Sub-area fault diagnosis method for transformer station grounding network
A substation grounding grid and fault diagnosis technology, applied in the field of electric power information, can solve problems such as low reliability of results, less data, and complex algorithm structure.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
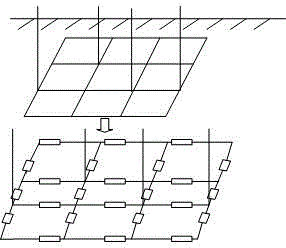
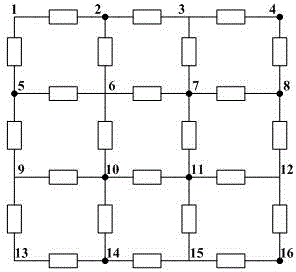
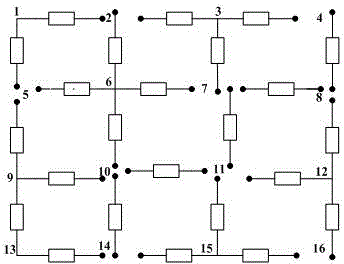
[0152] image 3 Shown is a substation grounding grid network topology diagram, with 16 nodes, of which 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 14, and 16 are accessible nodes. The specific decomposition of the grounding grid can be found in this article Figure 4-8 . Under normal conditions, the nominal resistance value of each branch is 60mΩ, and there are three existing branches that have failed, as follows: No. 1-2 branch becomes 300mΩ, No. 7-8 branch becomes 600mΩ, No. 11-15 The branch becomes 900mΩ.
[0153] Figure 4-8 They are the quasi-meta-block, meta-block, meta-network, accessible grounding grid, and intrinsic grounding grid obtained by hierarchical reduction of the topological structure of the grounding grid, Figure 9 It is the area diagram of grounding network division. According to the process of reducing the quasi-element block to the intrinsic grounding grid, each branch in the intrinsic grounding grid is traced up to the grounding grid layer by layer, Figure 8 Table 1 s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com