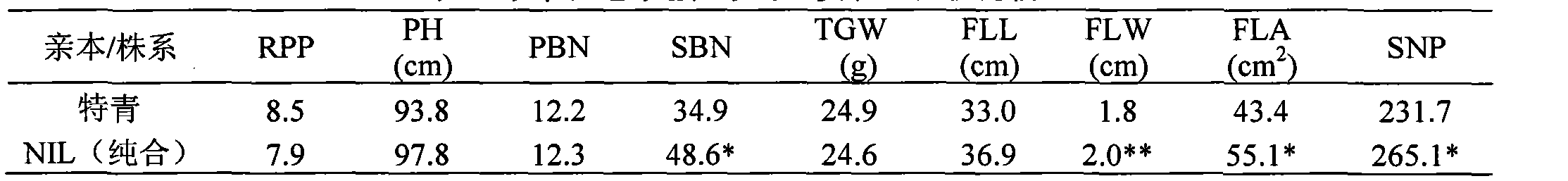Patents
Literature
32 results about "Source sink" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Source–sink dynamics is a theoretical model used by ecologists to describe how variation in habitat quality may affect the population growth or decline of organisms.. Since quality is likely to vary among patches of habitat, it is important to consider how a low quality patch might affect a population.
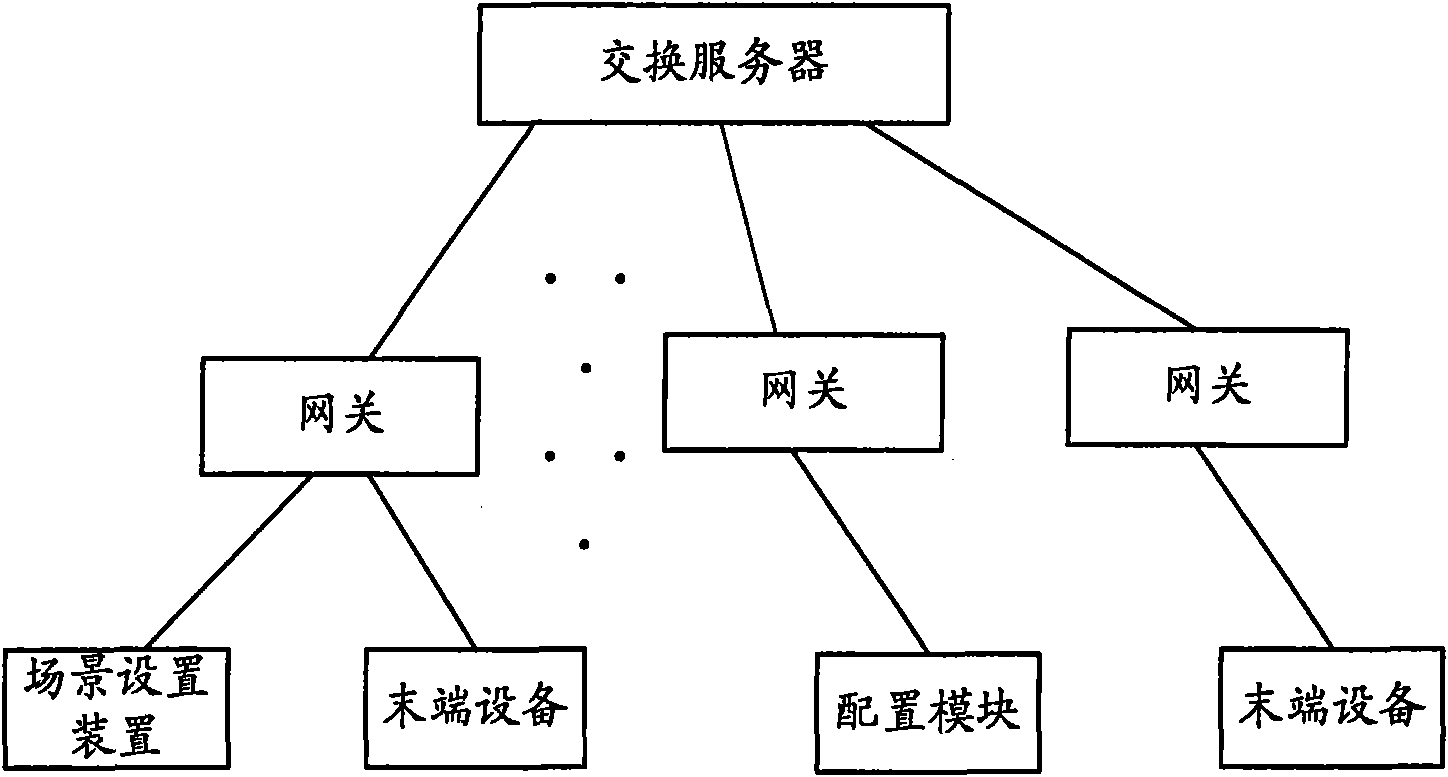
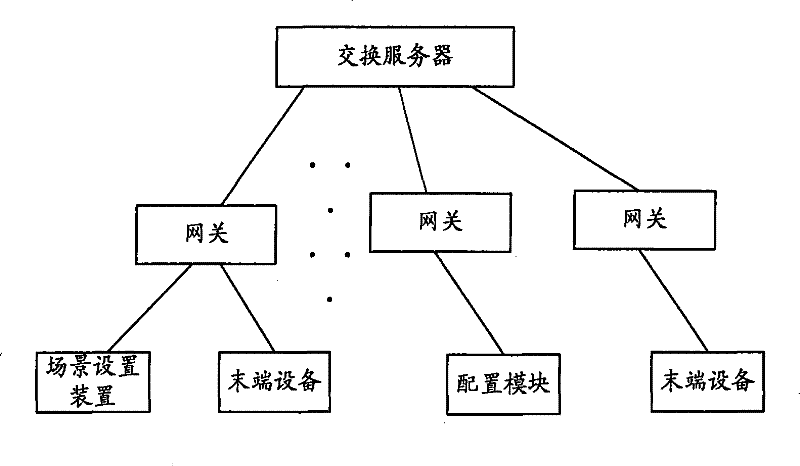
Digital home network system and scene mode configuration method thereof
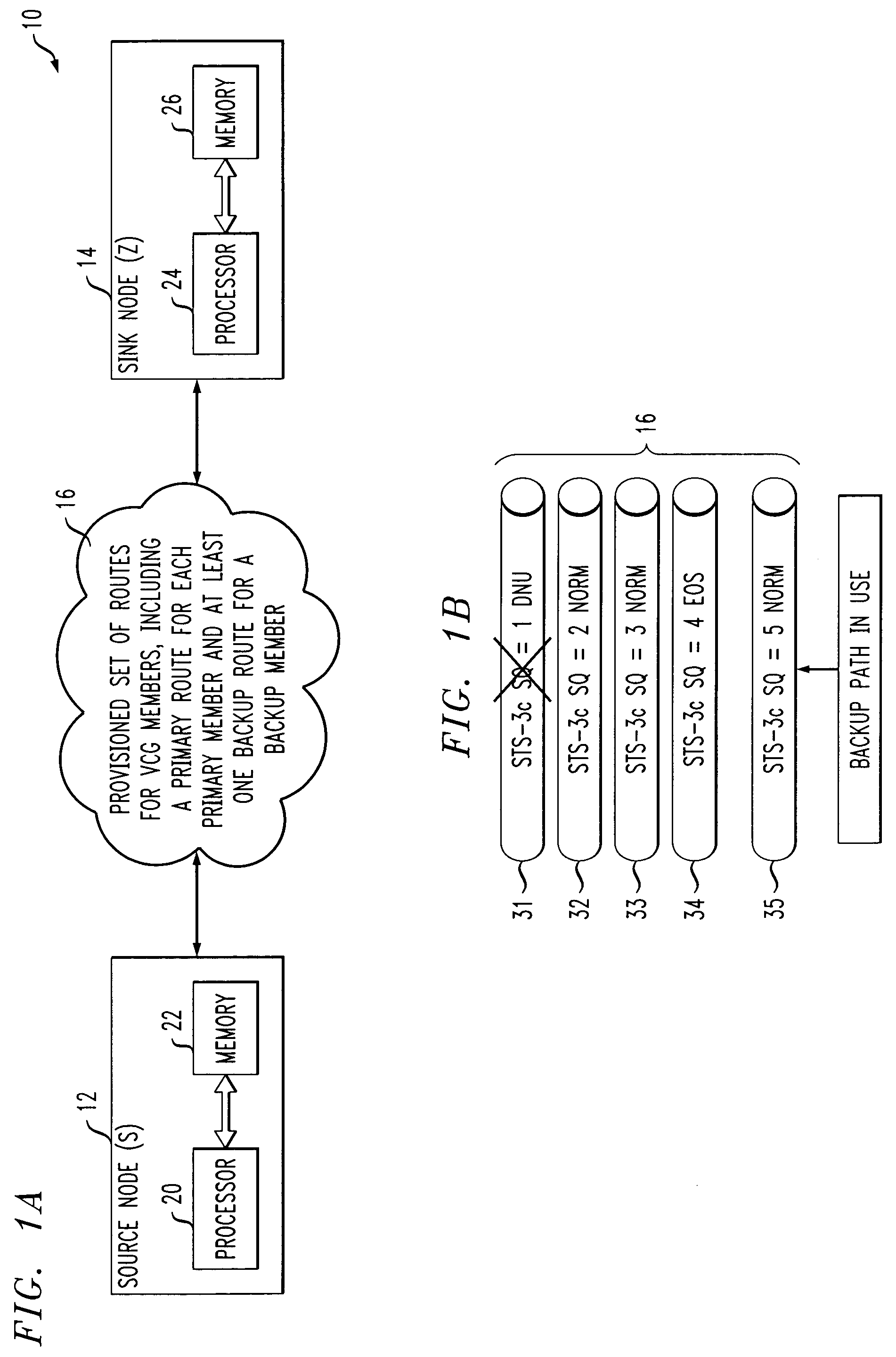
ActiveCN101594251AEasy to useEasy to modifyData switching by path configurationOperating systemSource sink
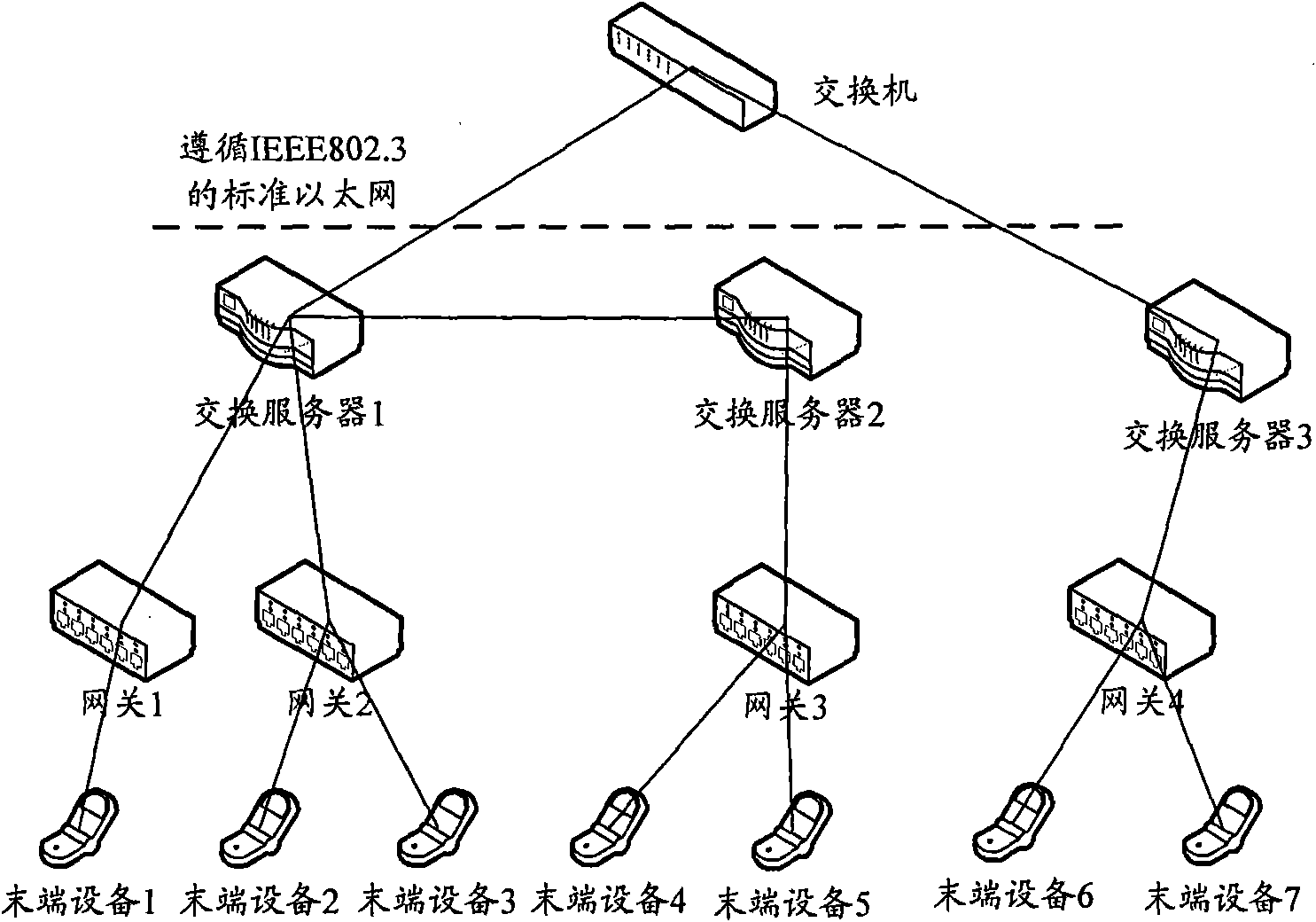
The invention provides a digital home network system and a scene mode configuration method thereof; the system comprises an exchange server and an end device, and the end device comprises a scene setting device; the invention is characterized in that the system further comprises a configuration module and an exchange server, the configuration module is used for providing the exchange server with a scene configuration file input externally, and the exchange server is used for transmitting the received scene configuration file and updating local source-sink relation according to the corresponding relation between a control end and a controlled end in the scene configuration file; the scene setting device is used for updating the configuration content stored locally with the configuration content in the scene configuration file when the scene configuration file is received. Using the above technical scheme, the configuration content of the built-in scene mode in the scene setting device can be changed according to actual needs, thus users can customize various scene modes simply and conveniently.
Owner:新动力(北京)建筑科技有限公司
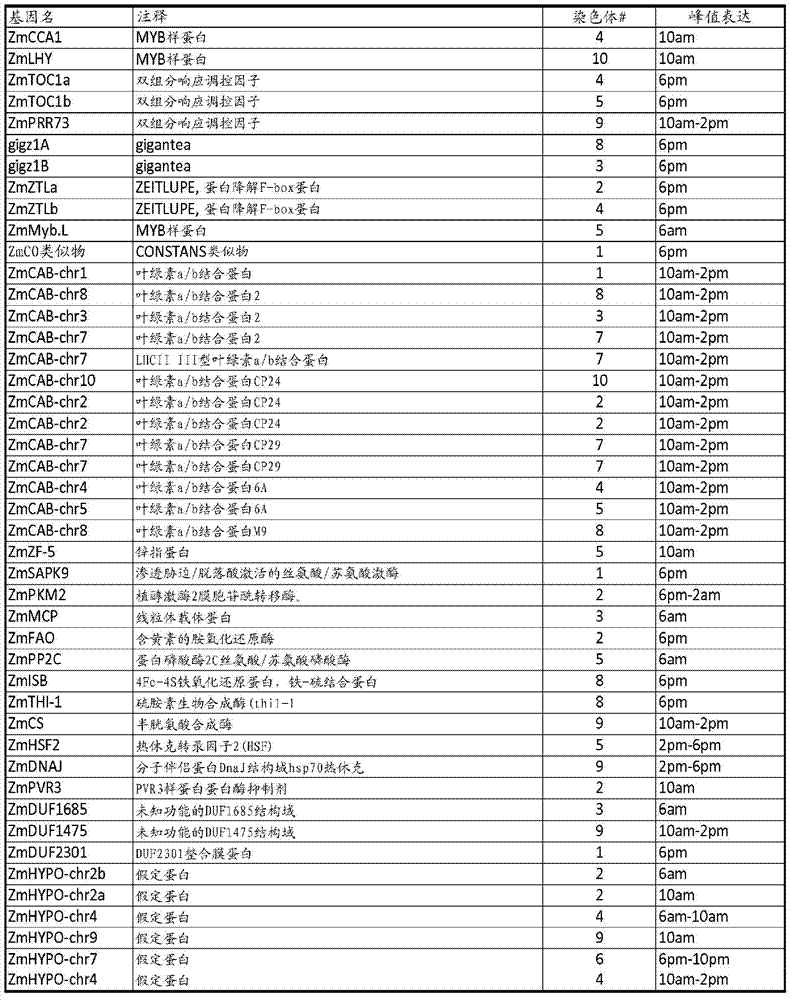
Identification of diurnal rhythms in photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic tissues from zea mays and use in improving crop plants
InactiveCN102906267AMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationGrowth plantPolynucleotide
The present disclosure provides polynucleotide sequences relating to the diurnal cycling in maize leaf and ear tissues. The disclosure provides polynucleotide sequences and the use of encoded polypeptides associated with the oscillation. The disclosed sequences are responsible for controlling plant growth, source-sink relationships and yield in crop plants.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
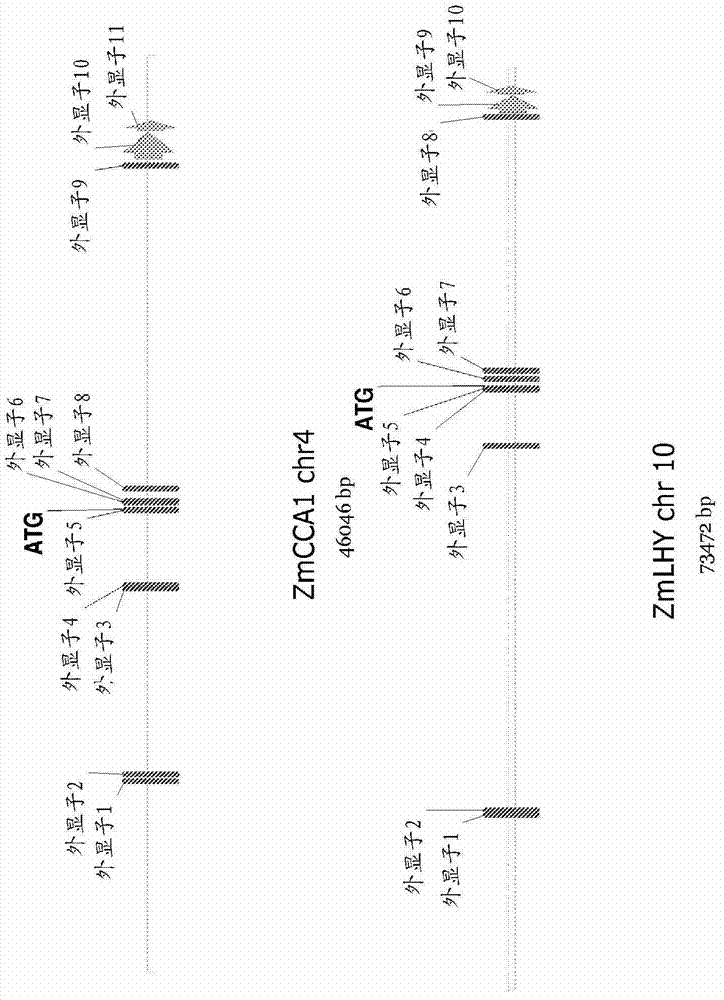
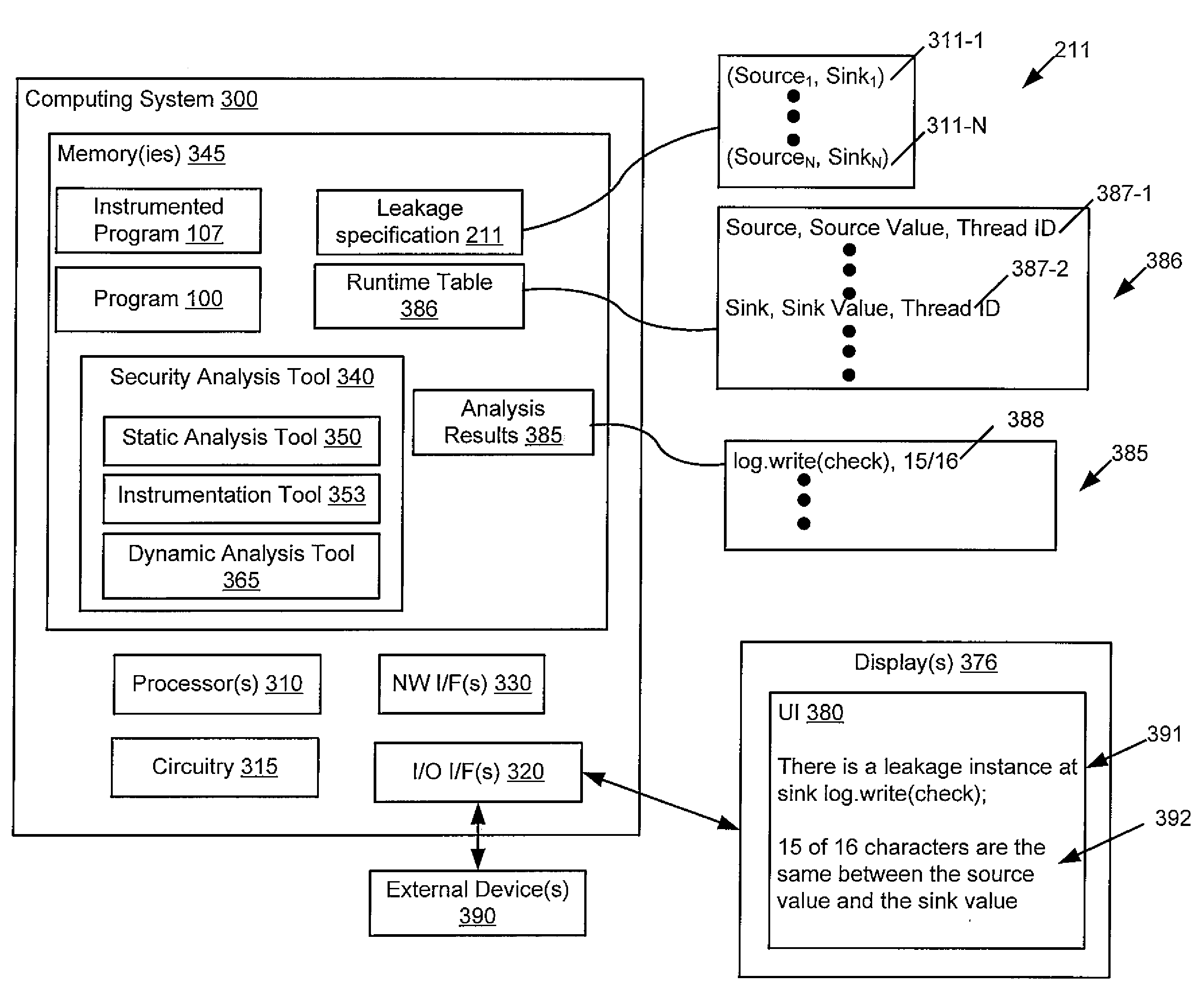
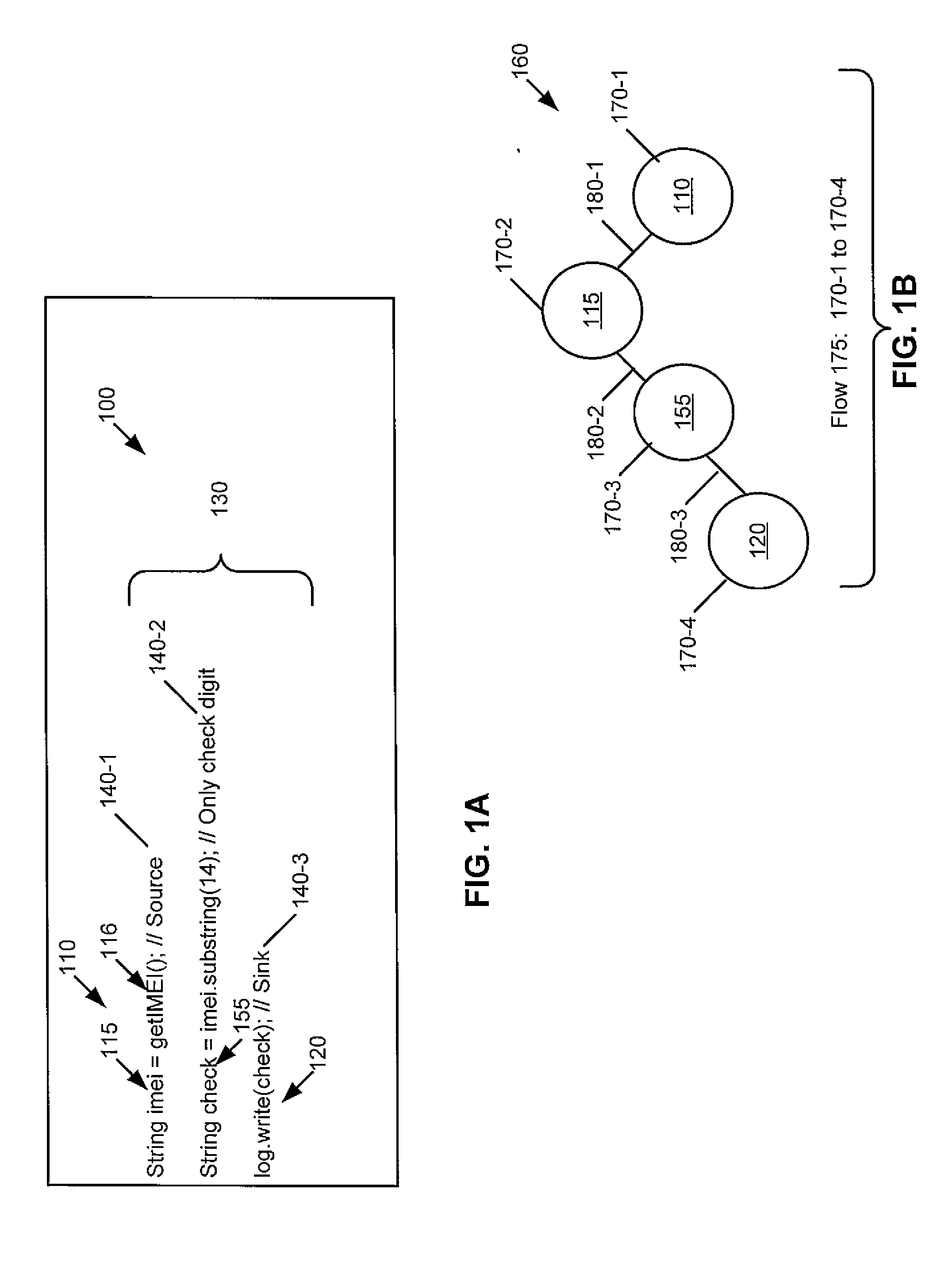
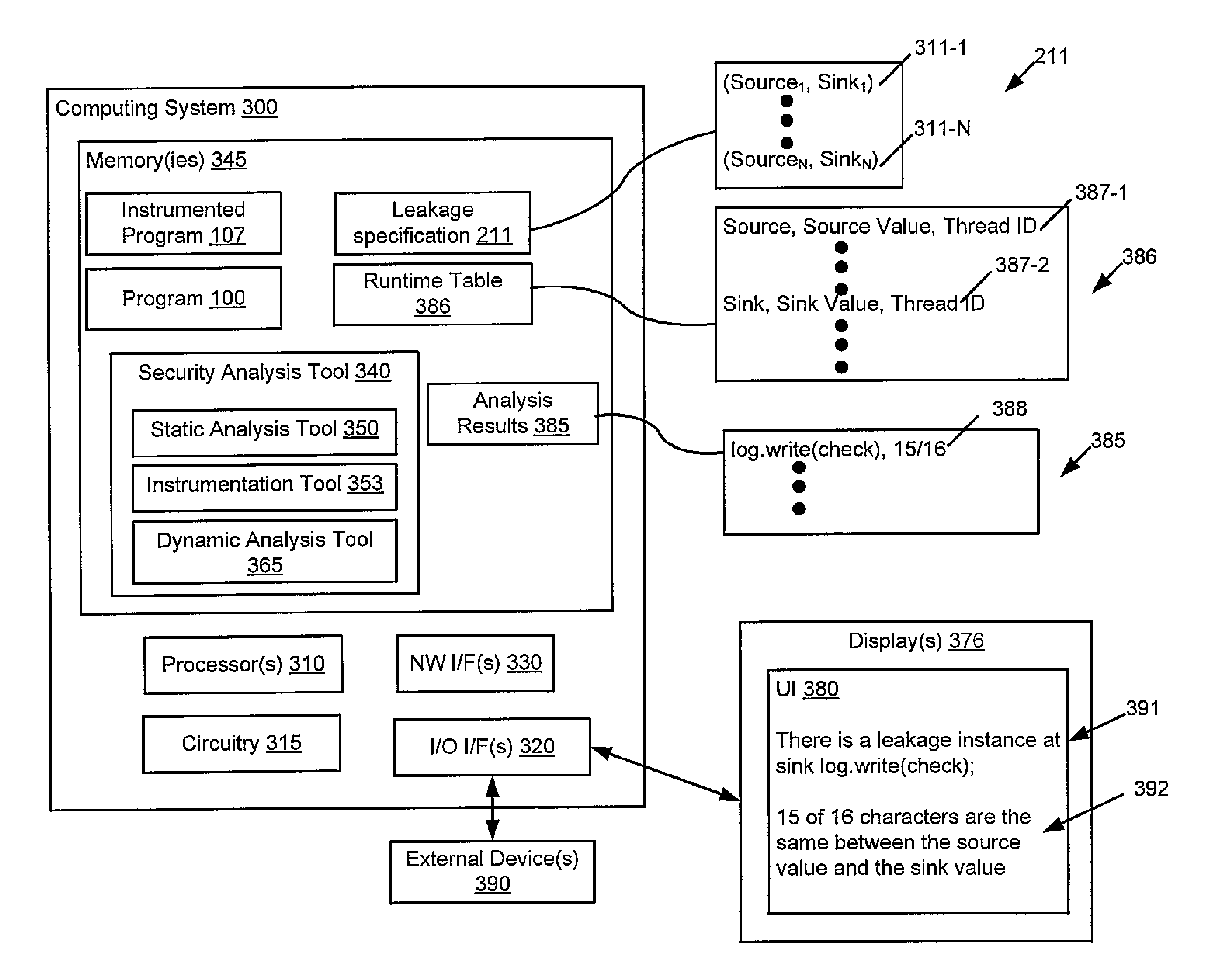
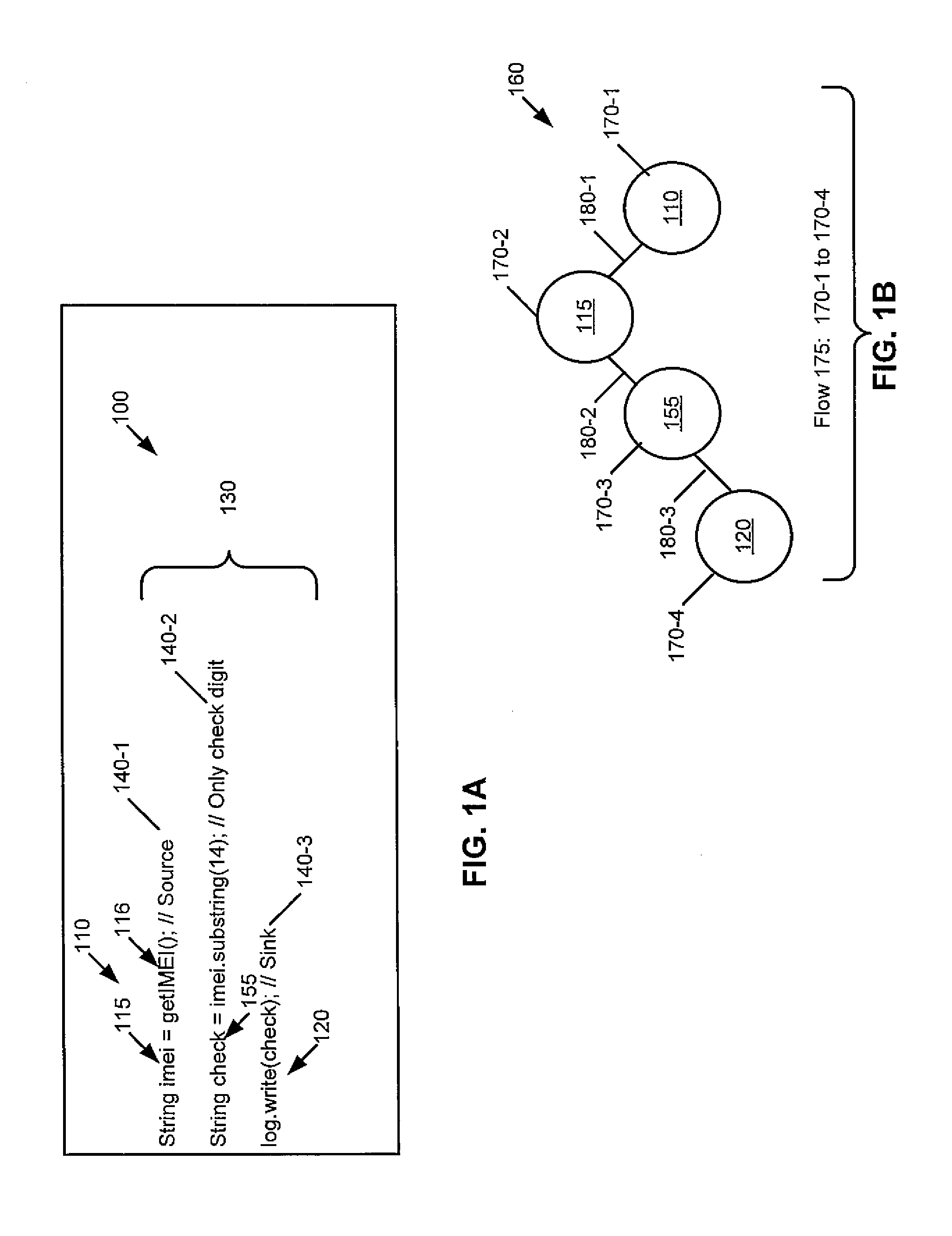
Quantitative analysis of information leakage vulnerabilities
