Impedance-self-adaptive inverter reactive voltage control parameter optimization method
An optimization method and voltage control technology, applied in reactive power compensation, conversion of irreversible DC power input to AC power output, AC network voltage adjustment, etc. Problems such as unreasonable parameter optimization and inverter parameter tuning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
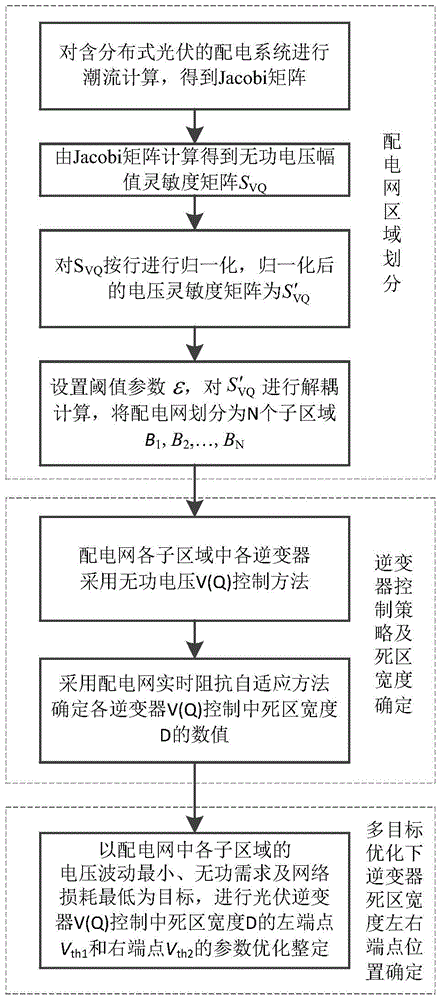
[0068] In this embodiment, the impedance adaptive inverter reactive voltage control parameter optimization method is carried out as follows:
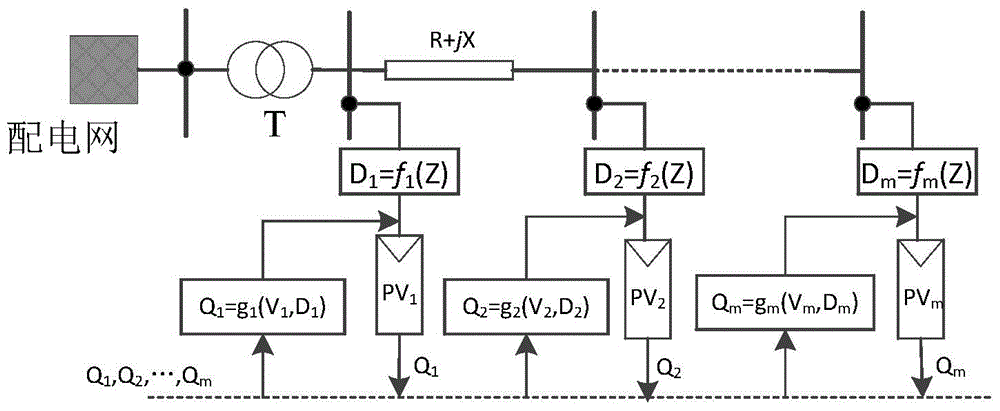
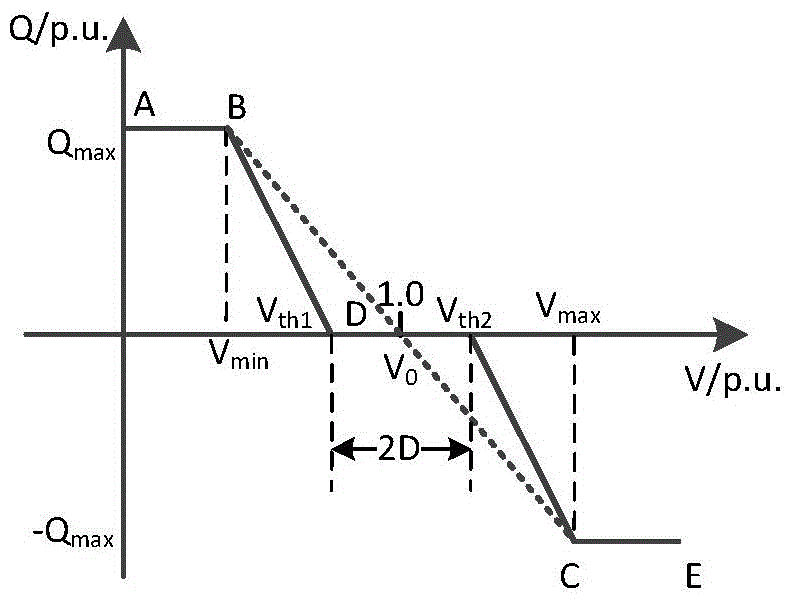
[0069] Step 1. Perform power flow calculation on the distribution network containing distributed photovoltaics, and obtain the Jacobi matrix J of the distribution network containing M PQ nodes and a balanced node M , M is a positive integer, and the total number of nodes of the distribution network is M+1; figure 1 Shown is the flow chart of the method for optimizing the reactive voltage control parameters of the inverter with impedance self-adaptation. figure 1 In this paper, the inverter reactive voltage control parameter optimization method is divided into three parts: distribution network area division based on epsilon decoupling algorithm, inverter control strategy based on impedance self-adaptation and reactive voltage control dead zone width The determination of the left and right endpoints of the dead zone width of the inverter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com