Hollow coil winding equipment
A technology of winding equipment and hollow coils, which is applied in the direction of coil manufacturing, conveying filamentous materials, and thin material processing, etc., which can solve the problems of inability to start winding operations immediately, short service life of winding fixtures, and reduced practicality of winding equipment. Sex and other issues, to achieve the effect of shortening the heating time, driving stability, and humanized design
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
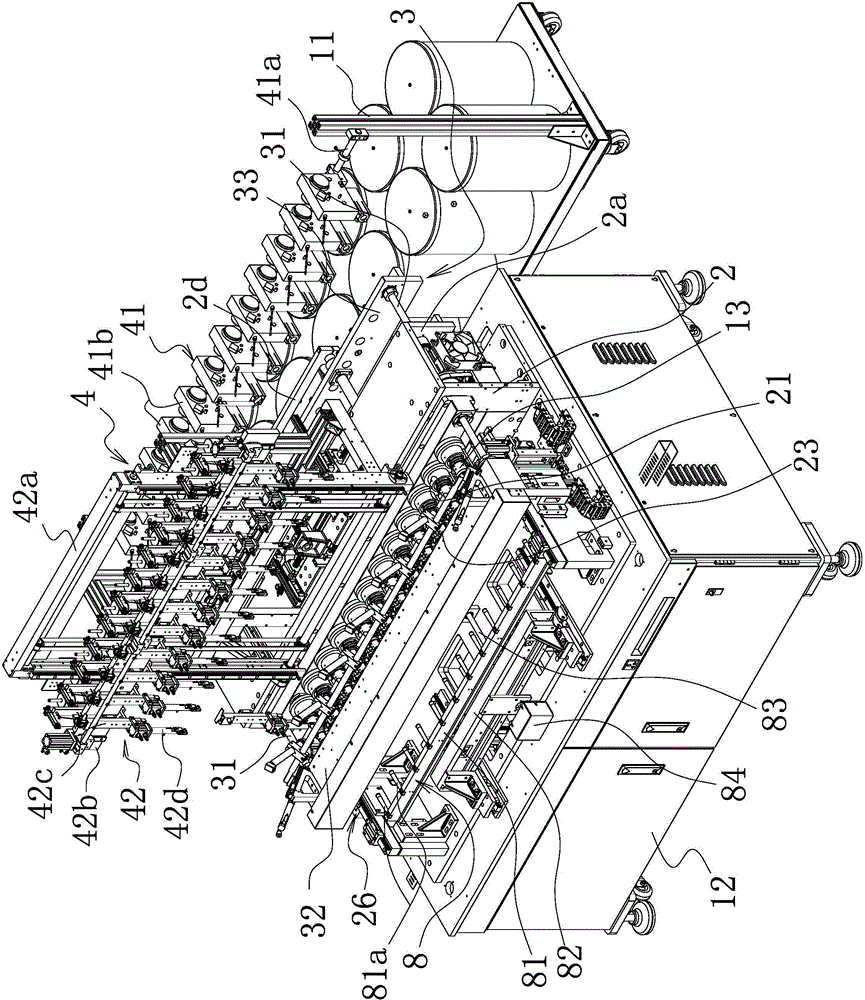
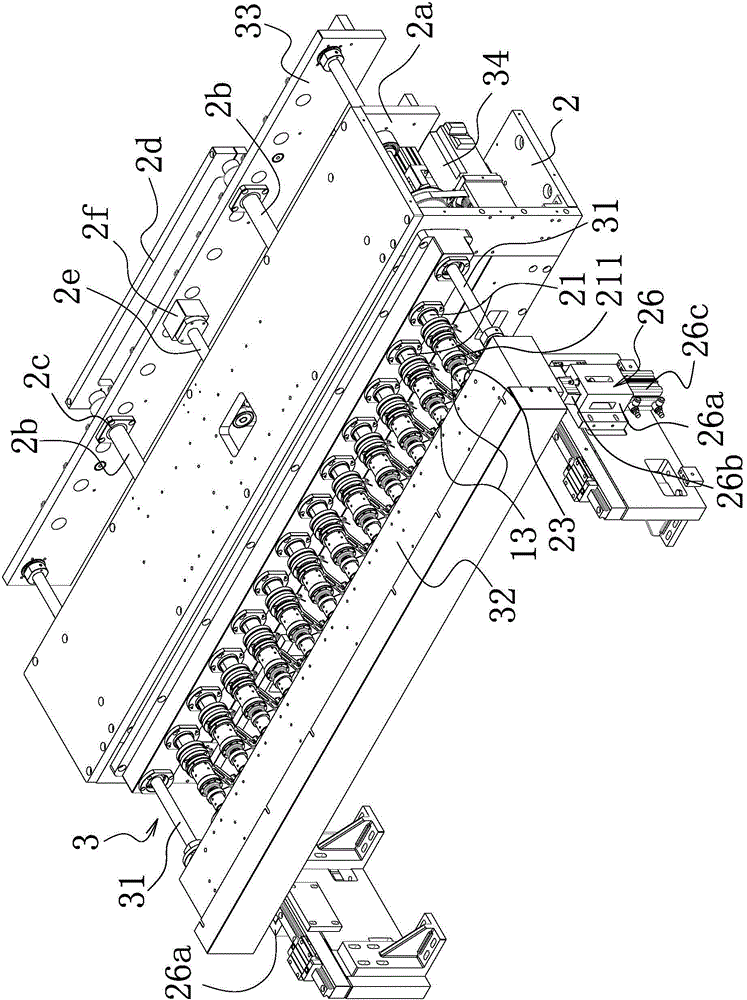
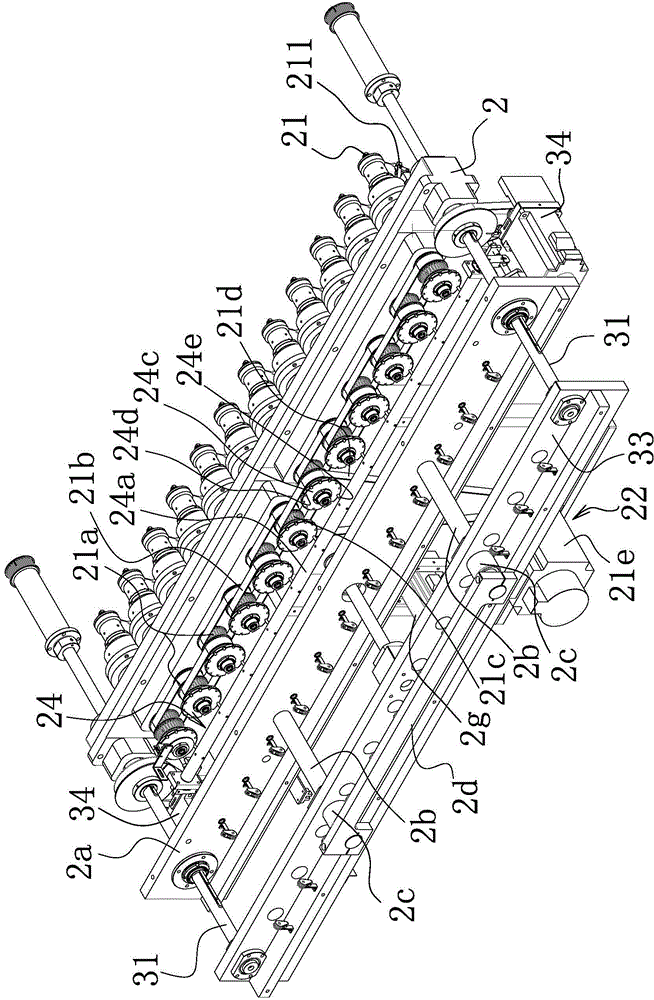
[0052] Such as Figure 1-4 As shown, the hollow coil winding equipment includes a bobbin unit 11, a stand 12 located on one side of the bobbin unit 11, and a number of winding jigs 13 formed by cooperating between a concave mandrel and a convex mandrel. Mounting seat 2 is provided on the mounting seat 2, and several spindles 21 corresponding to the winding fixture 13 and connected to the winding fixture 13 are arranged on the mounting seat 2. The spindle 21 is driven by a spindle that can drive it to rotate. Mechanisms 22 are connected, and the main shaft drive mechanism 22 includes a main shaft driving pulley 21a arranged on each main shaft 21 and a transmission timing belt 21b surrounding the main shaft driving pulley, and at least one of the several main shafts is provided with The driven driving pulley 21c is connected to the main driving pulley 21f provided on the main shaft driver 21e through a driving synchronous belt 21d. The spindle driver 21e is a drive motor.
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Such as Figure 15 As shown, the structure and principle of this embodiment are basically the same as those of Embodiment 1, so we will not repeat them here. The difference is that the constant tension control structure 42f includes a counterweight 42p connected to the lifting moving block 42c. A moving pulley 42q is provided on the top of the lifting moving block 42c, and the counterweight 42p and the lifting moving block 42c are connected by a stay rope 42s passing through the moving pulley 42q, and some fixed pulleys are arranged on the lifting moving block 42c.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com