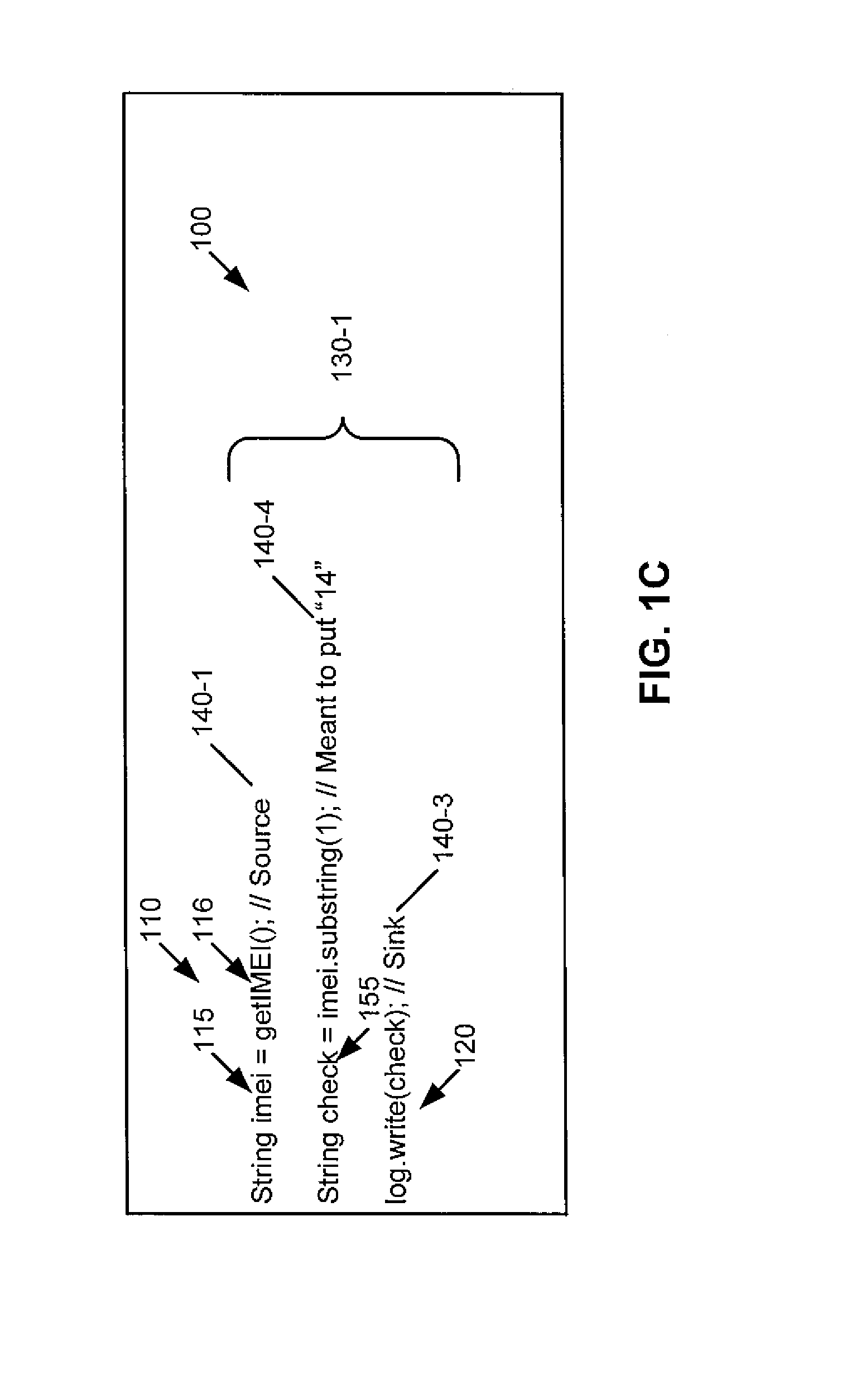
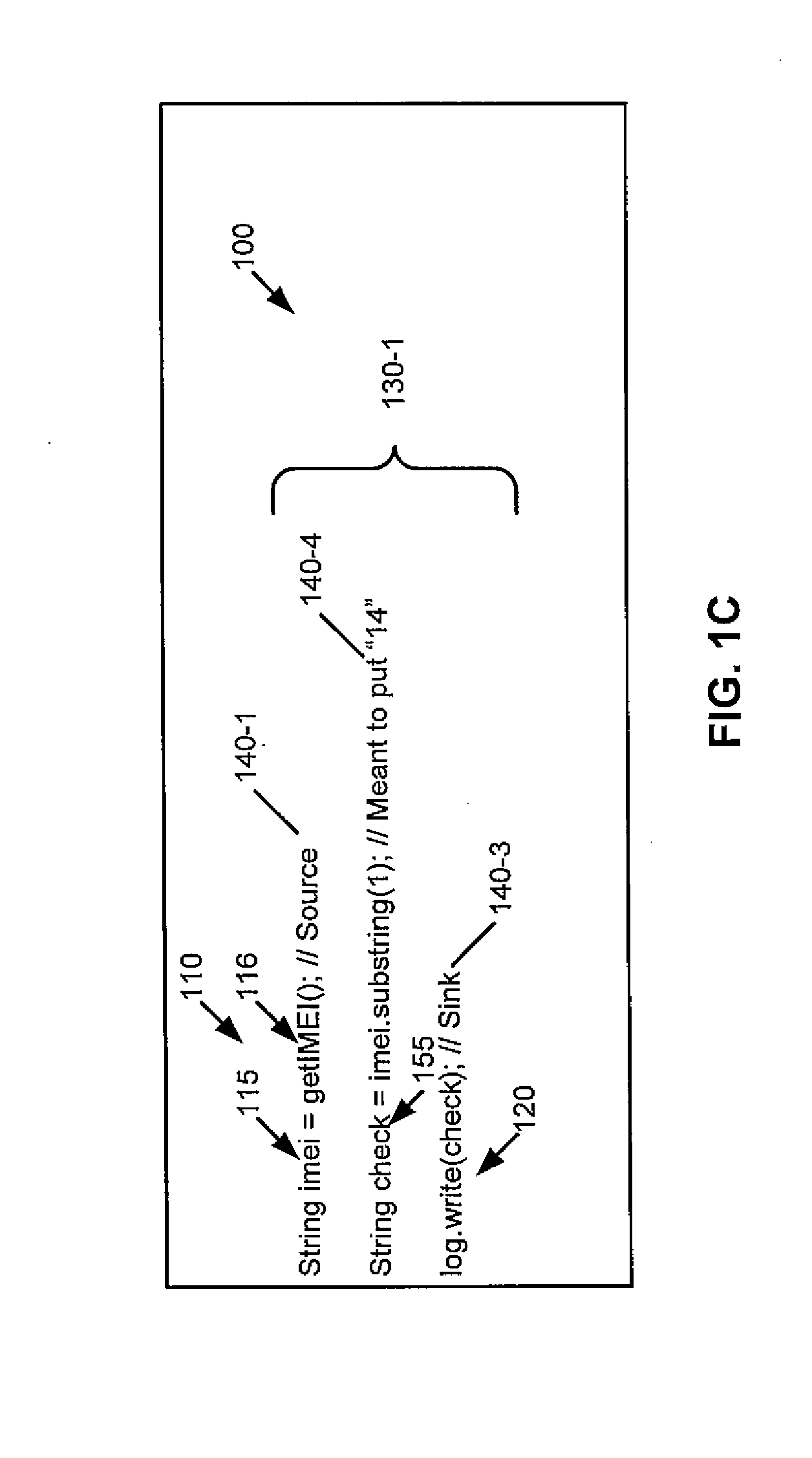
A method includes recording, during execution of a program and by a computing system, concrete values exhibited at source and sink statements in the program. The source statements read confidential information and the sink statements release the confidential information to an outside environment. The method includes determining, by the computing system, using at least the recorded concrete values and source-sink pairs whether information leakage meeting one or more quantitative criteria occurs by the program. Apparatus and program products are also disclosed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Constrained detailed placement
InactiveUS20080127017A1Computer programmed simultaneously with data introductionComputer aided designData setTheoretical computer science
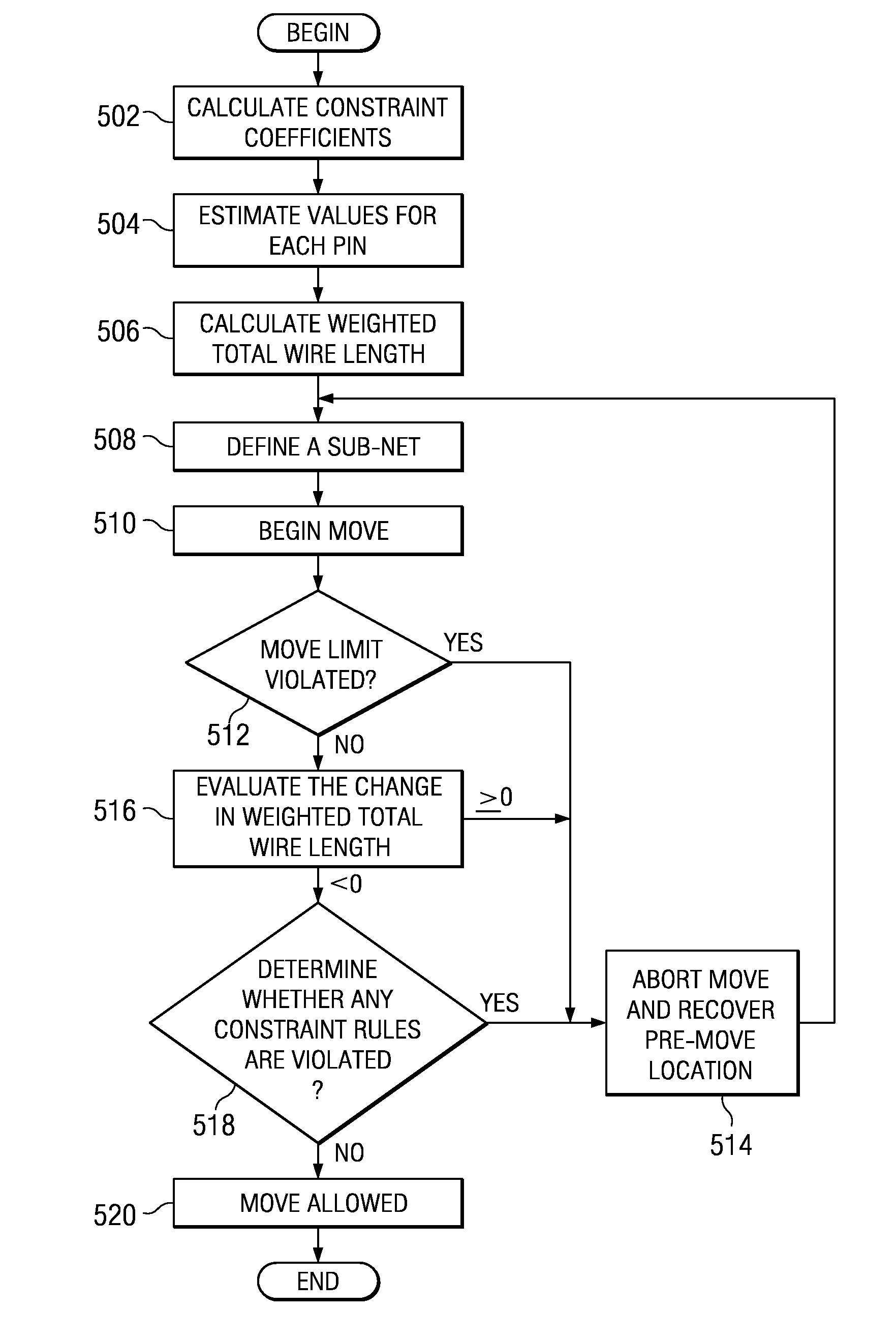
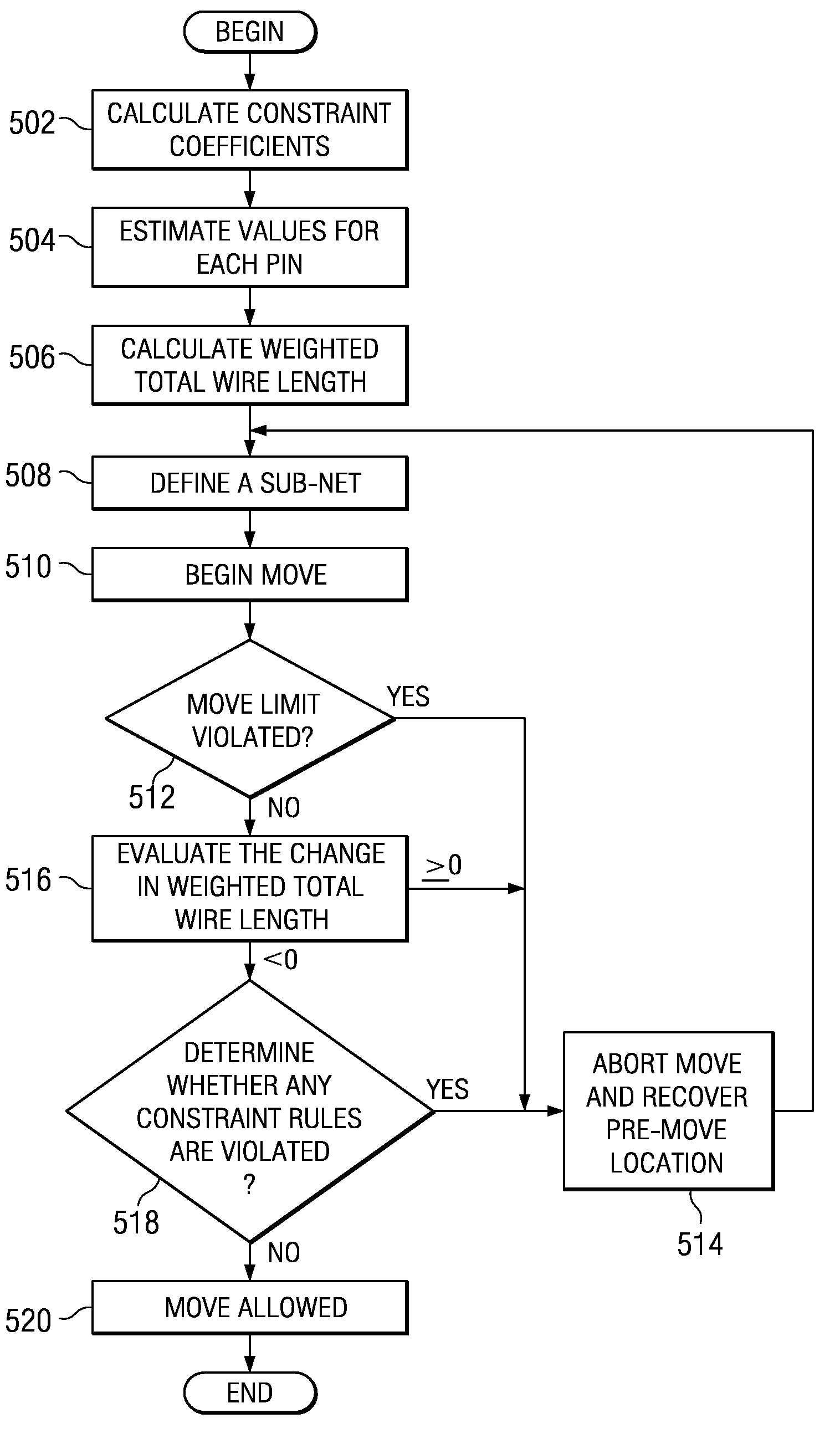
A computer implemented method and a computer program product which perform cell transforms that decrease overall wire length, without degrading device timing or violating electrical constraints. The process computes delay constraint coefficients for a data set. The process performs a detailed placement transform by moving a subset of cells, making the placement legal, computing a half perimeter wire length change for each output net that is a member of the subset of nets, and computing a Manhattan distance change for each source-sink gate pair within the move cells. The process computes a weighted total wire length incremented value for the transformed data set, if the move will not improve placement, the move transform is not allowed. Further, the process continues by evaluating arrival time constraints, electrical constraints and user configurable move limits for violations, restoring the move cells to the original placement if a violation is found.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Constrained detailed placement
InactiveUS7467369B2Computer programmed simultaneously with data introductionComputer aided designElectricityData set
The illustrative embodiments provide a computer implemented method which perform cell transforms that decrease overall wire length, without degrading device timing or violating electrical constraints. The process computes delay constraint coefficients for a data set. The process performs a detailed placement transform by moving a subset of cells, making the placement legal, computing a half perimeter wire length change for each output net that is a member of the subset of nets, and computing a Manhattan distance change for each source-sink gate pair within the move cells. the process computes a weighted total wire length incremented value for the transformed data set. Further, the process continues by evaluating arrival time constraints, electrical constraints, and user configurable move limits for violations, and restoring the move cells to the original placement if a violation is found.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
