. Furthermore, it is surprising that the tensile strength is increased to a maximum of 100% transfer and the Mode I fracture toughness is increased to a maximum of 300%, especially where a reinforcing interfacial phase is formed (Examples 15-18). These significant improvements were not observed in systems using high modulus carbon fibers. It is reasonable to assume that this result was achieved because these high modulus carbon fiber systems required higher modulus resin system...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shear strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com