Solid-state flash memory write cache system and method based on dynamic non-covering RAID technology
A RAID stripe and non-coverage technology, which is applied in the field of cloud storage system, can solve problems such as large single IO delay, performance bottleneck, hidden danger of reliability, etc., so as to improve service life and data security, improve write bandwidth, reduce wear effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0048] Below in conjunction with specific embodiment, further illustrate the present invention, should be understood that these embodiments are only used to illustrate the present invention and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention, after having read the present invention, those skilled in the art will understand various equivalent forms of the present invention All modifications fall within the scope defined by the appended claims of the present application.
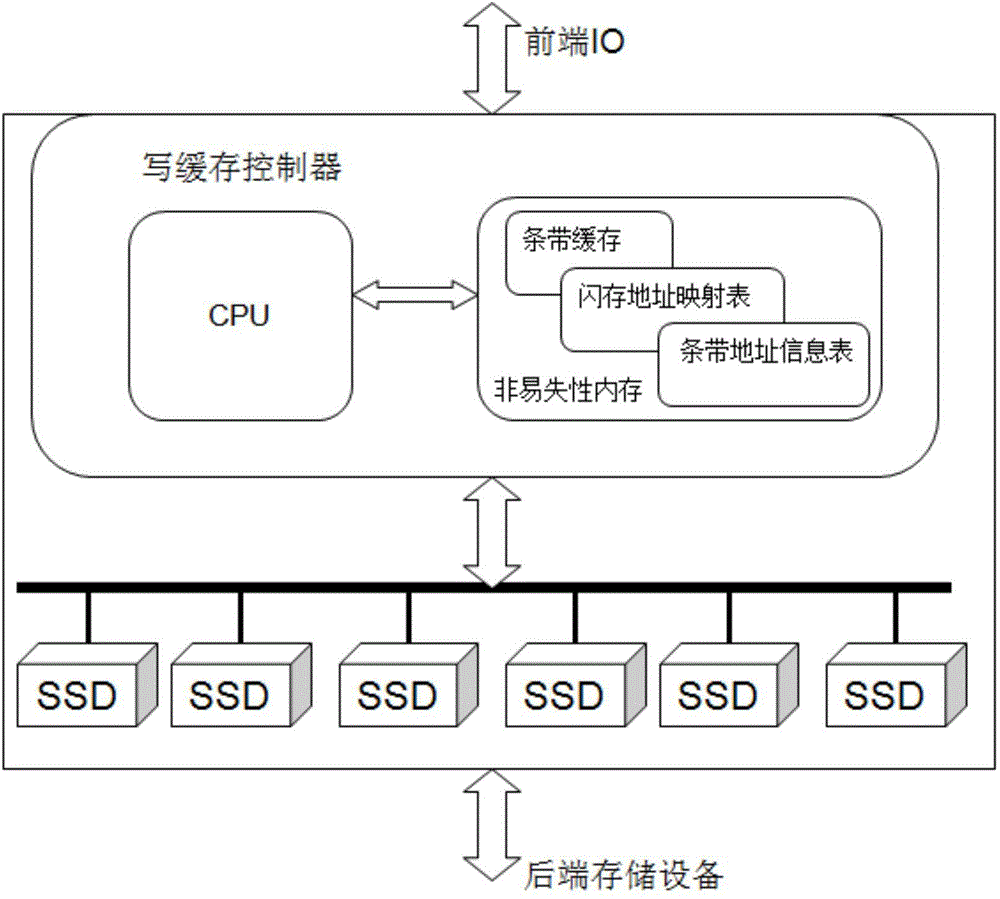
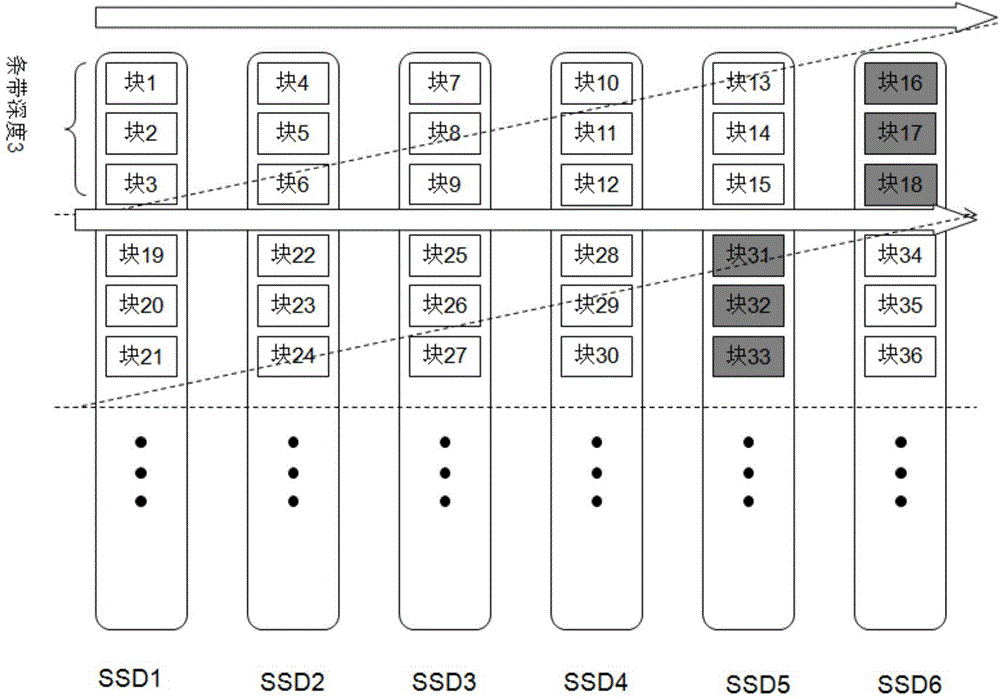
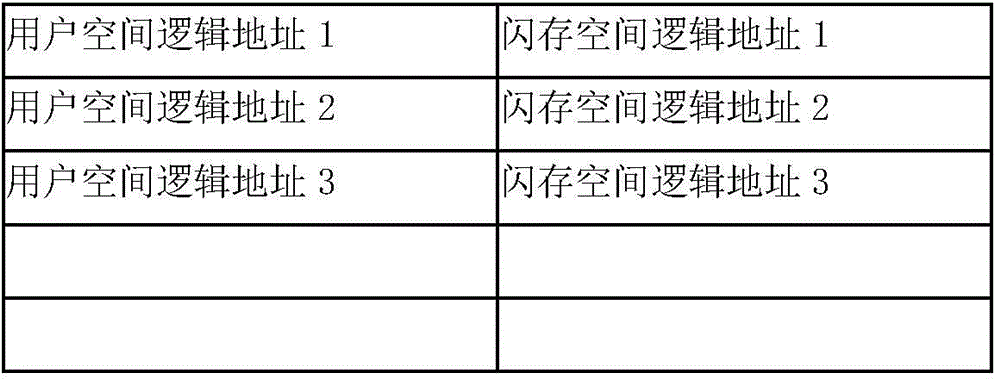
[0049] The core idea of the solid-state flash memory write cache system disclosed in the embodiment of the present invention is to use non-volatile memory (battery-protected DRAM or MRAM) as the cache of solid-state flash memory RAID, and the data written by the front end is first written into the cache, that is, non-volatile Memory, reassembled into a new RAID stripe in the cache, and then write the RAID stripe as a whole to multiple solid-state flash disks managed by the controller at the same ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com