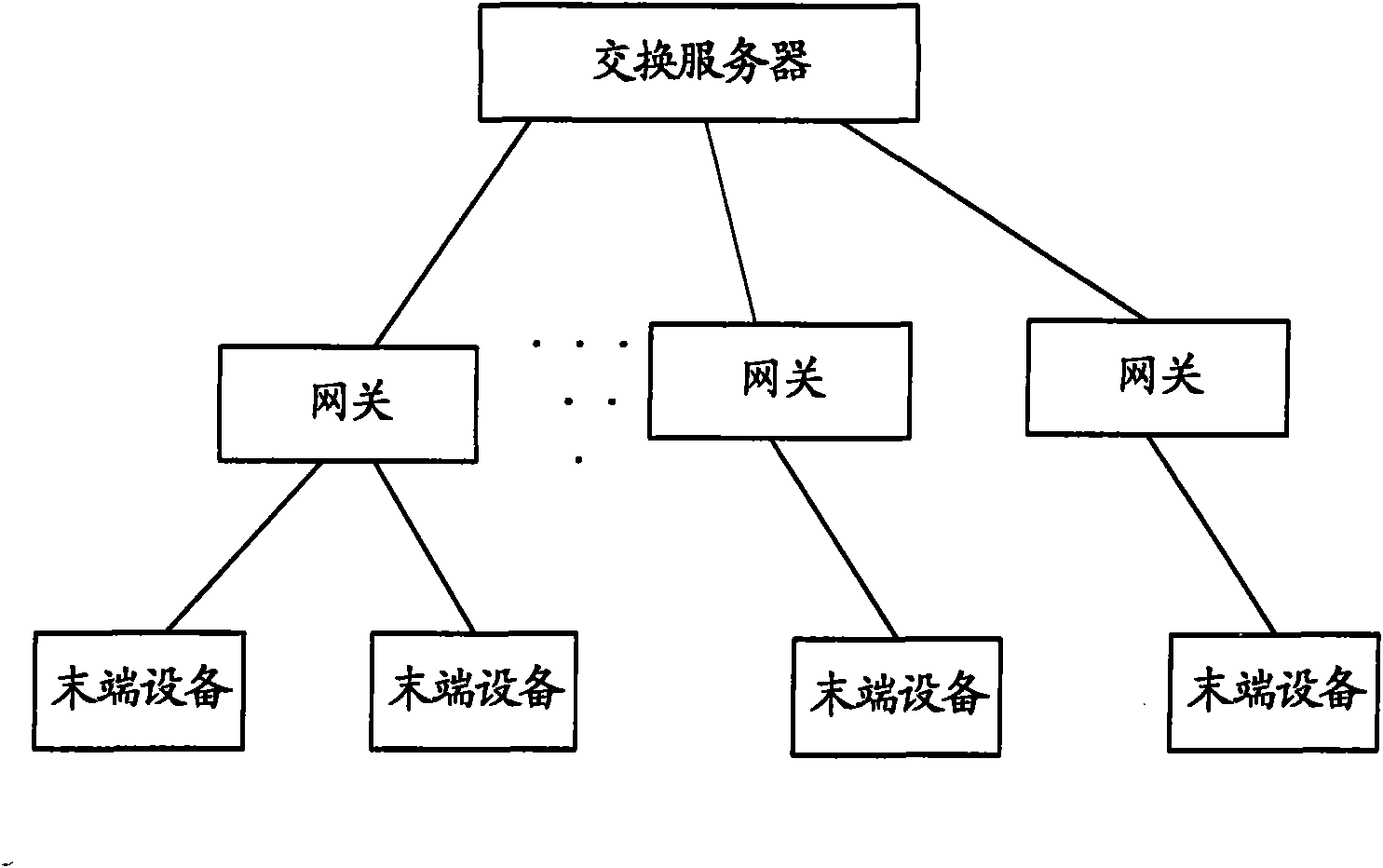
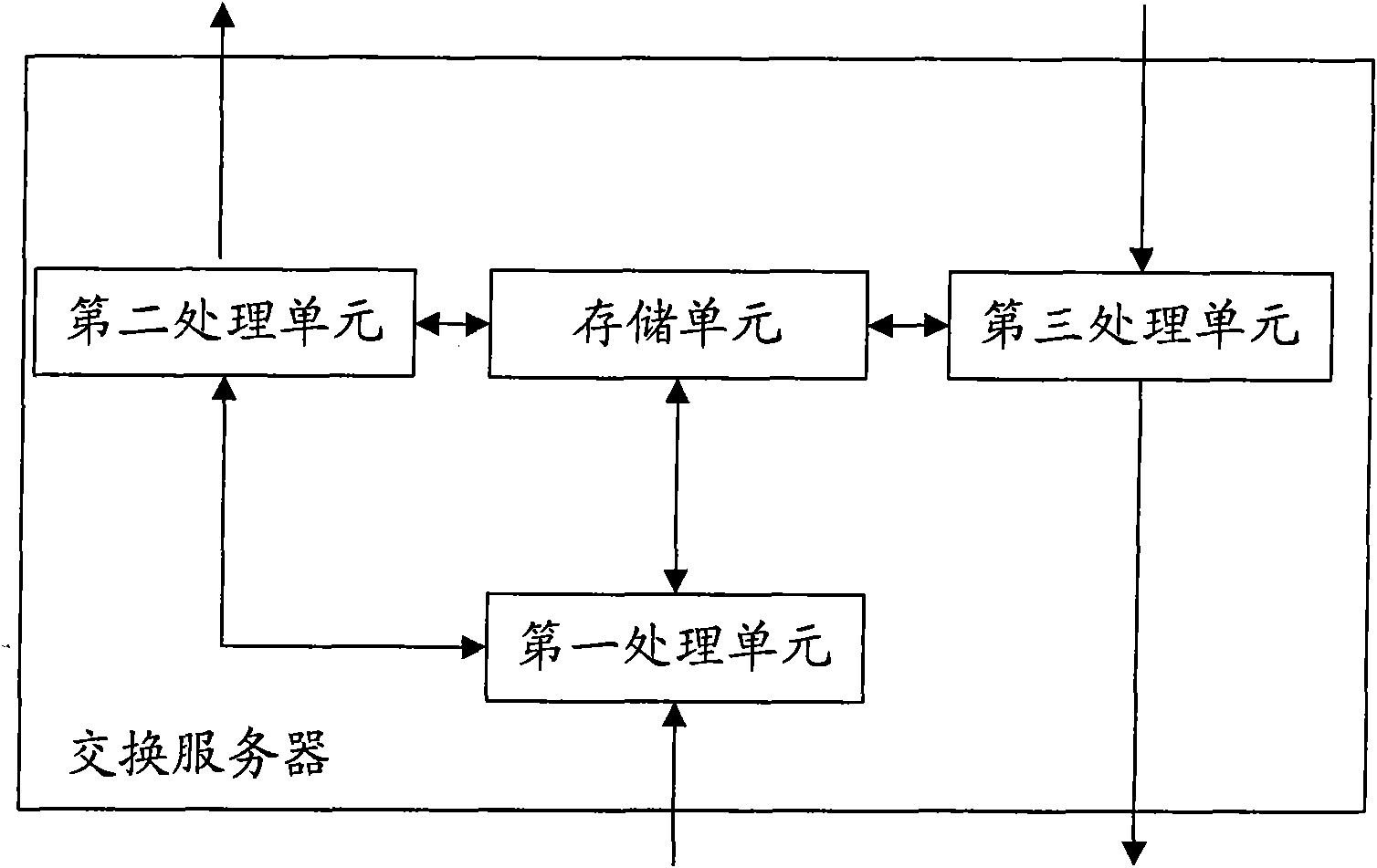
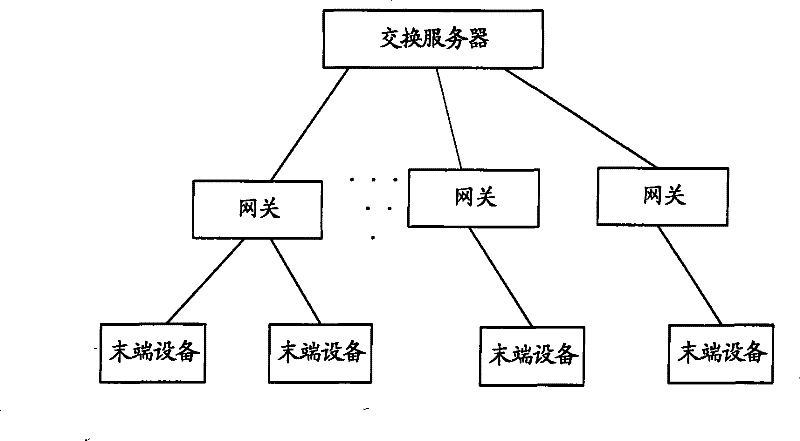
Exchange server, system and method for addressing and transmitting data in control network
InactiveCN101594297AShort processError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching by path configurationNetwork packetSource sink
The invention provides an exchange server, a system and a method for addressing and transmitting data in a control network, wherein the exchange server comprises a storage unit, a first processing unit and a second processing unit; the storage unit is used for storing a device map relation table and a source-sink relation table; the first processing unit is used for receiving a data packet sent by a source information node, inquiring the resource-sink relation table stored by the storage unit and obtaining and outputting the address of the exchange server, the ID of an end device and the information node number corresponding to a sink information node; the second processing unit is used for obtaining the address of a sink exchange server, the ID of the sink end device and the information node number, searching the device map relation table in the storage unit according to the ID of the end device corresponding to the sink information node when the address of the exchange server corresponding to the sink information node is the address of the exchange server, obtaining the address of the end device and sending the data packet with the sink information node number to the address. The invention simplifies the end device and saves the processing procedures of communication among end devices simultaneously.
Owner:新动力(北京)建筑科技有限公司
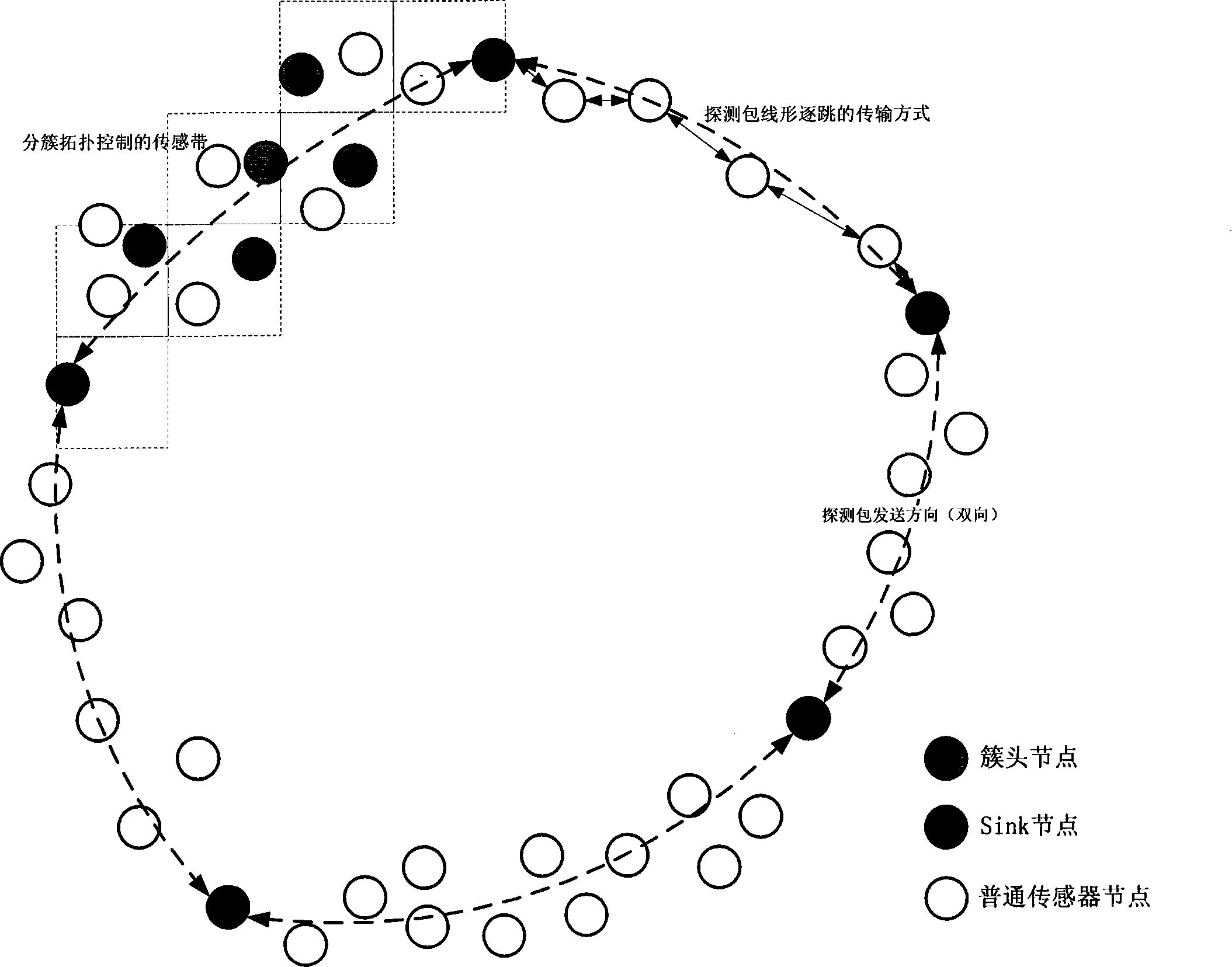
Band wireless sensor network diagnosis method
InactiveCN101247285ASimple methodEasy to implementData switching by path configurationLine sensorWireless mesh network
The invention belongs to the technical field of testing wireless sensor network, and designs a diagnostic method for ribbon pattern sensor network aiming at the characteristic of ribbon pattern sensor network. The network diagnostic method is operated on a routing layer, diagnosing the network connectivity, node state and the characteristic of other networks by the method that adjacent sink nodes exchange network explorer packet mutually. If all explorer packets can reach segment sink node successfully, the sensing belt from the source sink node to the destination sink node is considered to work normally. If each adjacent sink node learns to be in normal work state with the adjacent sensing belt, the whole network is regarded to be communicated effectively in normal work.
