Large-scale ceramic plate
A large-scale ceramic, high-quality technology, applied in the field of ceramic plates, can solve problems that have not been realized and need to be further improved
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~8、 comparative example 1~5
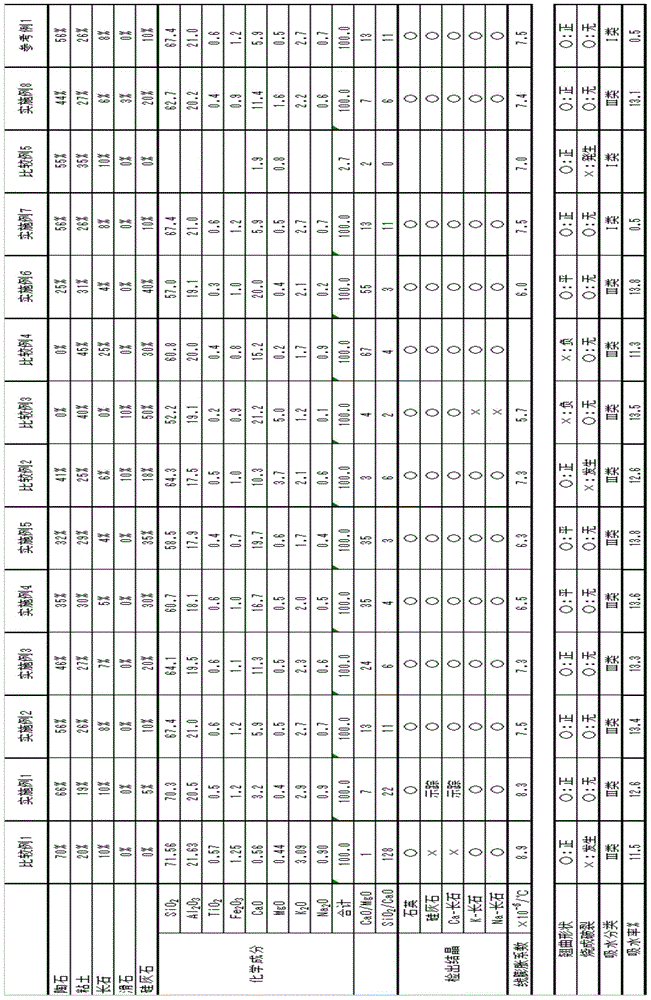
[0082] Preparation of raw material formulations
[0083] A raw material formulation was prepared by blending and mixing ceramic stone and clay as silicon-based minerals, feldspar and wollastonite as glassy minerals, and optionally talc at the contents listed in Table 1. Here, talc was not added to each raw material formulation of Examples 1-7 and Comparative Examples 1, 4, and 5. In addition, 10% by mass of talc was added to each of the raw material formulations of Comparative Examples 2 and 3, and 3% by mass of talc was added to the raw material formulation of Example 8. Then, water was added to each raw material formulation to obtain a plastic kneading clay whose moisture content was adjusted to 10% by mass or more and 25% by mass or less.
[0084] Shaping of raw material formulations
[0085] The obtained clay was molded into a cylindrical shape using an extrusion molding machine (extrusion molding machine described in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2010-23...
Embodiment 1~6 and 8
[0090] (Examples 1-6 and 8, Comparative Examples 1-4)
[0091] Firing of moldings
[0092] Each dried body produced was heated from room temperature to a maximum temperature of 1070° C. in 20 minutes using a roller kiln, kept at the maximum temperature for 7 minutes, cooled for 13 minutes, and released from the furnace to obtain a fired body.
[0093] layering of enamel
[0094] Contains water, glass frit and kaolin as raw materials, and the coefficient of linear expansion after firing is 5.4×10 -6 The paste-like enamel whose blend of glass frit and kaolin was adjusted by / °C was adjusted to have a specific gravity of 1.7-1.9 and a viscosity of 200-350 MPa·s, and was coated on the fired body so as to have a dry thickness of 0.3-0.4 mm.
[0095] refire
[0096] Next, the fired body coated with enamel was heated from room temperature to a maximum temperature of 1050° C. in 20 minutes using a roller kiln again, maintained at the maximum temperature for 7 minutes, cooled ...
Embodiment 7、 comparative example 5
[0098] Pre-firing of moldings
[0099] The obtained dried bodies were heated from normal temperature to the highest temperature of 1050° C. in 20 minutes using a roller kiln, kept at the highest temperature for 10 minutes, cooled for 13 minutes, and released from the furnace to obtain calcined bodies.
[0100] layering of enamel
[0101] Contains water, glass frit and kaolin as raw materials, and the coefficient of linear expansion after firing is 5.4×10 -6 The paste-like enamel whose blend of glass frit and kaolin was adjusted by / °C was adjusted to a specific gravity of 1.7 to 1.9 and a viscosity of 200 to 350 MPa·s, and was applied to the calcined body so as to have a dry thickness of 0.3 to 0.4 mm.
[0102] fired
[0103] Next, the calcined body coated with enamel was heated from normal temperature to the highest temperature of 1140° C. in 10 minutes using a roller kiln, kept at the highest temperature for 10 minutes, cooled for 13 minutes, and released from the fu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com