Method for manufacturing a metallic or ceramic component by selective laser melting additive manufacturing
A laser melting additive, selective technology for the manufacture of metal or ceramic components/three-dimensional products, hot gas path components to achieve novel laser "idle" times, increased production rates, reduced idle times and jump delays
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
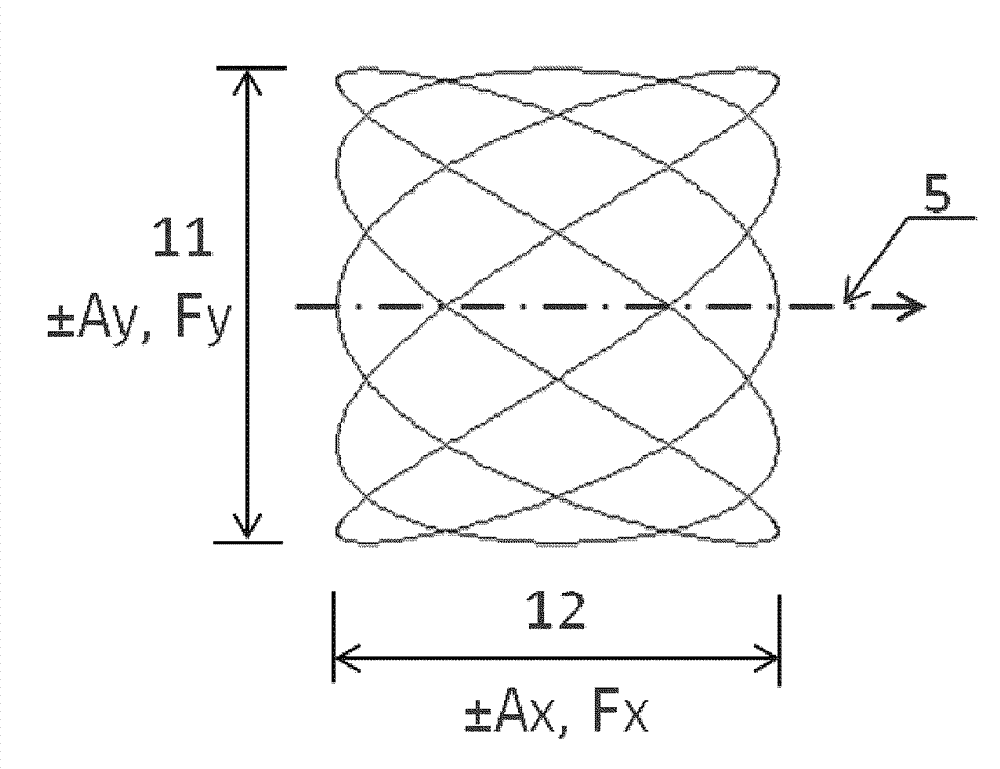
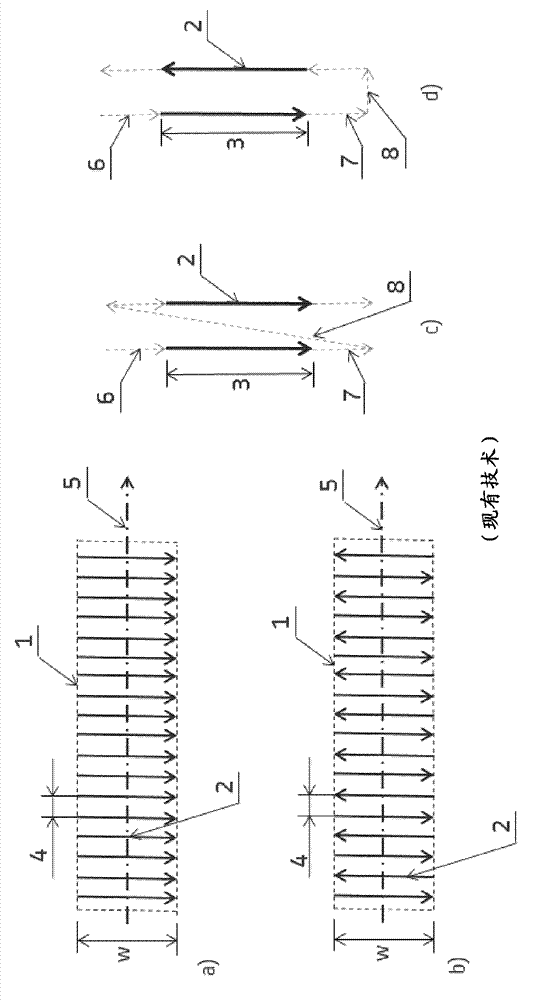
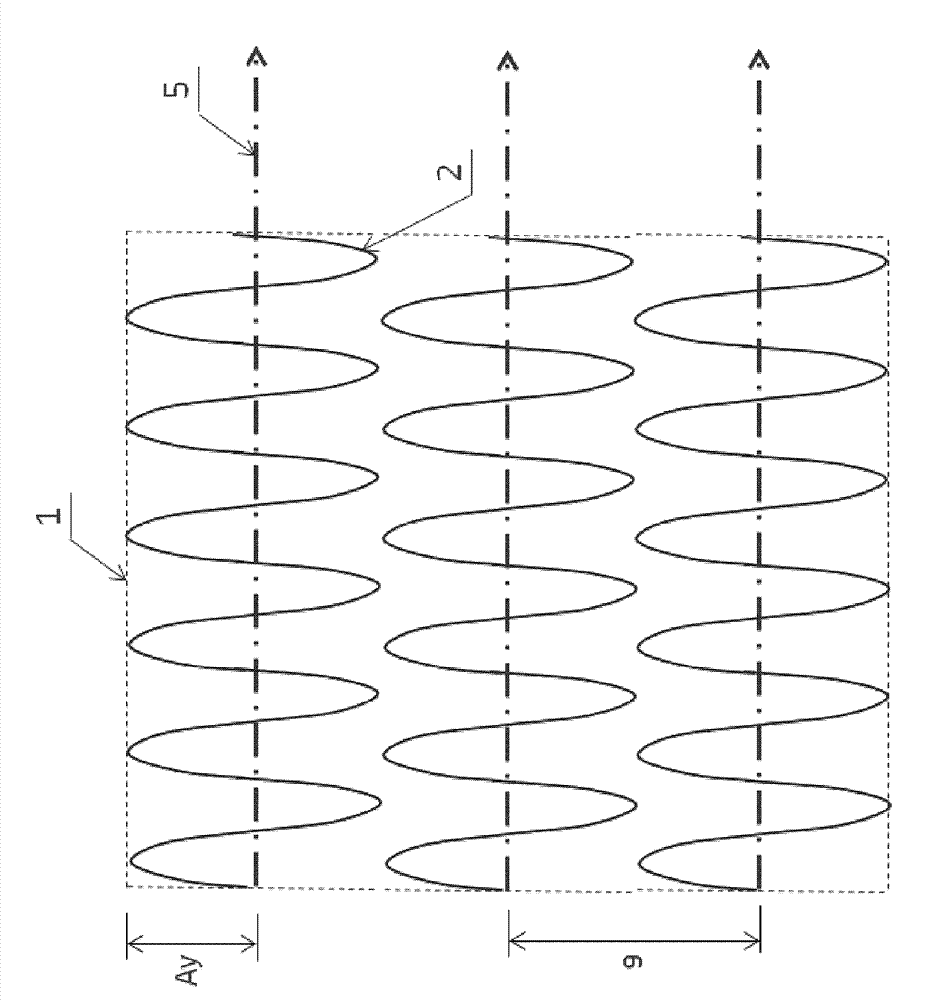
[0051] As mentioned above, the general idea of the method is to use a rocking and scanning strategy by selective laser melting (SLM) to produce functional elements of high design complexity. These additive manufacturing processes will benefit from higher production rates using novel beam scanning techniques.
[0052] A good example of such an application is a combustor swirler for a gas turbine, where many sections of large dimensions have to be melted by means of a laser beam. The manufacture of such components usually requires many machine hours. However, a significant portion of the overall fabrication time is "laser idle" time, ie, secondary "non-melt" operations where the laser is switched off and therefore cannot be produced. A typical example is the deposition of a new powder layer, but also the laser reset movement from the end of a melt track to the start of the next melt track with its associated laser on / off delay. A significant portion of this "laser idle" time...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com