Owner:JIAXING WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS CENT CAS
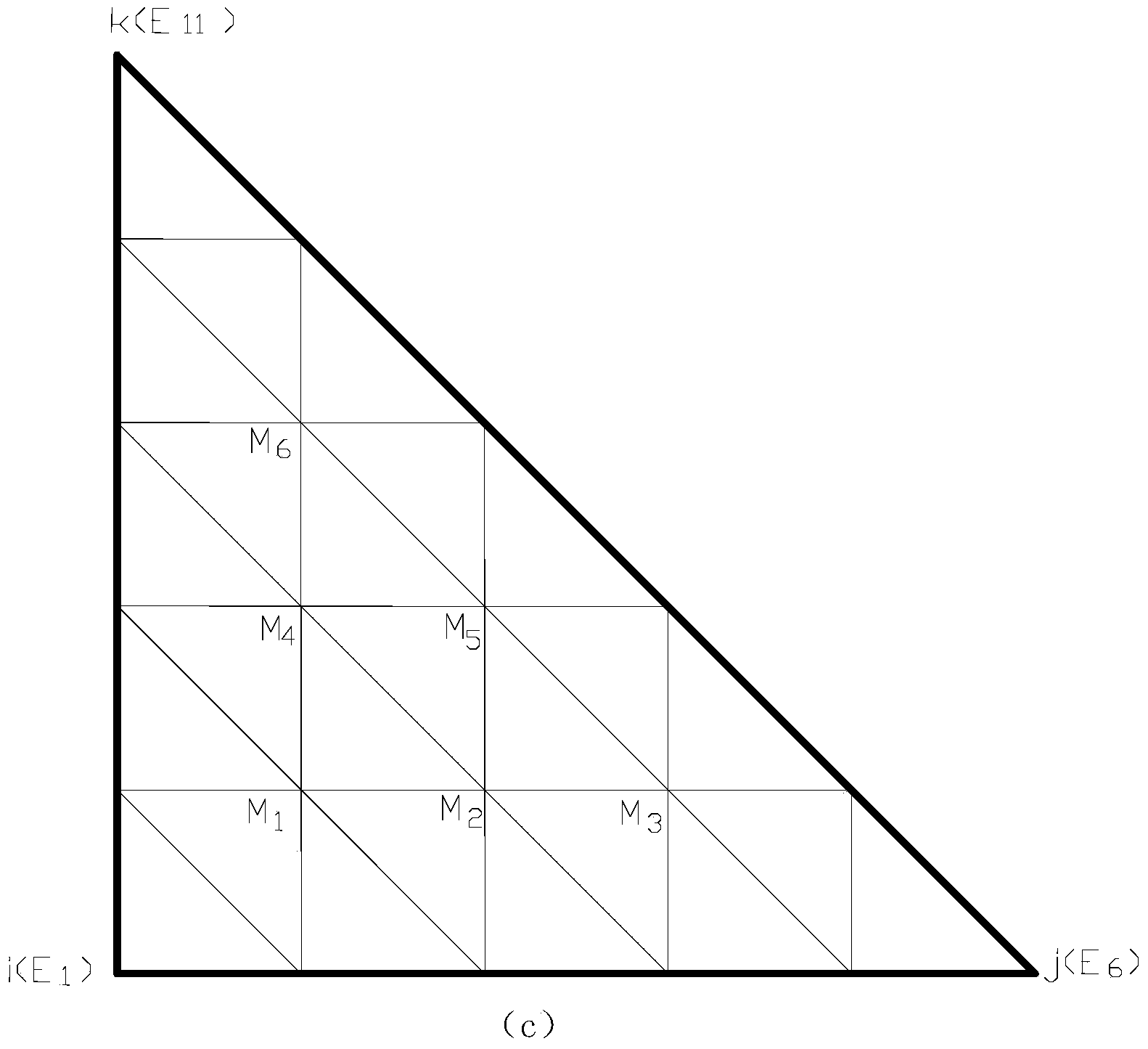
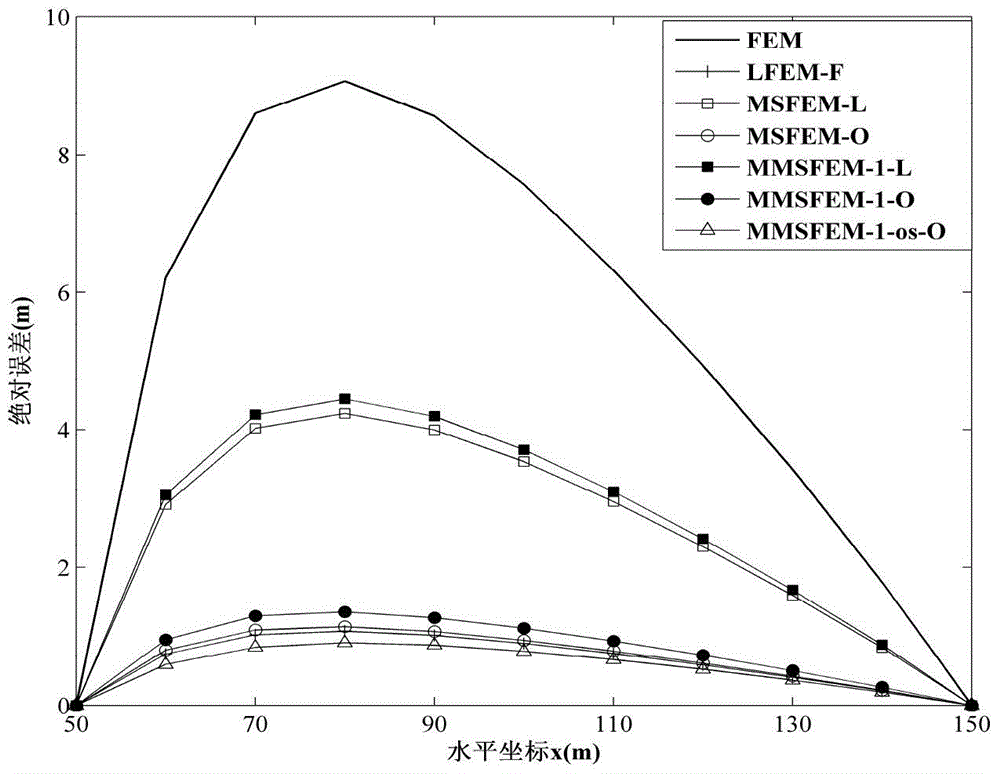
Improved multi-scale finite element method for stimulating two-dimensional water flow movement in porous media
ActiveCN103778298AReduce the numberReduce the amount of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsPorous mediumMixed finite element method
The invention discloses an improved multi-scale finite element method for stimulating two-dimensional water flow movement in porous media. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, converting a problem to be solved into a variational form; determining a boundary condition, setting a grid cell size h, subdividing a research area, and obtaining coarse grid cells; subdividing each coarse grid cell; according to a permeability coefficient K and the boundary condition of a basis function, solving the problem of degenerating elliptic type, and determining the basis function; according to the basis function, obtaining cell stiffness matrixes, and adding the same to obtain a total stiffness matrix; according to the boundary condition of the research area and a source sink term, obtaining a right-hand side; adopting an effective calculating method to solve the simultaneous equations of the total stiffness matrix and the right-hand side; and obtaining the hydraulic heads of all nodes in the research area. Through various simulation tests, the obtained result coincides with the analytical solution. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention is similar to the same in precision, but the calculating time of the method is less than 10% of the calculating time in the prior art. The efficiency is greatly improved when the method is used for solving wide-range, long-time or complicated problems.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Soil heavy metal enterprise pollution source recognition method based on source-sink spatial variable inference
ActiveCN108595414AAccurate analysisExtended analysis methodCharacter and pattern recognitionNatural language data processingData setStatistical analysis
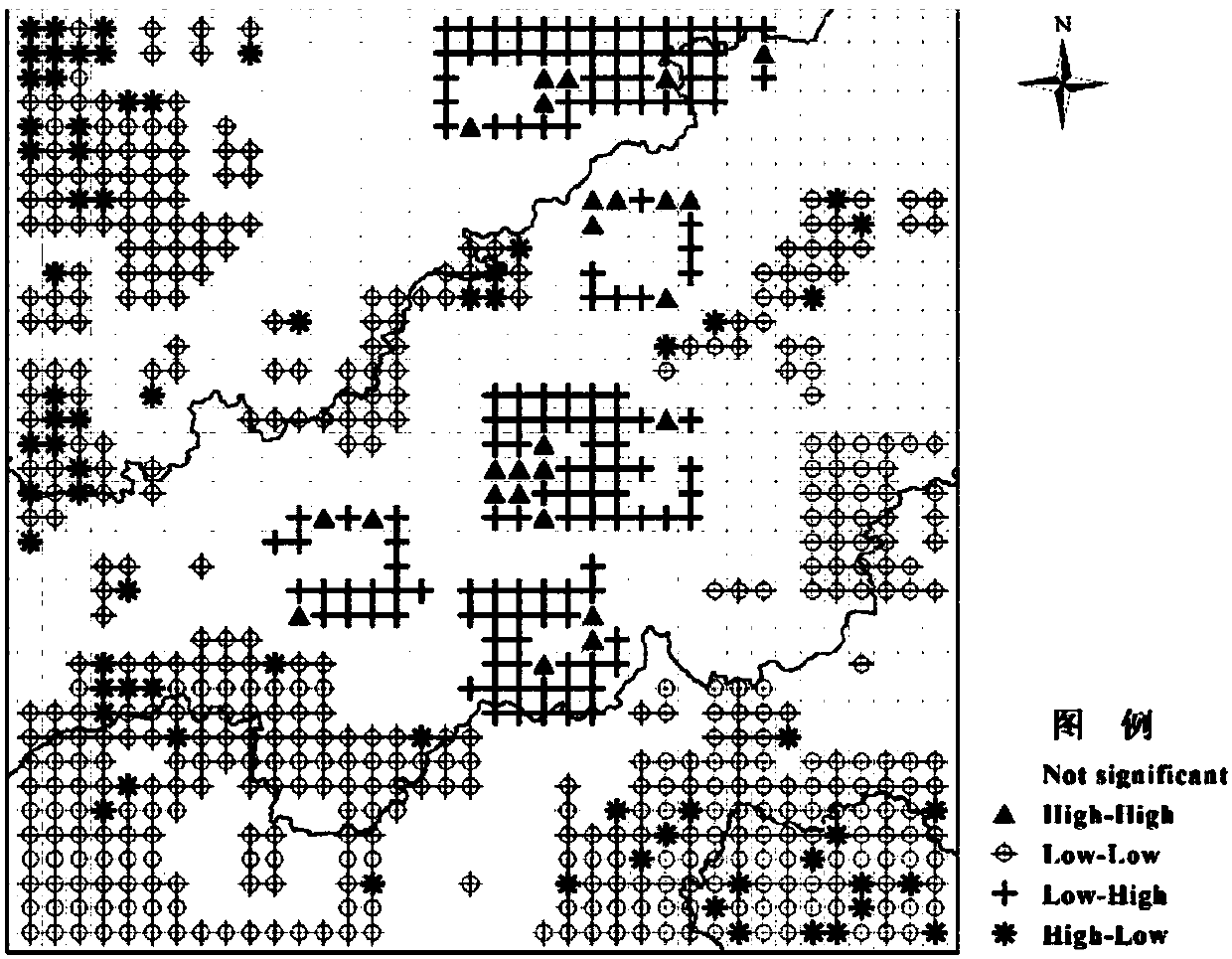
The invention discloses a soil heavy metal enterprise pollution source recognition method based on source-sink spatial variable inference. According to the method, first, pollution enterprise data, enterprise POI data and heavy metal pollution data in a to-be-studied region are acquired, enterprise industry category distribution of a dataset is adjusted, and a training dataset and a test dataset are separated after word segmentation processing is performed to eliminate local vocabularies; second, according to corpora established through the two datasets, the word frequency of words in all samples is subjected to statistical analysis to serve as text features corresponding to the samples, the samples of the training set are used to train a polynomial naive Bayesian model, and the model is assessed through scores of the test set; and last, industry categories and heavy metal pollution indexes are predicted according to the acquired enterprise data, numerical statistical analysis is performed in a grid generated according to the topological shape of the study region, a double-variable spatial self-correlation method is used to perform spatial analysis, the spatial distribution relation between pollution and enterprises is judged, and heavy metal point source and surface source pollution regions in the study region are recognized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
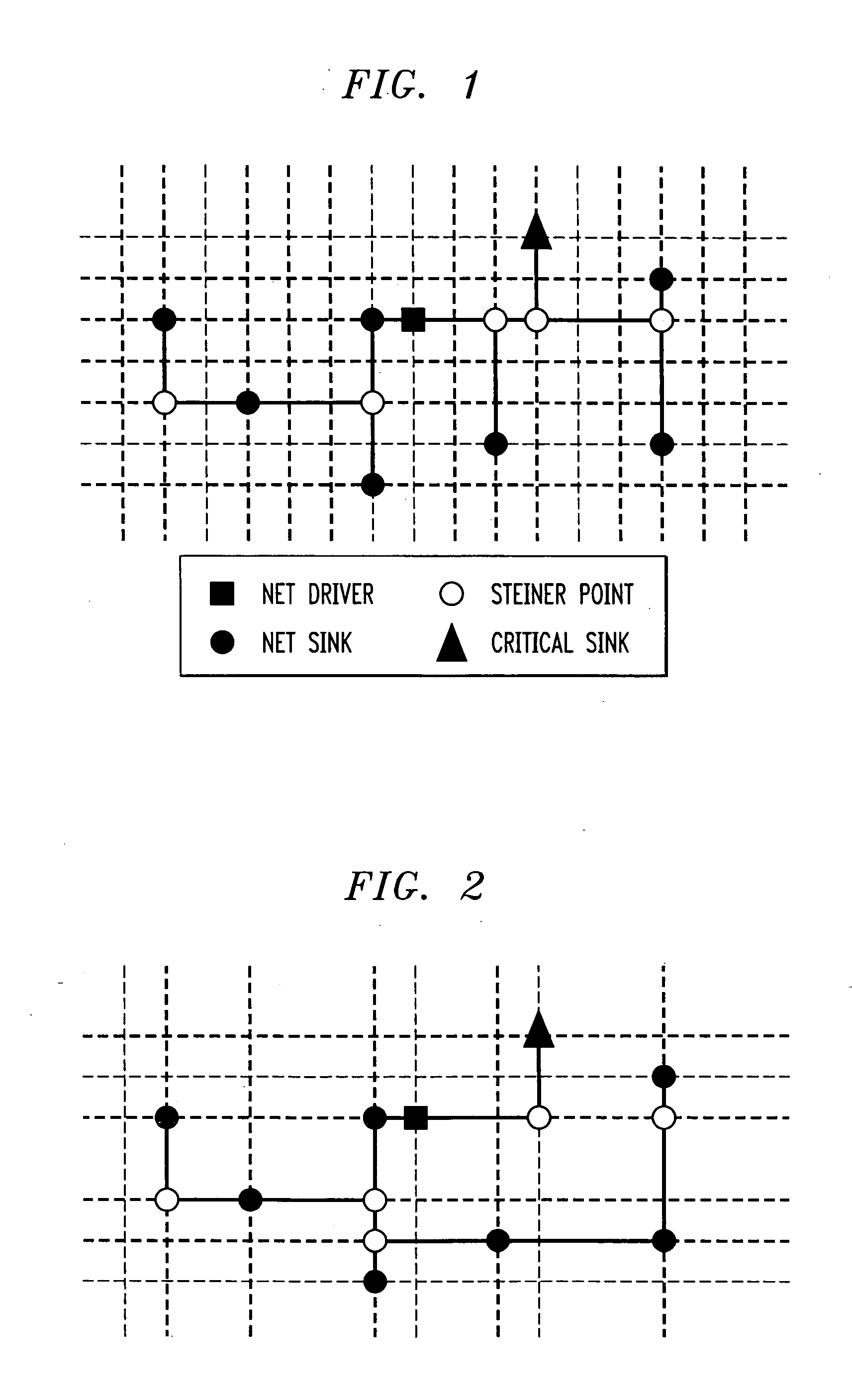
Methods and Apparatus for Providing Flexible Timing-Driven Routing Trees
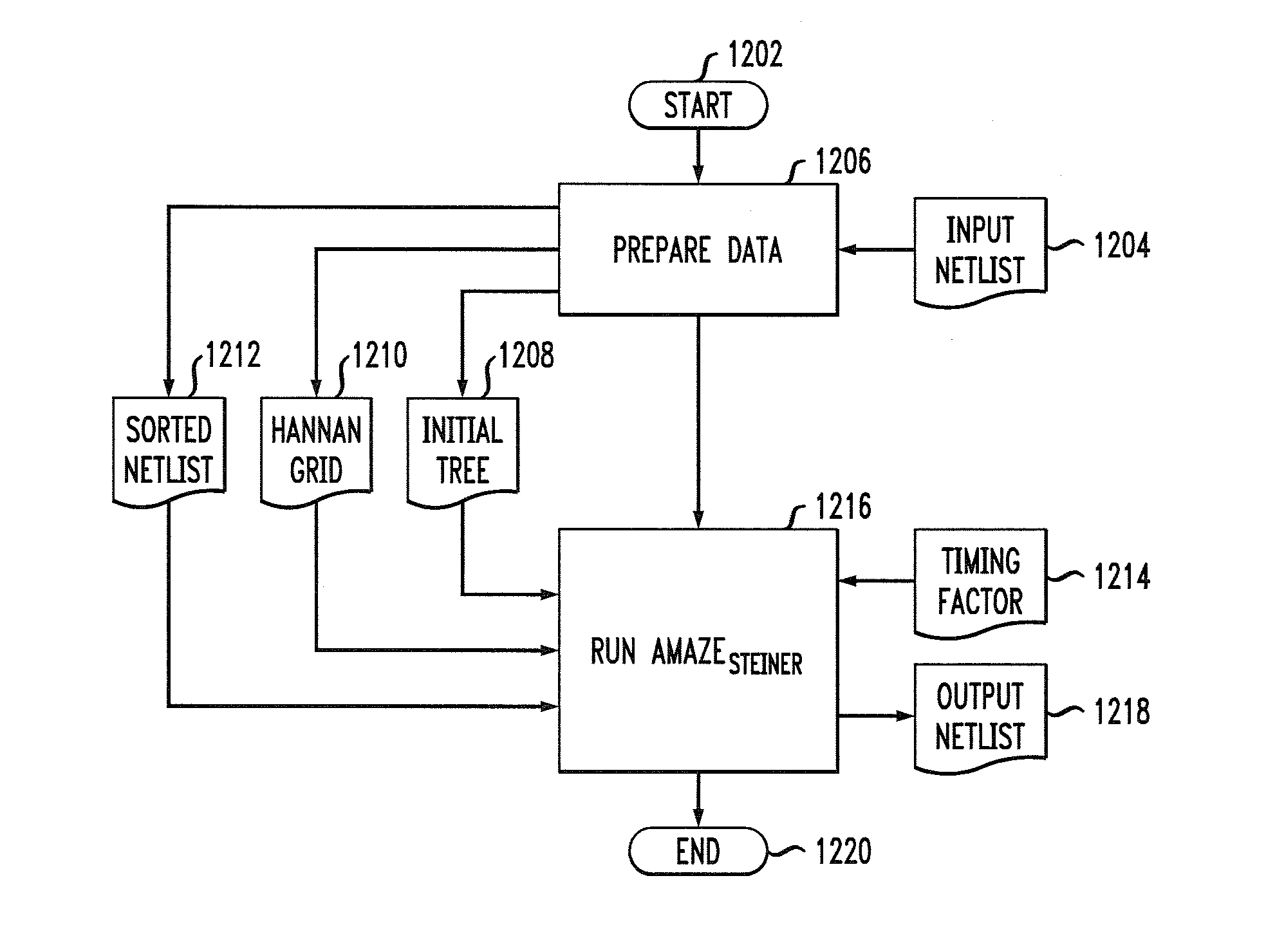
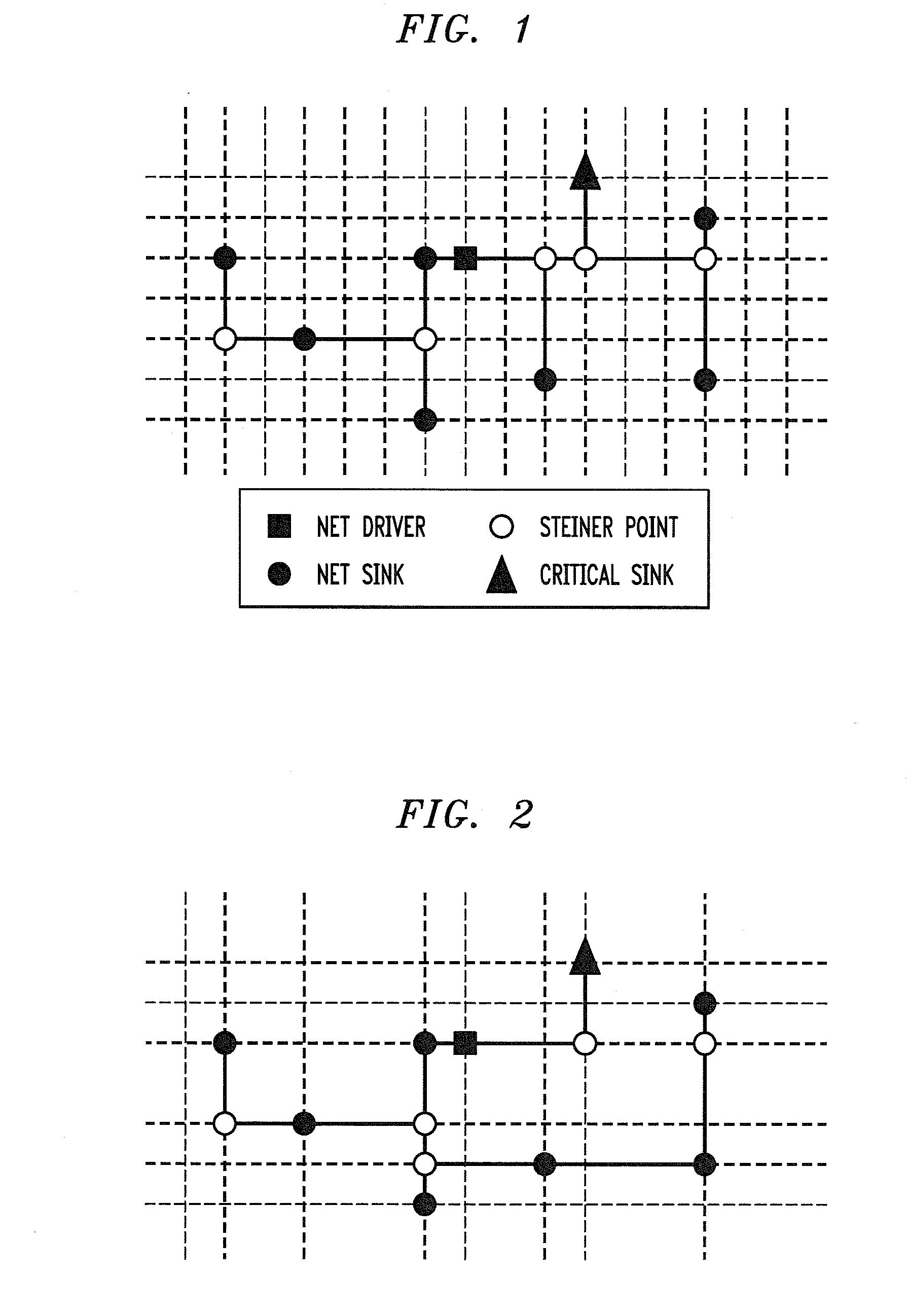
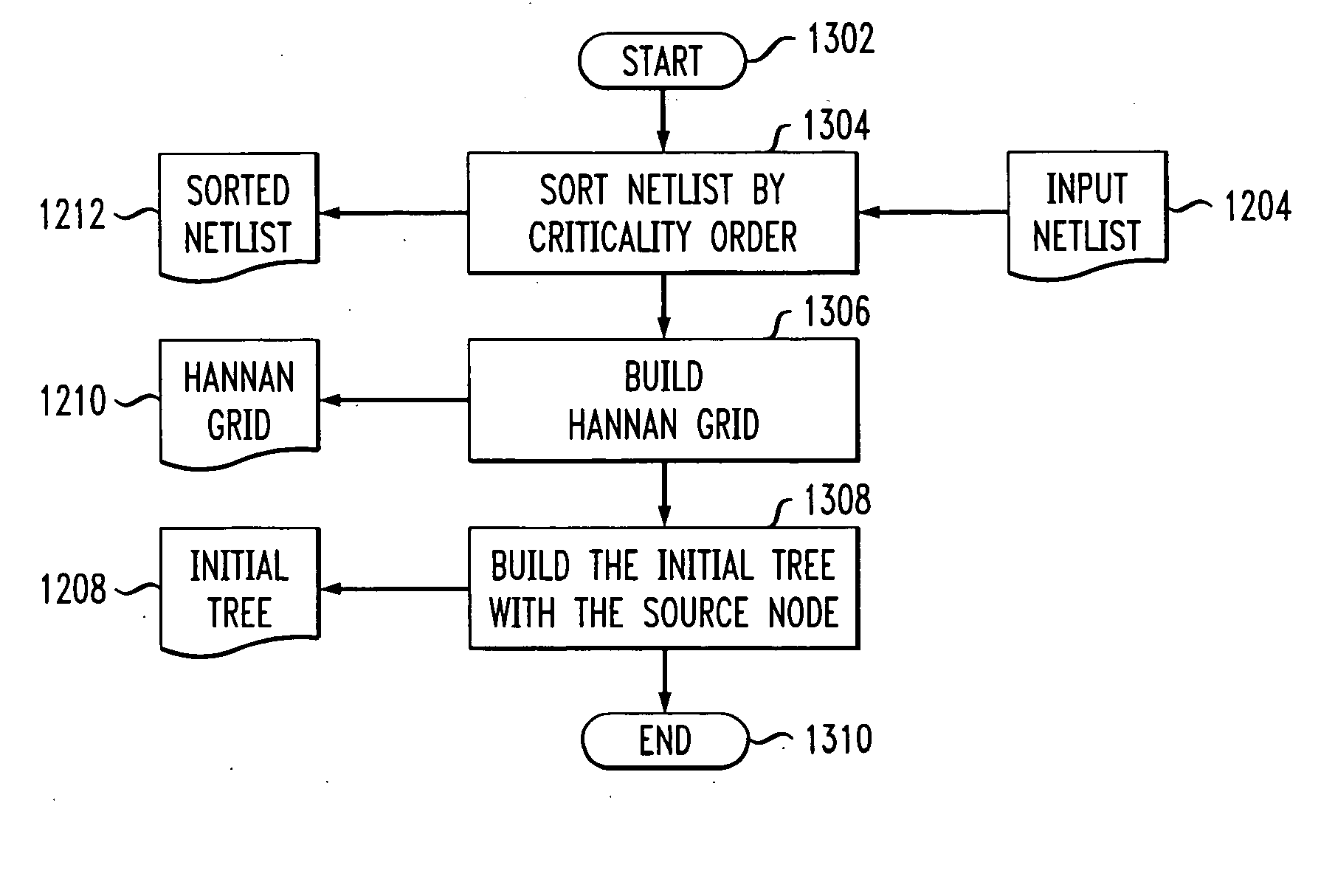
InactiveUS20080170514A1Efficient mechanismReduce congestionData switching by path configurationTheoretical computer scienceTree generation
A method of producing a flexible timing-driven routing tree is provided. Two or more target nodes are sorted in accordance with data criticality. A source-sink grid is built from one or more source nodes and the two or more target nodes. An initial routing tree is built comprising the one or more source nodes. A routing tree generation algorithm is executed on the initial routing tree, utilizing the sorted two or more target nodes and the source-sink grid in accordance with a user-defined timing factor to construct a flexible timing-driven routing tree. The user-defined timing factor specifies an extent of isolation for a routing path from a given one of the one or more source nodes to a given one of the two or more target nodes.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Methods and apparatus for providing flexible timing-driven routing trees
InactiveUS20070159984A1Efficient mechanismReduce congestionData switching by path configurationTheoretical computer scienceTree generation
