Genes controlling photoperiod sensitivity in maize and sorghum and uses thereof
A photoperiod, sensitive technology, applied in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, applications, etc., can solve problems such as undetected
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0261] Example 1: Identification and cloning of maize photoperiod regulator ZmCCT10 gene
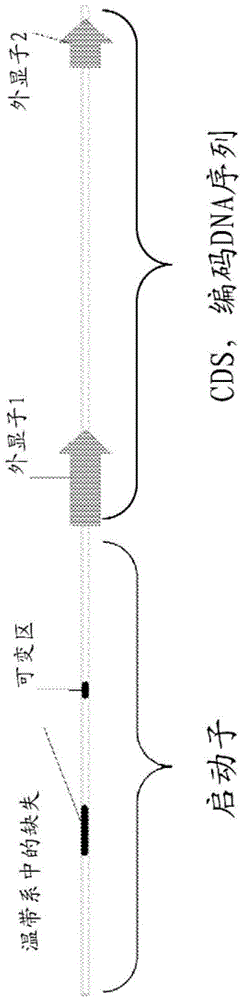
[0262] Current genetic research on photoperiod sensitivity in maize is based on QTL (quantitative trait loci) mapping of flowering time. Four major photoperiod-sensitive loci were identified (Genetics (2010) 184:799-812 ("Genetics", 2010, Vol. 184, pp. 799-812)), and the major QTLs were mapped to Chromosome 10 (Genetics 183: 1555-1563 (Vol. 183, pp. 1555-1563)). The QTL on chromosome 10 was mapped to the CCT domain gene (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2012) 109 (28) ("Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America", 2012, Vol. 109, No. 28)). The CCT domain (representing the three underlying gene C ONSTANS, C ONSTANS-LIKE, T OCl) is a carboxy-terminal approximately 45 amino acid peptide rich in basic residues and contains a putative nuclear localization signal (Science (2000) 289(5480): 768-71 ("Science", 2000, Vol. 289 , Issue 5480, pp. 768-771))....
example 2
[0264] Example 2: Identification and Cloning of Sorghum Photoperiod Regulators SbCCT1 and SbCCT6 Genes
[0265] Sorghum is a short-day plant native to northern Africa. Similar to maize, sorghum is photoperiod sensitive and is widely cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions. To identify sorghum CCT homologous genes, "Sorghum predicted coding sequence (JGI, Joint Genome Institute v.1.4) (N)" has been searched by BLAST using ZmCCT10 and rice Ghd7 coding nucleotide and amino acid sequences as query items. Rice Ghd7 (representing grain number, plant height and heading date 7) is a CCT gene used as a major negative regulator of flowering time under non-permissive long-day conditions (Itoh, et al., (2010) Nat Genet.42 (7):635-8 (Itoh et al., 2010, Nature Genetics, Vol. 42, No. 7, pp. 635-638)). Two predicted coding DNA sequences have been found, Sb06g000570.1 and Sb01g029080.1, located on chromosome 6 and chromosome 1, respectively. These genes were named SbCCT1 and Sb...
example 3
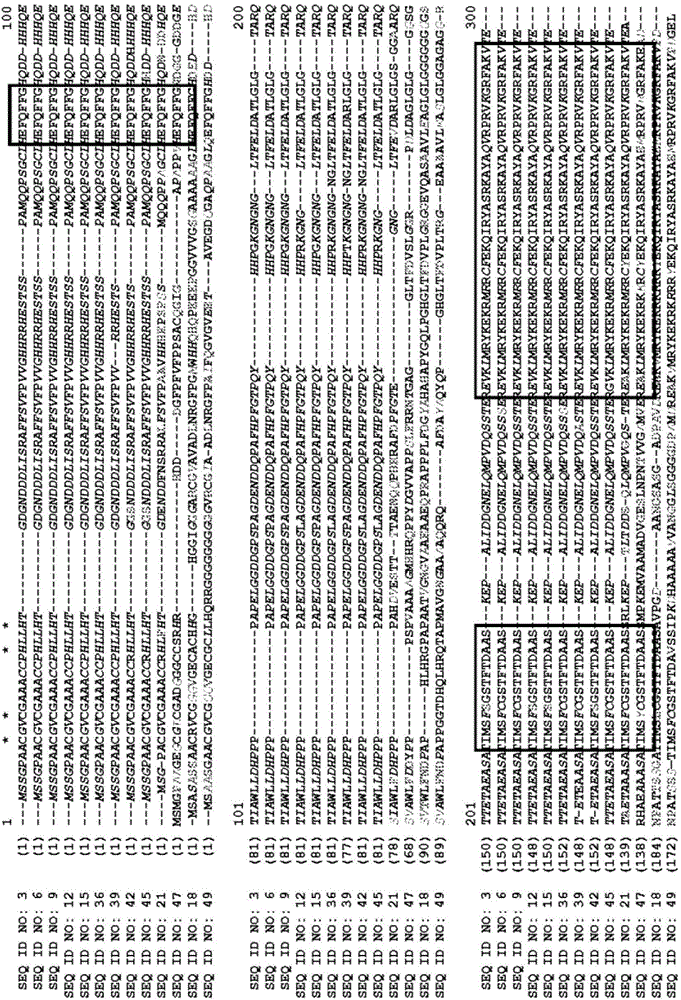
[0266] Example 3: Phylogenetic analysis and functional domains of ZmCCT10 predicted polypeptides
[0267] The CCT (stands for CONSTANS, CO-like and TOCl) domain is a highly conserved basic module of approximately 43 amino acids found near the C-terminus of plant proteins commonly involved in light signal transduction. This basal protein is encoded by the Arabidopsis CONSTANS gene, which controls flowering time by linking the circadian clock to downstream flowering genes (Suarez-Lopez, et al., (2001) Nature 410:1116-1120 (Suarez-Lopez, et al., (2001) Nature 410:1116-1120 (Suarez-Lopez, et al., -Lopez et al., 2001, Nature, Vol. 410, pp. 1116-1120)).
[0268] To elucidate the phylogenetic relationship of ZmCCT10 proteins with other CONSTANS and CO-like plant proteins, 54 proteins were selected from different plant species including Arabidopsis, rice, maize and sorghum. A phylogenetic consensus tree was constructed with 1000.00 tree bootstrapping values. ZmCCT10 protein...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com