Acinetobacter sp. for degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and application of acinetobacter sp.
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and Acinetobacter technology, applied in the field of Acinetobacter strains to degrade polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, can solve the problems of secondary pollution, difficult to remove, high processing cost and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1 Isolation and identification of Acinetobacter W145
[0019] The long-term oil-contaminated soil from Shengli Oilfield was used as the screening soil. The specific screening scheme is as follows:
[0020] 1) Take 10g of soil, add it to 100ml of inorganic salt medium MSM containing 250mg / L phenanthrene, culture with shaking at 28°C for 7 days, take 10ml of the culture and transfer it to another 100ml of inorganic salt medium MSM containing 250mg / L phenanthrene ; Transplant five times in succession to obtain a culture solution enriched with microorganisms.
[0021] 2) Take 0.1ml of the culture solution obtained in step 1), spread it on the MSM solid plate containing 250mg / L phenanthrene, and after static culture at 28°C for 5 days, transfer the colonies grown on the plate to the MSM solid plate containing 250mg / L phenanthrene On the MSM solid plate, continue to culture and grow until a single colony appears on the plate.
[0022] 3) Pick a single colony grown o...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Example 2 Verification of the Degradation Ability of Acinetobacter W145 to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
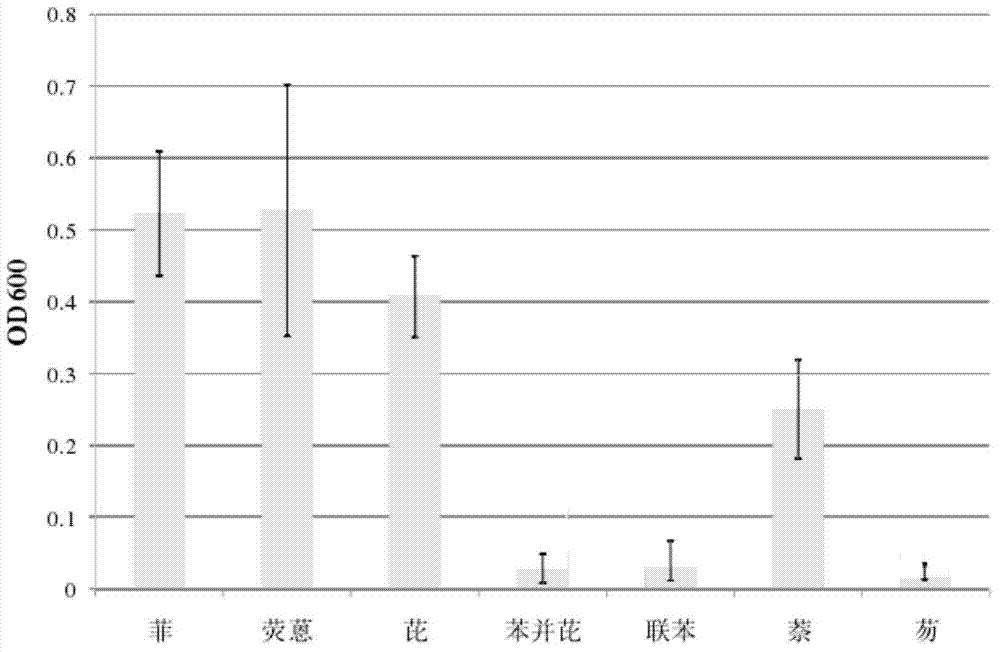
[0027] The inventors studied the ability of the W145 strain to degrade common polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Based on 100ml of MSM medium without carbon source, add different polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons as the sole carbon source; then insert 10 6 CFU of Acinetobacter W145, cultured at 28°C with shaking for 5 days, measured the OD of the culture 600 absorbance value. The medium without any carbon source was used as negative control. Since no carbon source other than polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons was added to the medium, the growth rate and biomass of the strain reflected the ability of the strain to degrade and utilize polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
[0028] Such as figure 1 As shown, Acinetobacter W145 has strong degradation ability to fluoranthene, pyrene and phenanthrene, and also has certain degradation ability to naphthalene, but almost no ...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3 Degradation Efficiency of Acinetobacter W145 to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
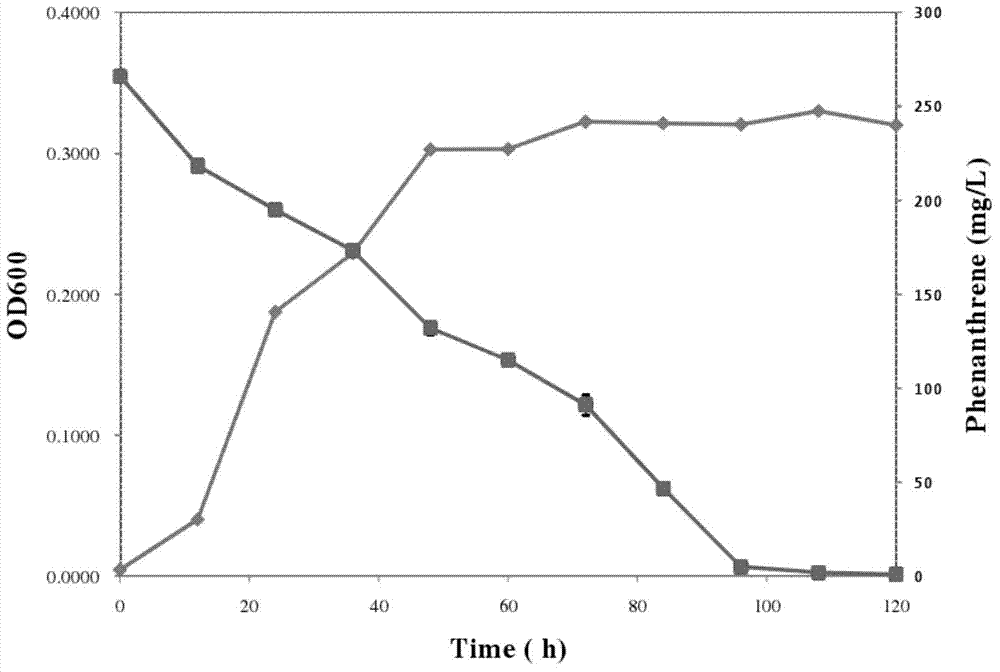
[0030] In order to further analyze the degradation efficiency of Acinetobacter W145 to PAHs, the growth rate and degradation rate of Acinetobacter W145 were tested with phenanthrene as the only carbon source. Acinetobacter W14 in the logarithmic growth phase was inoculated with 1% inoculum into MSM medium with 250 mg / L phenanthrene as the sole carbon source, and cultured with shaking at 28°C. Meanwhile, measure the OD of the culture every 12 hours 600 value and concentration of residual phenanthrene.
[0031] Such as figure 2 As shown, Acinetobacter W145 has the ability to degrade phenanthrene from the beginning of inoculation, and the degradation ability and strain growth increase rapidly after 12 hours, and, as the residual phenanthrene concentration in the culture decreases, the growth of the strain gradually enters the plateau . After 100 hours of inoculation, phenanthr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com