A method of producing a flexible timing-driven routing tree is provided. Two or more target nodes are sorted in accordance with data criticality. A source-sink grid is built from one or more source nodes and the two or more target nodes. An initial routing tree is built comprising the one or more source nodes. A routing tree generation algorithm is executed on the initial routing tree, utilizing the sorted two or more target nodes and the source-sink grid in accordance with a user-defined timing factor to construct a flexible timing-driven routing tree. The user-defined timing factor specifies an extent of isolation for a routing path from a given one of the one or more source nodes to a given one of the two or more target nodes.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Plug and play method based on SpaceWire
The invention discloses a plug and play method based on the SpaceWire, and belongs to the field of satellite-borne equipment self-management. The method includes the steps that firstly, SpaceWire node devices which have access to all ports in a network are detected by utilizing a network manager, the types of the SpaceWire node devices are determined, and the topological relation between the SpaceWire node devices is determined; secondly, if a new SpaceWire node device has access to one port in the network or an original device is pulled out, a route informs the network manager to trigger the network manager to launch topological information updating aiming at the port; thirdly, the network manager has access to all SpaceWire node devices in the network according to the topological relation and reads a service register of each SpaceWire node device; fourthly, source sink types of the SpaceWire node devices are judged according to source sink attributes in service information, corresponding information sink of each information source is found, and therefore source sink matching of all SpaceWire node devices can be obtained. The plug and play method is applied to plug and play of SpaceWire devices.
Owner:NO 513 INST THE FIFTH INST OF CHINA AEROSPACE SCI & TECH
Closely interlocked molecular mark of rice new gene source-sink 1 (SS1)
The invention relates to a molecular marking method of a rice new gene source-sink 1 (SS1), and belongs to the fields of super-high-yield breeding of rice and molecular genetics. The essence of the invention is as follows: according to the interlocking separation law, an F2 secondary separation group constructed by autocopuation of a near-isogenic line carrying a SS1 heterozygous segment is takenas a test material for constructing a set of crossing and stacking system of a target segment, phenotype is further combined for performing high-precision interlocking analysis on a target gene, through two years of two-point repeated identification, the SS1 is finally precisely positioned in an interval of 55Kb on the fourth chromosome and a PCR (polymerase chain reaction)-based molecular mark FL41 which is closely interlocked with the SS1 is further obtained. Through the application of the molecular marking method in the super-high-yield breeding of rice, genotype individuals which can simultaneously affect the characters of a library (the number of grains per panicle) and a source (the flag leaf width and the leaf area) can be fast accurately identified, the early generation selection of breeding material can be performed further and the process of the super-high-yield molecular breeding of rice can be greatly accelerated.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Ancient landform recovery method based on source-sink system
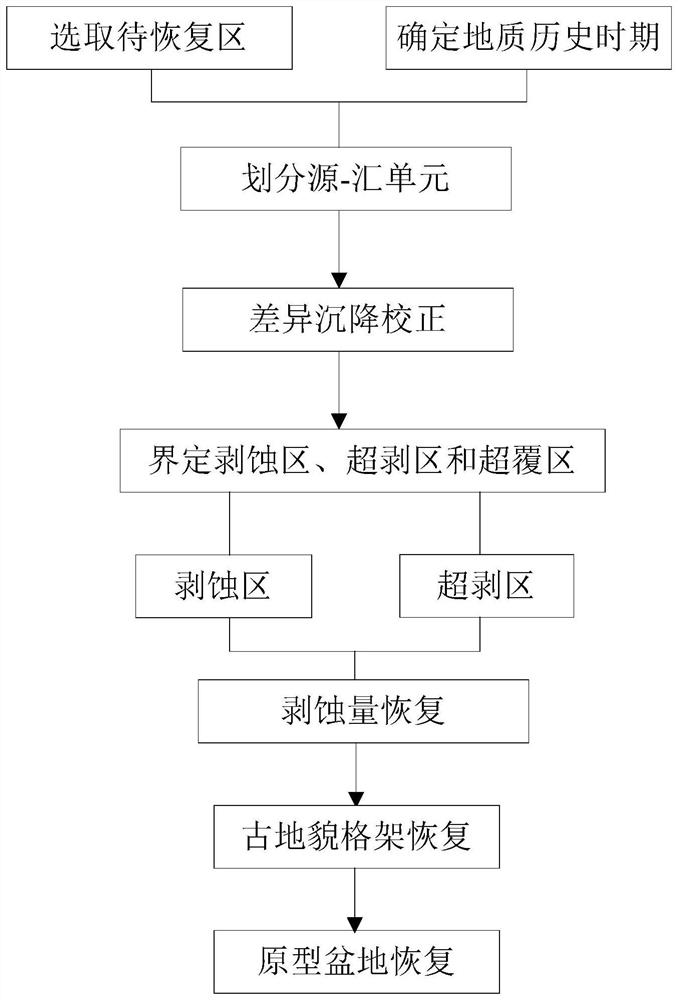
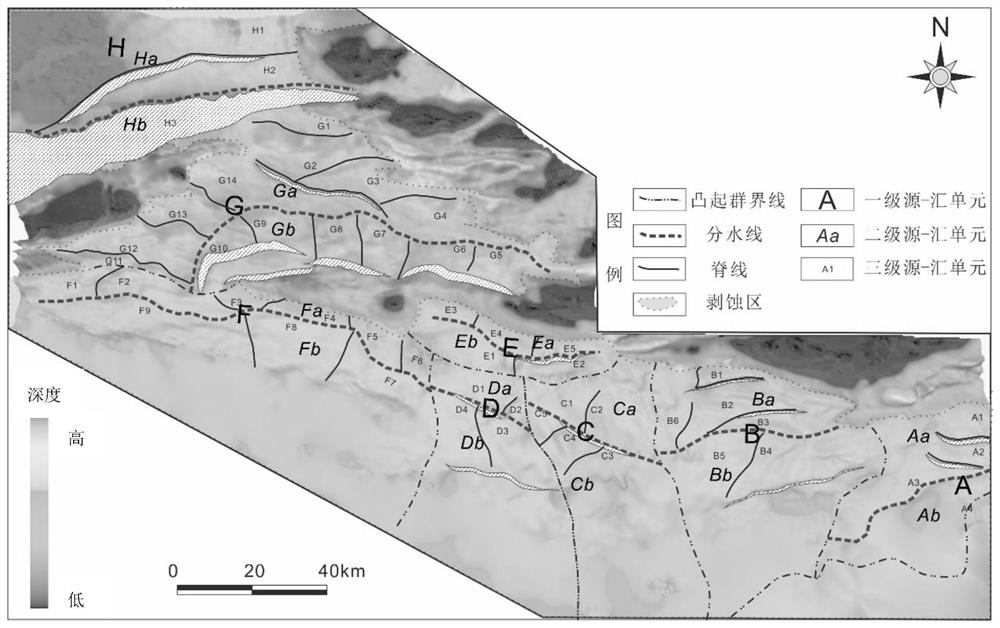
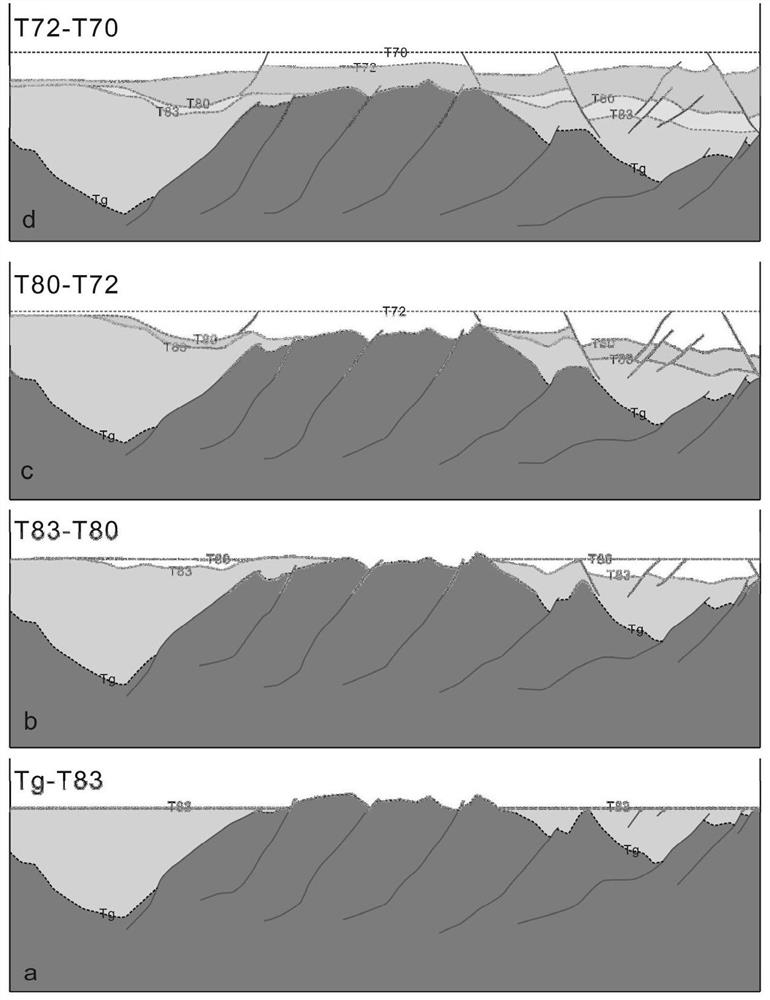
PendingCN112327355ARestore intuitiveRecovery scienceSeismic signal processingLithologyMaterial distribution
The invention discloses an ancient landform recovery method based on a source-sink system. The ancient landform recovery method comprises the steps that: S1, selecting a to-be-recovered region, and determining a geological history period; S2, dividing source-sink units of a geological history period on the basis of the residual landform; S3, based on a structural evolution rule of the to-be-recovered region, determining a differential settlement rule and a deposition reference surface, and performing differential settlement correction; S4, defining the ranges of a denudation region, an over-stripping region and an over-covering region based on the unconformity interface characteristics of the to-be-recovered region and the seismic facies difference of different lithologies, and performingdenudation amount recovery on the denudation region and the over-stripping region based on the principle of conservation of substances of the source-sink system; and S5, superposing images obtained inthe step S3 and the step S4 to complete recovery of the ancient landform framework. According to the ancient landform recovery method, the denudation region material source and the total material amount are recovered more visually and scientifically, so that ancient landform and prototype basins in the deposition period are established, and guidance is provided for research on denudation and deposition region material distribution, landform evolution, reservoir characteristics, reservoir body distribution and the like.
Owner:中海石油(中国)有限公司深圳分公司
Genes controlling photoperiod sensitivity in maize and sorghum and uses thereof
The present disclosure provides polynucleotide sequences controlling the photoperiod sensitive trait in maize. The disclosure provides polynucleotide sequences and the use of encoded polypeptides associated with the photoperiod sensitivity. The disclosed sequences are responsible for controlling plant growth, source-sink relationships and yield in crop plants.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
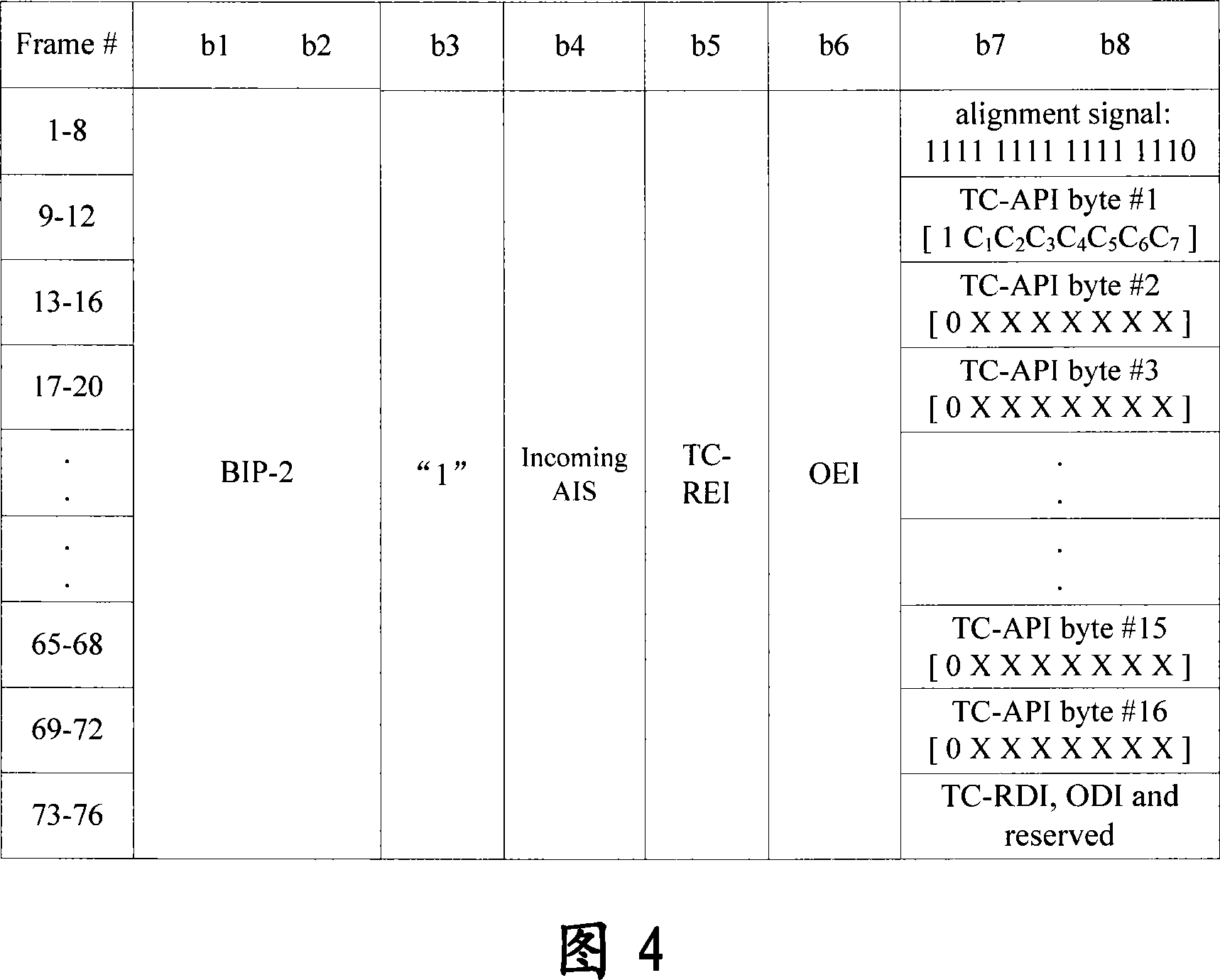
A method for sub-network connection protection via serial monitoring function
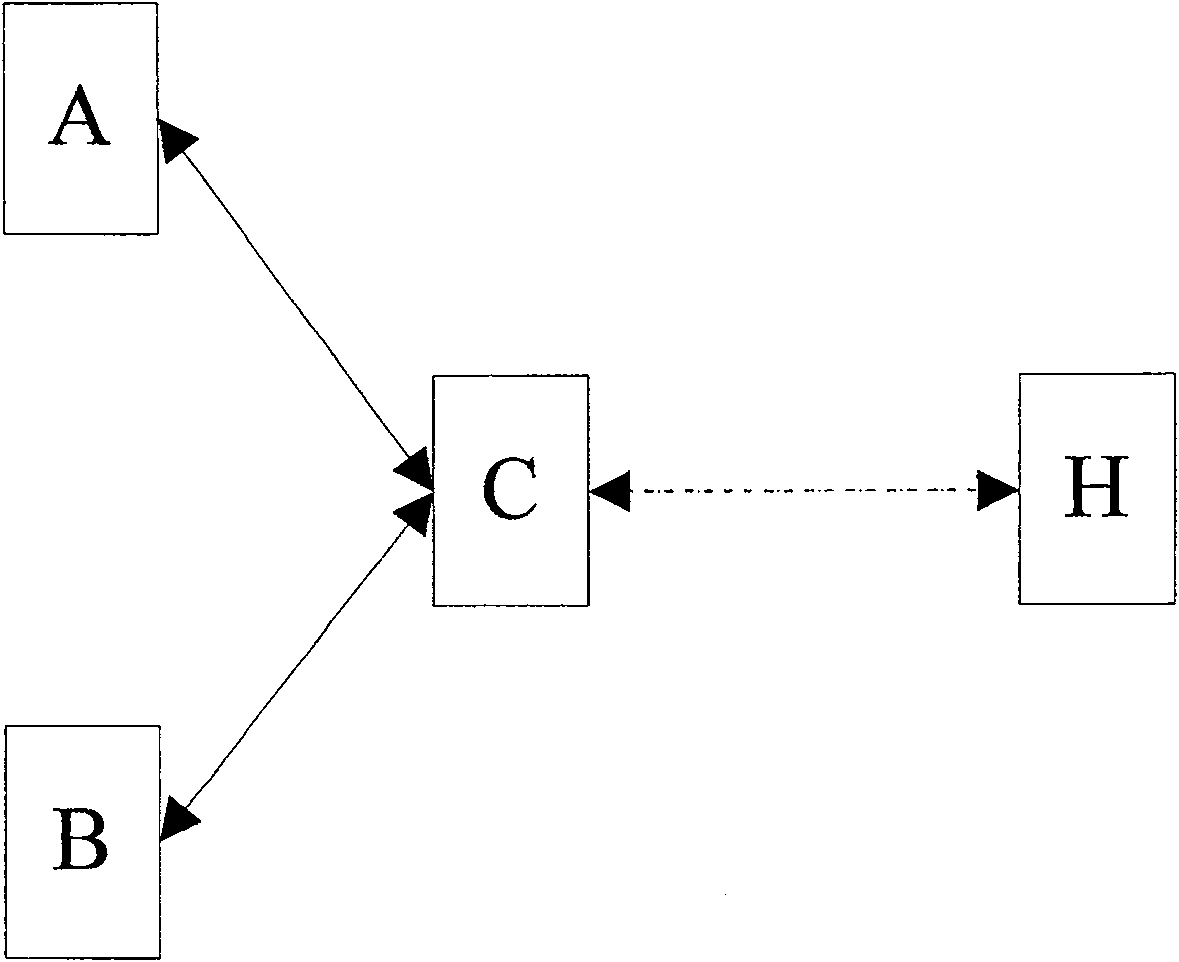
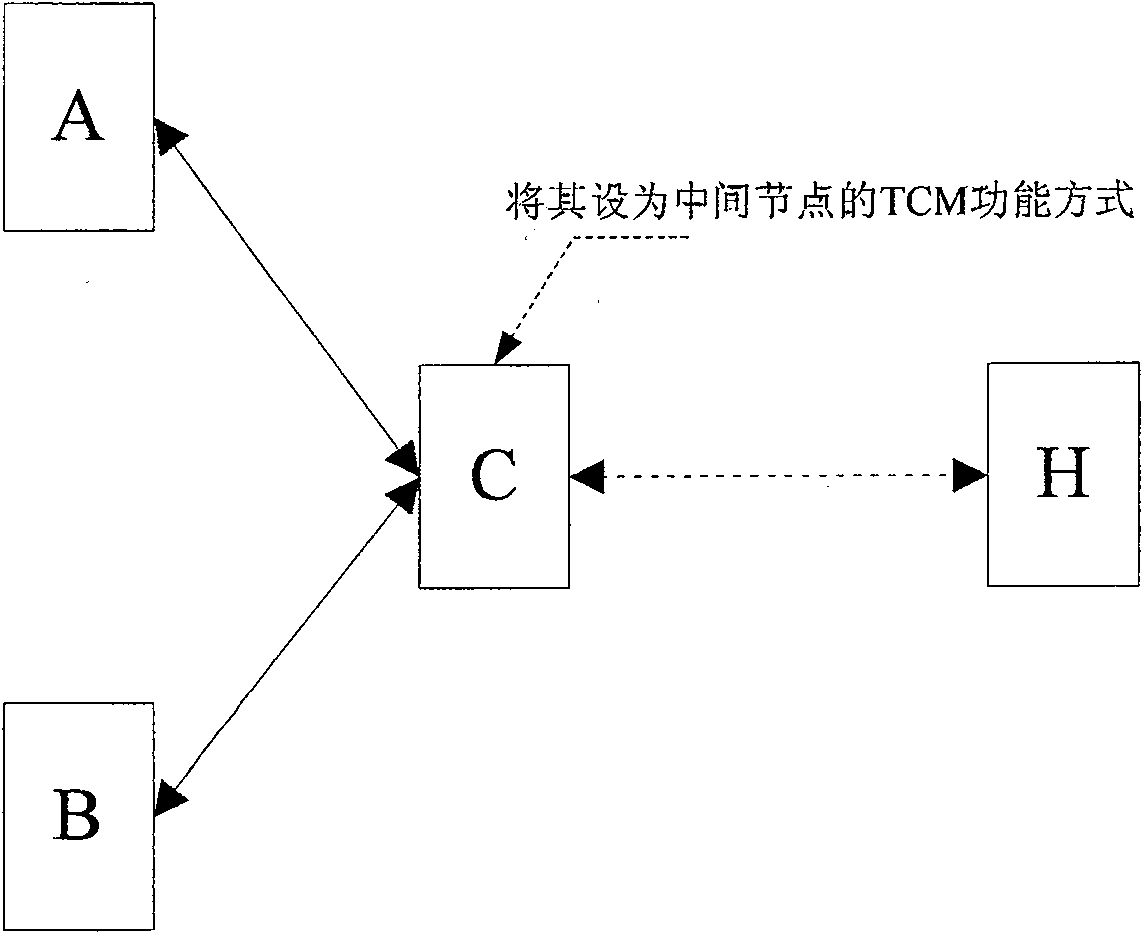
ActiveCN101145990AThe phenomenon of frequent switchingTime-division multiplexTransmission path multiple useNetwork connectionByte
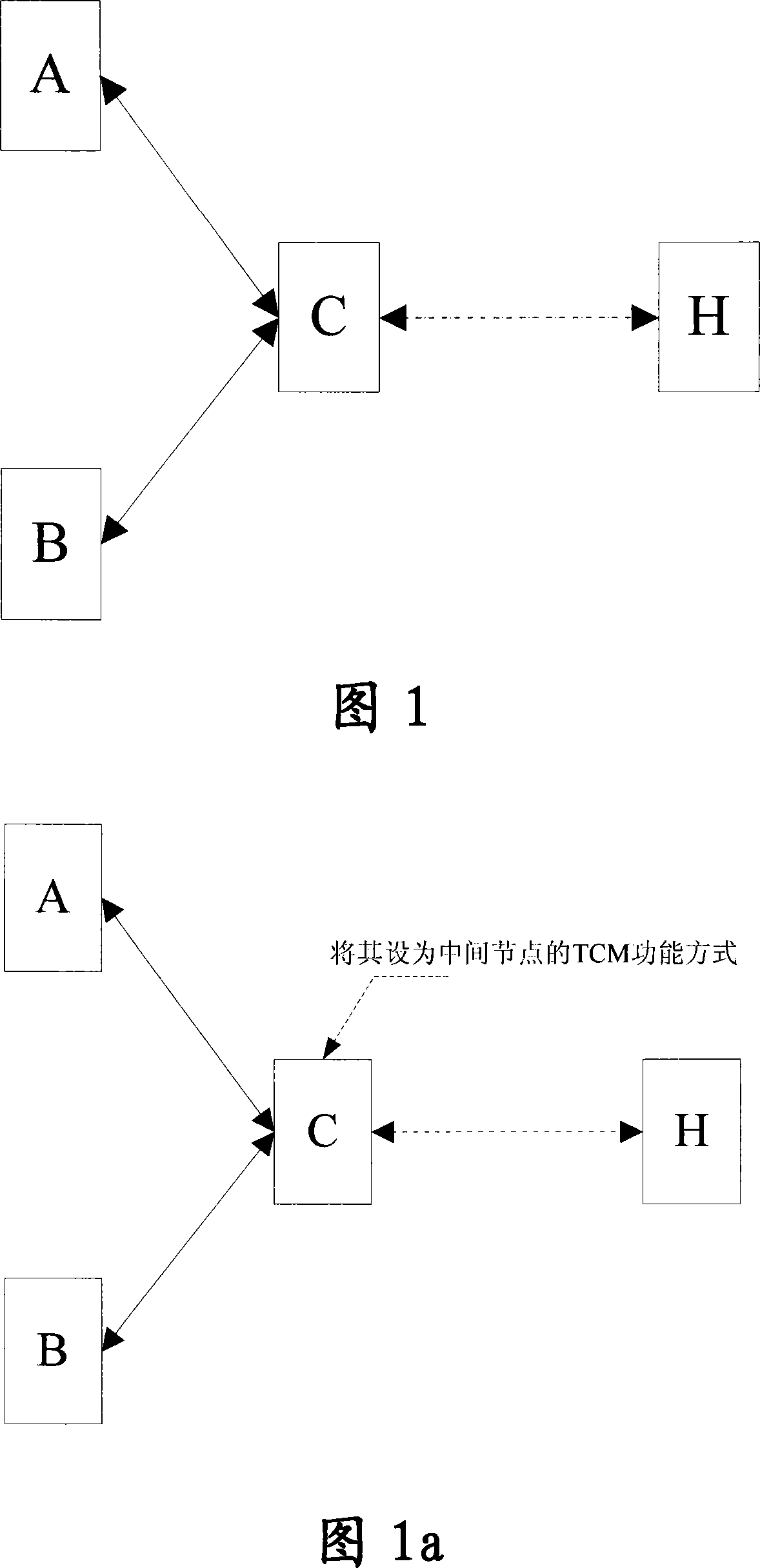
The invention provides a method for achieving sub-network connection protection through TCM function, suitable for the condition of two TCM source-sink SDH regions, which includes (a) setting SN equipped with sub-network connection protection as middle node TCM function manner; and (b) respectively detecting signals transmitted from two source ends SN by the SN equipped with sub-network connection protection, and executing switching operation to switch operation from the working channel to the protection channel when an incoming alarm instruction signal (Incoming AIS) information is detected in the signal transmitted by the current working channel at N1 or N2 byte and the protection channel signal is available. The invention can normally execute switching to obviate operation interruption or frequent switching when a net element equipped with sub-network connection protection is set to a mode not supporting source / sink end and when the net element receives a signal with TC-IAIS information.
Owner:ZTE CORP
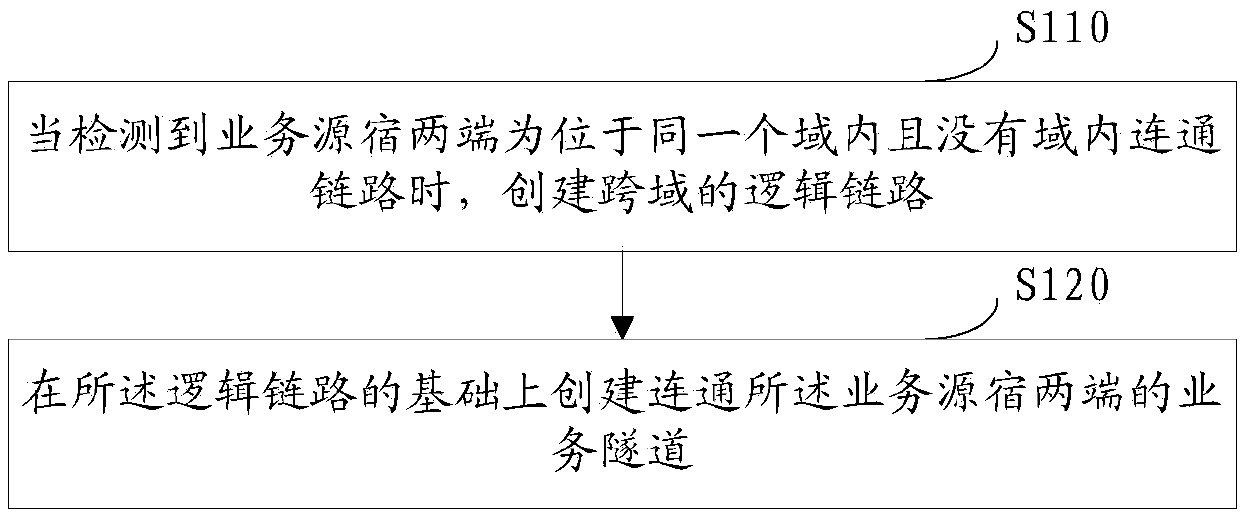
Cross-domain service intercommunication method, network equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN109788018AImprove connectivityImprove intercommunication efficiencyTransmissionCommunication linkSource sink
The embodiment of the invention discloses a cross-domain service intercommunication method, network equipment and a storage medium. The cross-domain service intercommunication method applied to the super controller SC can comprise the following steps: when detecting that two ends of a service source sink are located in the same domain and no intra-domain communication link exists, creating a cross-domain logic link; And creating a service tunnel communicated with the two ends of the service source sink on the basis of the logic link.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM LTD RES INST +1
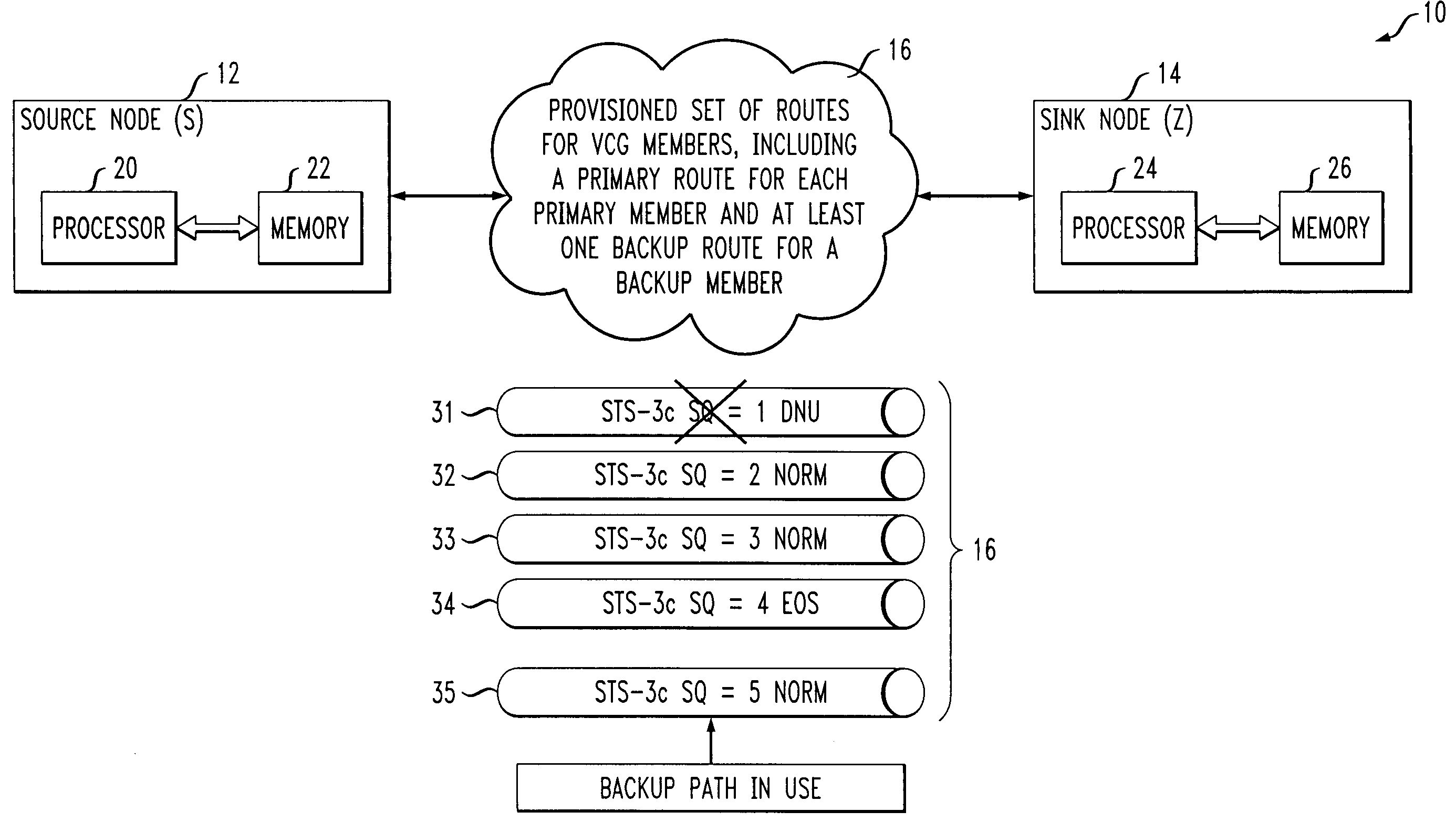
Route determination method and apparatus for virtually-concatenated data traffic
ActiveUS7518990B2Control impactEasy to transportError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityData traffic
Virtually-concatenated data traffic is routed in a network comprising at least first and second nodes. The first and second nodes may comprise a source-sink node pair, an ingress-egress node pair, or any other pair of network nodes. For a given traffic demand, a plurality of routes for routing the traffic demand through the network are determined. Each of the routes corresponds to a member of a virtually-concatenated group, such that different portions of the traffic demand are assigned to different members of the virtually-concatenated group.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
An elastic optical network spectrum allocation method based on multi-hop routing
ActiveCN109936782AImprove resource utilizationSpectrum Allocation OptimizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsFrequency spectrumResource utilization
The invention discloses an elastic optical network spectrum allocation method based on multi-hop routing, and belongs to the technical field of elastic optical network and spectrum resource allocation. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a hop count threshold model of a multi-hop route under the upper limit of energy consumption, selecting a group of intermediate multi-hop nodesas virtual routes, carrying out spectrum allocation on services, and the like. According to the method, firstly, an intermediate multi-hop node threshold value is calculated under the constraint of energy consumption, then, an intermediate multi-hop routing node is reasonably selected, the modulation format grade of each section of short optical path is flexibly selected between source sink nodesaccording to the transmission distance, spectrum resource distribution is optimized, and the purpose of improving the overall resource utilization rate of the network is achieved under the constraintof energy consumption.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF ENG
Noninvasive method of source-sink regulation in rice
ActiveUS20150282432A1Overcome disadvantagesSeed and root treatmentCultivating equipmentsPollinationThinning
A noninvasive method of source-sink regulation in rice belongs to the technical field of rice production. In this method, the source-sink relationship is regulated by a rice sterile line and its identical type of maintaining line being subjected to mixed-planting and insulated pollination, or sowing and transplanting at different times and insulated pollination, so as to construct rice plant samples with gradient difference of source-sink levels. The present invention is a kind of native, natural noninvasive method of source-sink regulation, which could broaden the traditional thinking of source-sink theoretical research, especially overcome the deficiency in conventional methods such as leaf-cutting, spikelet-thinning that lead to physical injury or physiological interference. The method provides a brand new approach and solution for thoroughly investigating source-sink relationship in rice, wheat, maize and other crops, and will play an important role in enriching crop source-sink theory and also promoting the development of the related disciplines.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
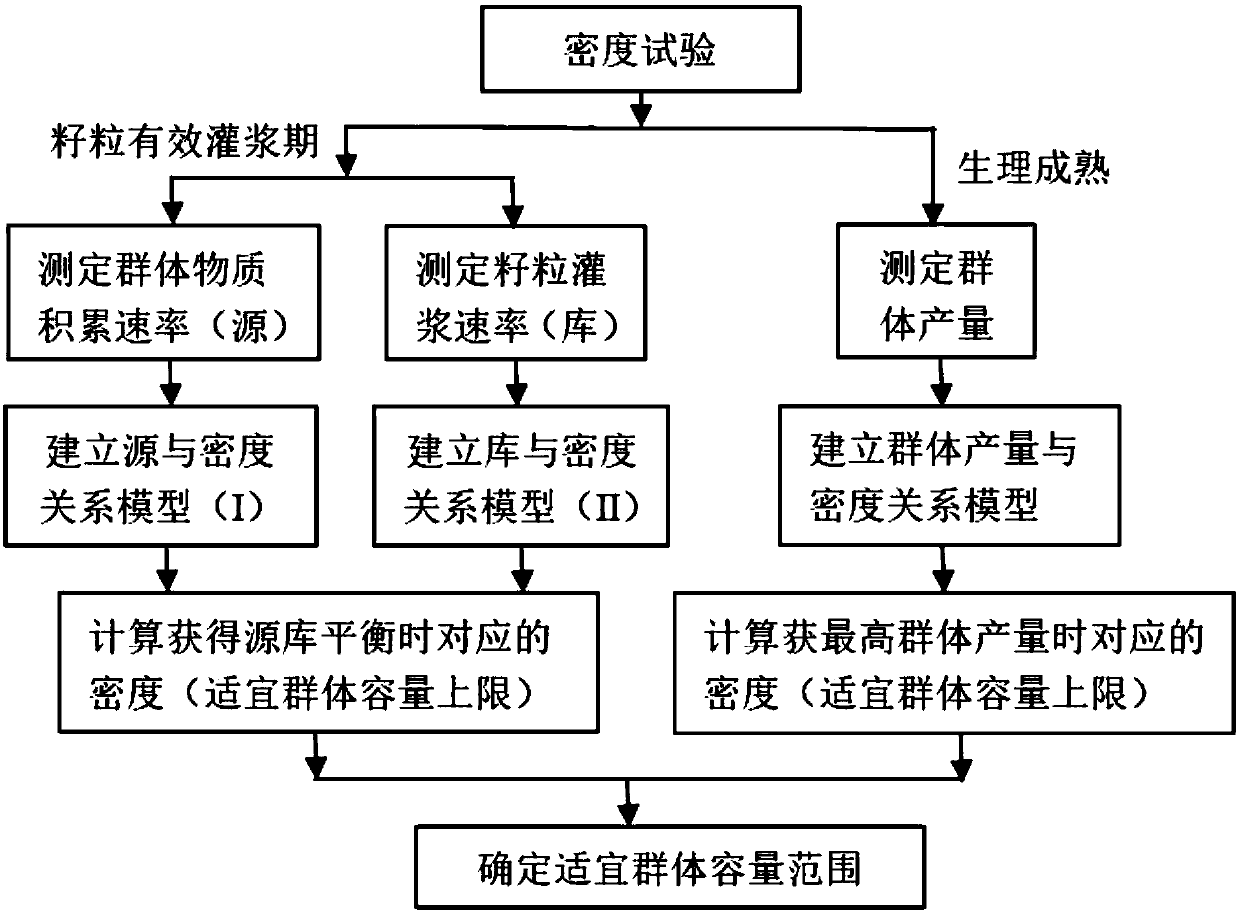
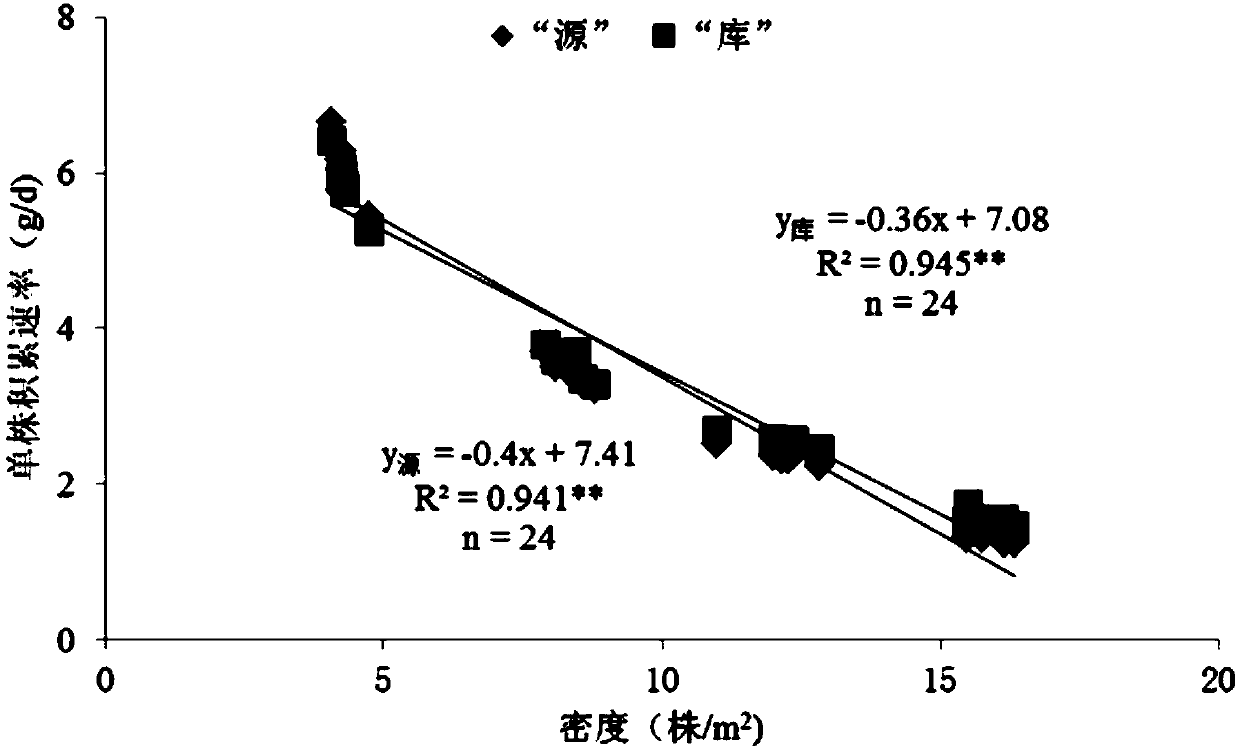
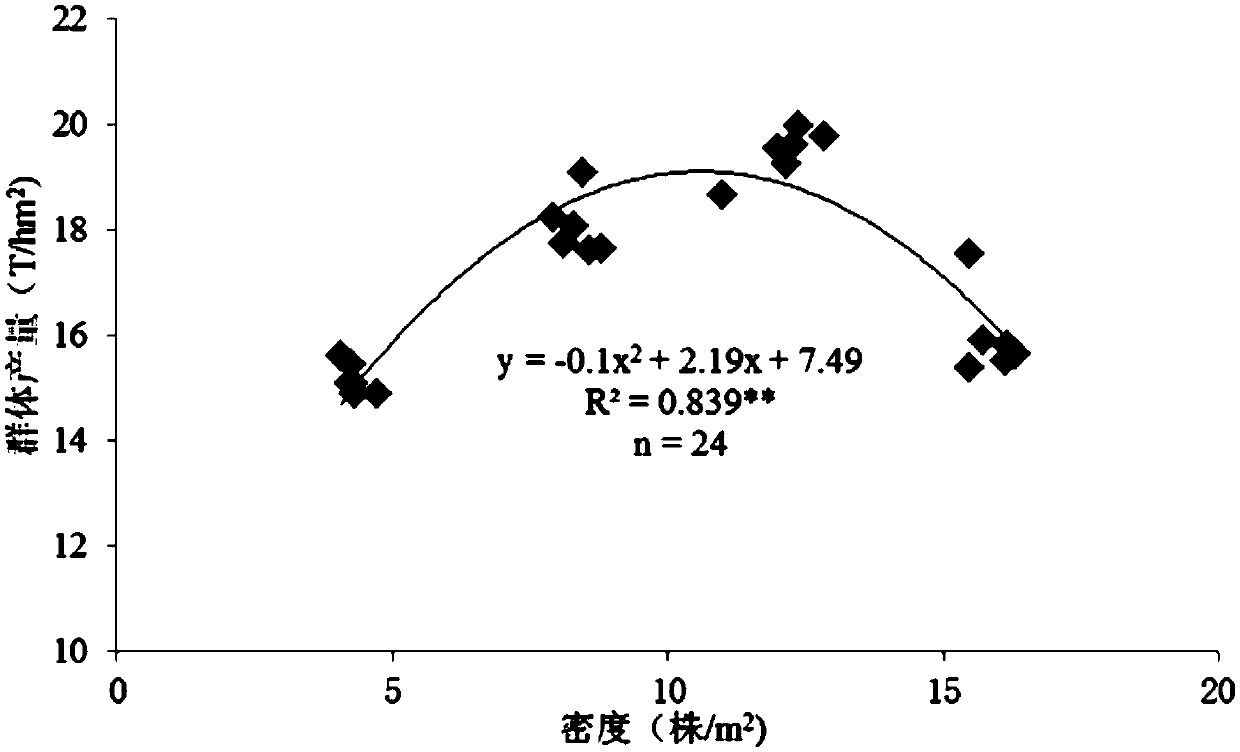
Method for determining suitable population size of corns on basis of source-sink relationship
InactiveCN109089789APromote high-yield cultivation researchDensity small footprintCereal cultivationLower limitMicro environment
The invention relates to the field of corn planting density measurement, in particular to a method for determining a suitable population size of corns on the basis of a source-sink relationship. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a relation model I for a single-plant dry matter accumulation rate and a harvesting density in an effective grouting period of seeds, establishing a relation model II for a single-plant seed accumulating rate and a harvesting density in an effective grouting period of the seeds, combining the relation model I to the relation model II, and taking the intersected point of the relation model I and the relation model II as the lower limit of the suitable population size; and after physiological maturity, measuring the population size under the condition of different densities, establishing a secondary function model of the population size and the harvesting density, and carrying out secondary derivation on the model to obtain the upper limit ofthe suitable popularization size. The method determines the suitable popularization size on the basis of dynamic change of the source-sink relationship of corns in a yield forming process, then a reasonable population structure is construction, a high-luminous-efficiency micro-environment is created, then production is guided, and a good foundation is provided for high yield of the corns.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
An improved multiscale finite element method for simulating two-dimensional water flow in porous media
ActiveCN103778298BReduce the numberReduce the amount of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALDimensional simulation
The invention discloses an improved multi-scale finite element method for stimulating two-dimensional water flow movement in porous media. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, converting a problem to be solved into a variational form; determining a boundary condition, setting a grid cell size h, subdividing a research area, and obtaining coarse grid cells; subdividing each coarse grid cell; according to a permeability coefficient K and the boundary condition of a basis function, solving the problem of degenerating elliptic type, and determining the basis function; according to the basis function, obtaining cell stiffness matrixes, and adding the same to obtain a total stiffness matrix; according to the boundary condition of the research area and a source sink term, obtaining a right-hand side; adopting an effective calculating method to solve the simultaneous equations of the total stiffness matrix and the right-hand side; and obtaining the hydraulic heads of all nodes in the research area. Through various simulation tests, the obtained result coincides with the analytical solution. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention is similar to the same in precision, but the calculating time of the method is less than 10% of the calculating time in the prior art. The efficiency is greatly improved when the method is used for solving wide-range, long-time or complicated problems.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
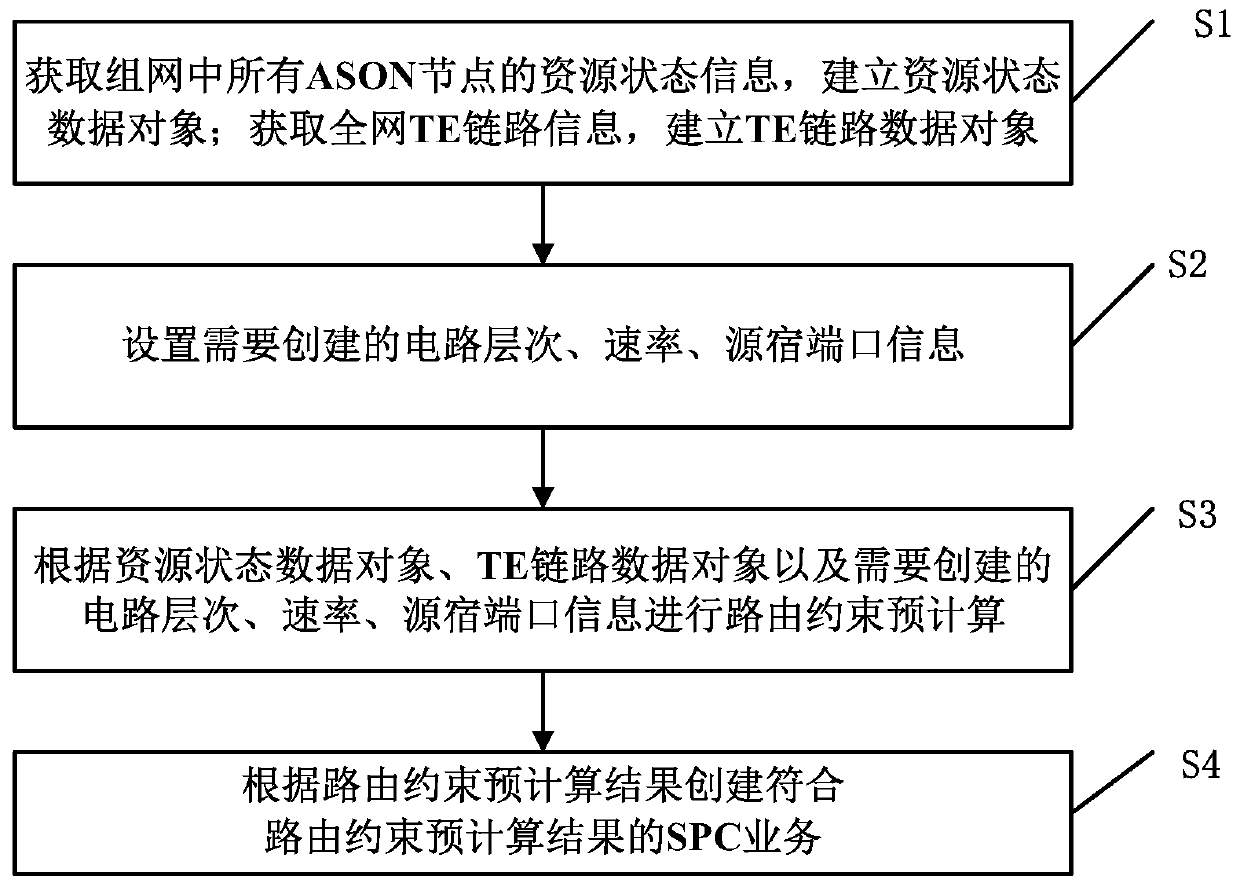
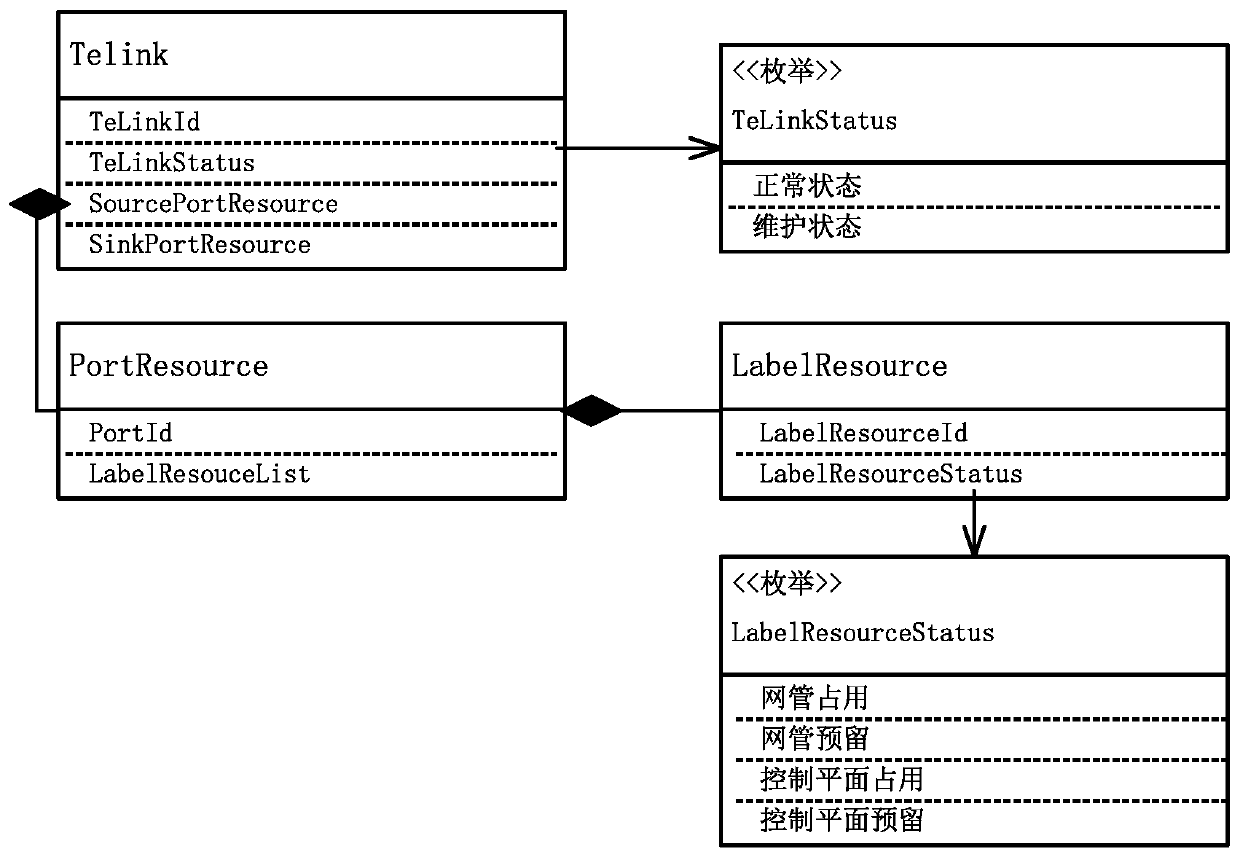
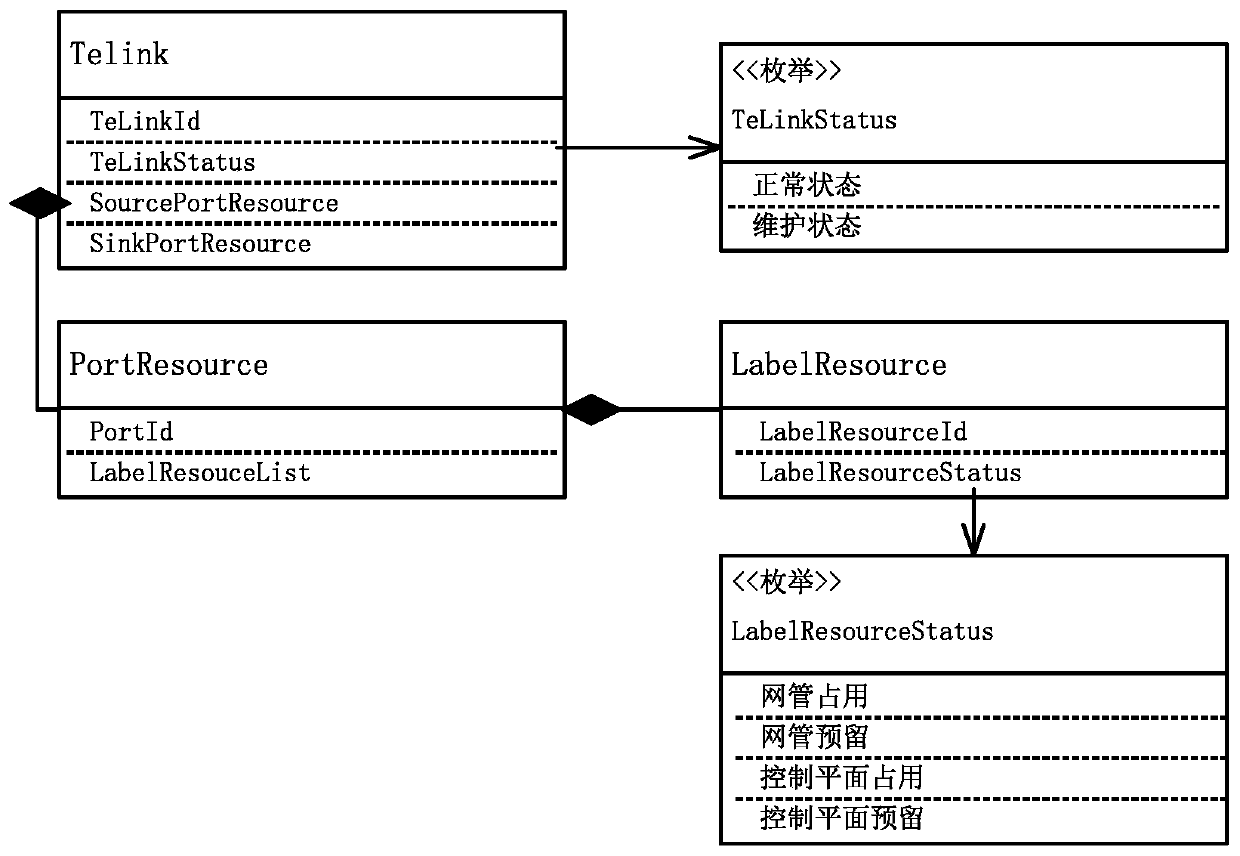
Routing constraint precomputation method and system based on control plane resources
ActiveCN109996131AReduce repeated trial-and-error operations for selecting routing constraintsOptimize the creation processMultiplex system selection arrangementsPrecomputationLink data
The invention discloses a routing constraint precomputation method and system based on control plane resources, and relates to the technical field of communication equipment management, and the methodcomprises the steps: obtaining the resource state information of all ASON nodes in a network, and building a resource state data object; obtaining whole network TE link information, and establishinga TE link data object; setting a circuit level, a rate and source and sink port information which need to be created; performing routing constraint precomputation according to the resource state dataobject, the TE link data object and the circuit level, rate and source sink port information to be created; and creating an SPC service conforming to the routing constraint precomputation result according to the routing constraint precomputation result.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
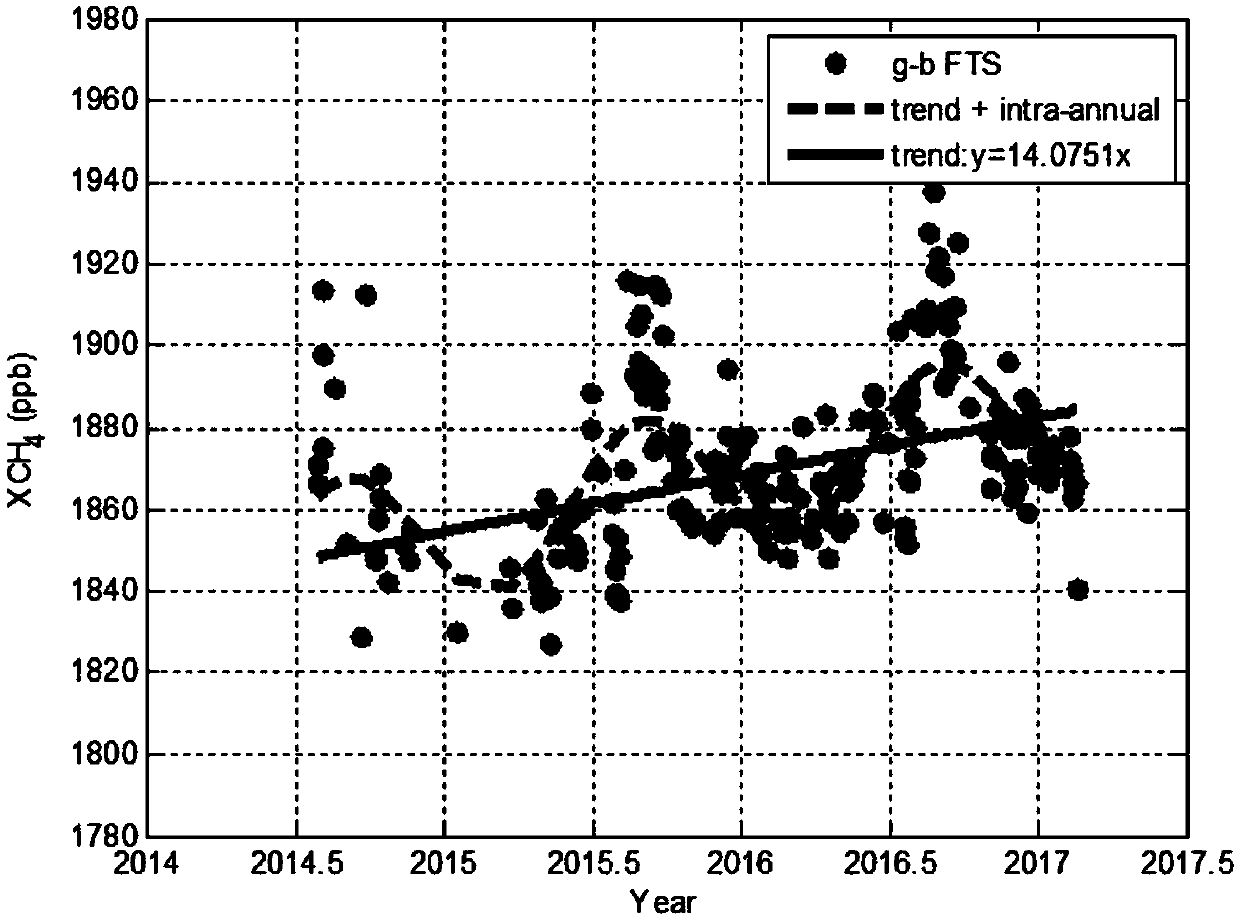
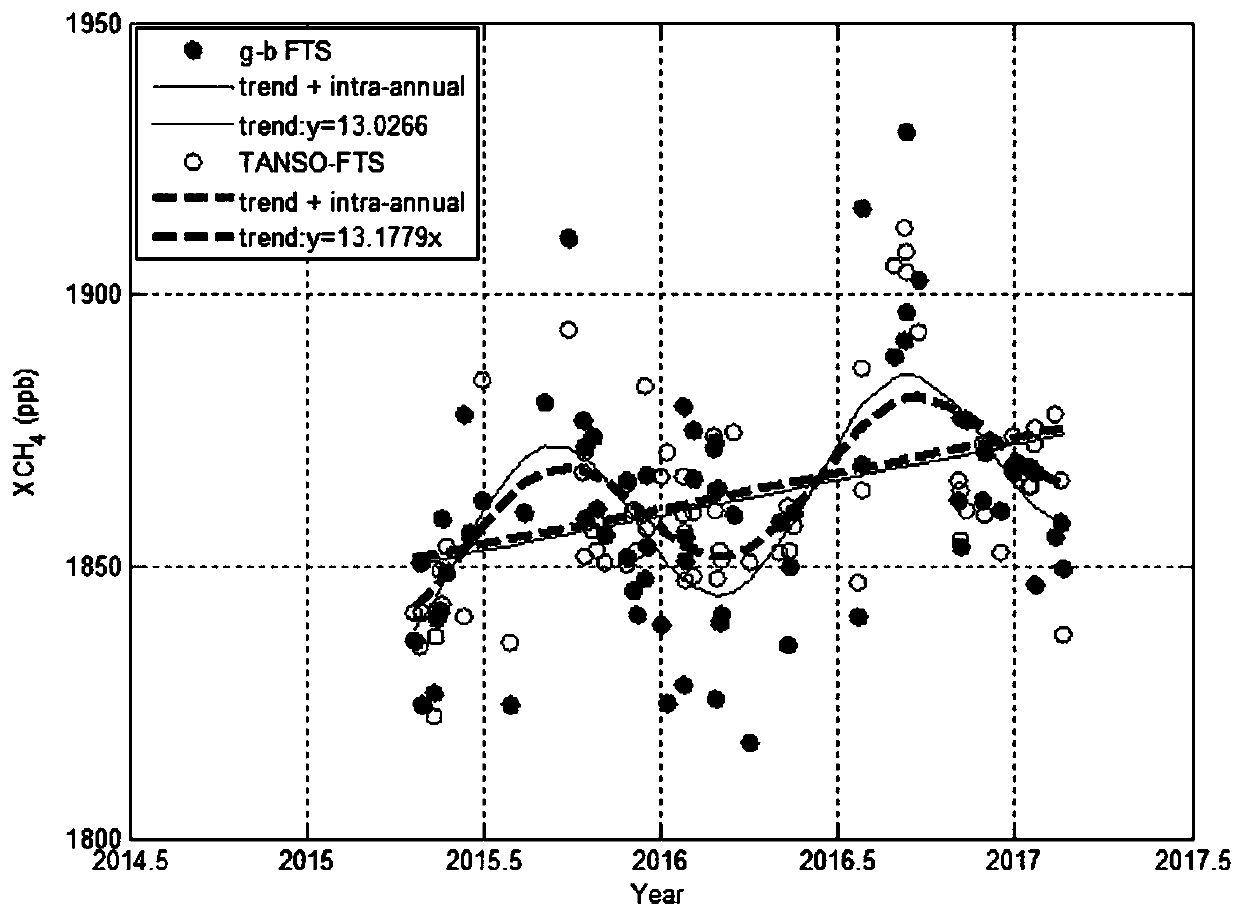
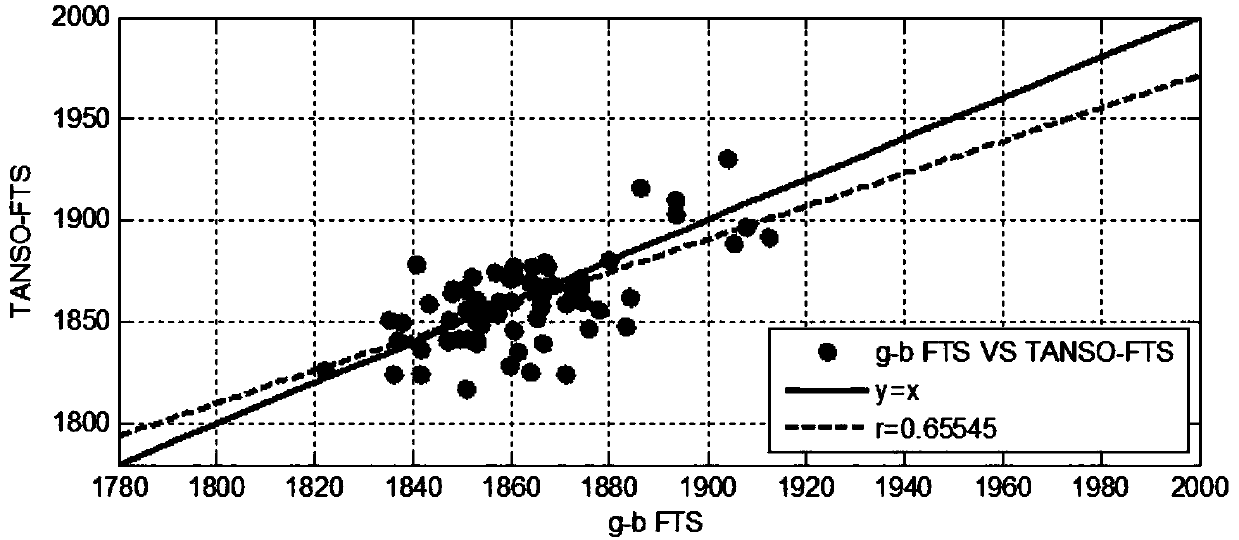
Method for statistically analyzing long-term change trend and seasonal change rule of atmospheric methane
InactiveCN107861914AAccurately quantify long-term trendsAccurately Quantify Seasonal VariationsComplex mathematical operationsData setStatistical analysis
The invention discloses a method for statistically analyzing the long-term change trend and seasonal change rule of atmospheric methane. The method includes the steps of firstly, building a long-termchange trend and seasonal change rule model V: V(t, b)=b0+b1cos2Pit+b2sin2Pit+b3cos4Pit+b4sin4Pit+..., and building a function model F: F(t, a, b)=at+V(t, b) for base-, airborne- or satellite-borne-observed active-passive atmospheric methane total column concentration data; secondly, using the bootstrapped sampling technology to perform strict fitting analysis on non-Gaussian-distribution data. The method has the advantages that by building the low-order Fourier series model and strict statistical analysis, the average trend and strict estimated seasonal change value of a given data set can beobtained, and the long-term change trend and seasonal change rule of the methane can be accurately quantified; the method is significant to fields such as atmospheric probing and weather change, applicable to the analysis of base-, airborne- or satellite-borne-observed active-passive atmospheric methane observation data and capable of providing valuable data sources for the source-sink analysis and dynamic change research and simulation of the atmospheric methane.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quantitative Analysis Of Information Leakage Vulnerabilities
InactiveUS20150193623A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionTechnical standardComputing systems
A method includes recording, during execution of a program and by a computing system, concrete values exhibited at source and sink statements in the program. The source statements read confidential information and the sink statements release the confidential information to an outside environment. The method includes determining, by the computing system, using at least the recorded concrete values and source-sink pairs whether information leakage meeting one or more quantitative criteria occurs by the program. Apparatus and program products are also disclosed.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Digital home network system and its scene mode configuration method
ActiveCN101594251BEasy to useEasy to modifyData switching by path configurationNetworked systemOperating system
Owner:新动力(北京)建筑科技有限公司
Band wireless sensor network diagnosis method
InactiveCN101247285BSimple methodEasy to implementData switching by path configurationLine sensorWireless mesh network
The invention belongs to the technical field of testing wireless sensor network, and designs a diagnostic method for ribbon pattern sensor network aiming at the characteristic of ribbon pattern sensor network. The network diagnostic method is operated on a routing layer, diagnosing the network connectivity, node state and the characteristic of other networks by the method that adjacent sink nodesexchange network explorer packet mutually. If all explorer packets can reach segment sink node successfully, the sensing belt from the source sink node to the destination sink node is considered to work normally. If each adjacent sink node learns to be in normal work state with the adjacent sensing belt, the whole network is regarded to be communicated effectively in normal work.
Owner:JIAXING WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS CENT CAS
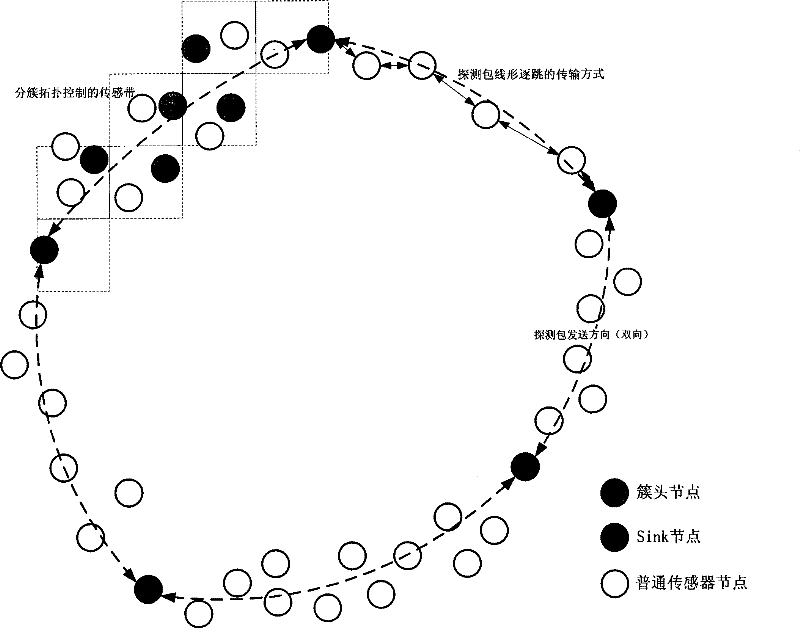
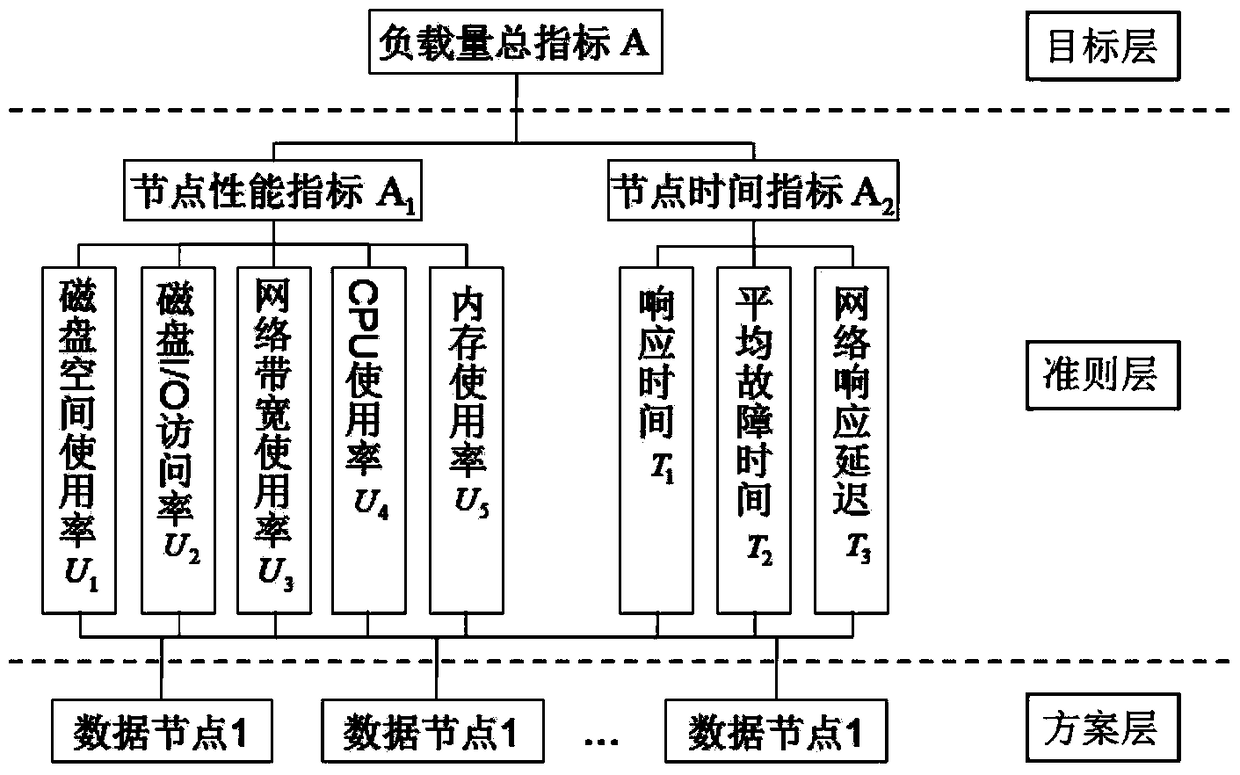
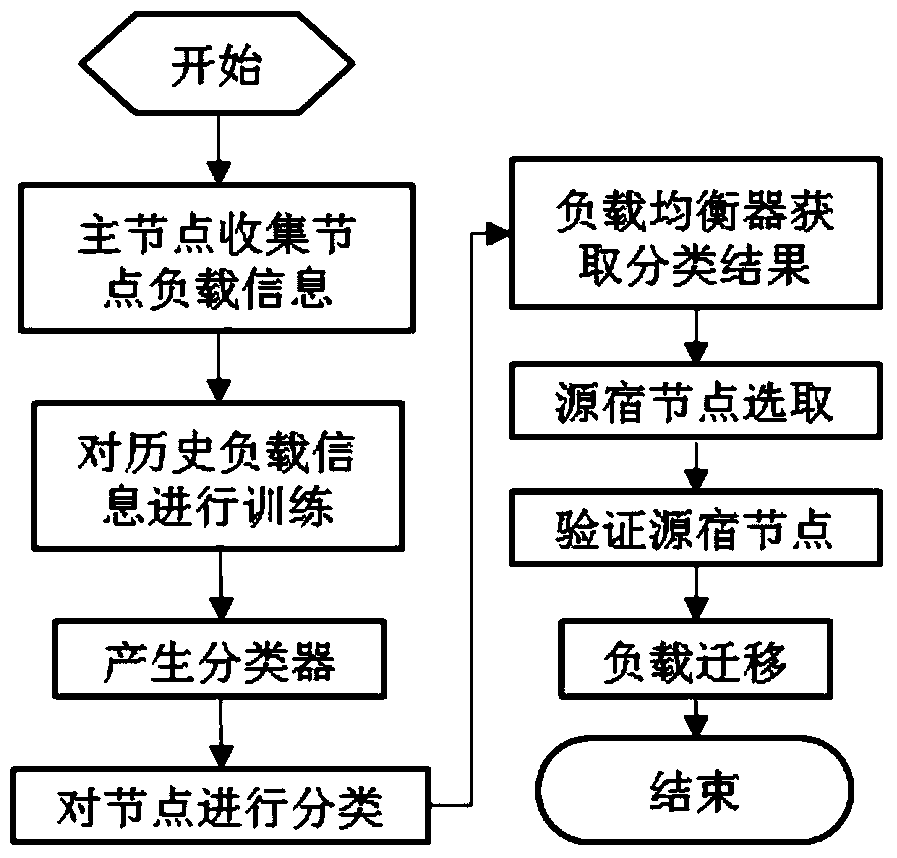
Selection method of hdfs load source and sink nodes based on multiple metrics
InactiveCN104978236BSolve the problem of cluster performance degradationImprove performanceResource allocationSpecial data processing applicationsThe InternetData node
The present invention discloses an HDFS load source and sink node selection method based on multiple measurement indexes and belongs t the field of internet data storage. The HDFS load source and sink node selection method based on the multiple measurement indexes comprises the following steps of: 1, quantizing load values of data nodes by adopting an AHP method; 2, carrying out sorting on the data nodes by adopting a naive bayesian algorithm and carrying out internal sorting according to the actual load values of the nodes, which are obtained by quantization in the step 1; and 3, selecting source and sink nodes according to a defined node selection strategy. The HDFS load source and sink node selection method based on the multiple measurement indexes has the following beneficial effects of effectively solving the problem of reduction of cluster performance, which is caused by inaccuracy of selecting HDFS source and sink nodes, enabling an HDFS cluster to have a better balanced effect, reducing the load balancing frequency of the HDFS cluster, reducing consumption of resources, which are used for load balancing, of the HDFS cluster and effectively improving integral performance of the HDFS cluster.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Process for converting storage reserves of dicot seeds into compositions comprising one or more gene products
InactiveCN1407850APlant phenotype modificationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyDownstream processing
The present invention is related to a process based on a source-sink principle, for producing products of interest from crushed or uncrushed germinating dicot seeds comprising an expression system, which is induced or can be induced during germination. The product is either a seed derived composition comprising one or more gene products. Alternatively, it is a product of interest obtained by placing the composition in contact with a substrate, containing a substance capable of being transformed by the seed derived composition as such, dried or in down-stream processed form.
Owner:UNICROP LTD
A method for sub-network connection protection via serial monitoring function
ActiveCN100571171CThe phenomenon of frequent switchingTime-division multiplexTransmission path multiple useNetwork connectionByte
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com