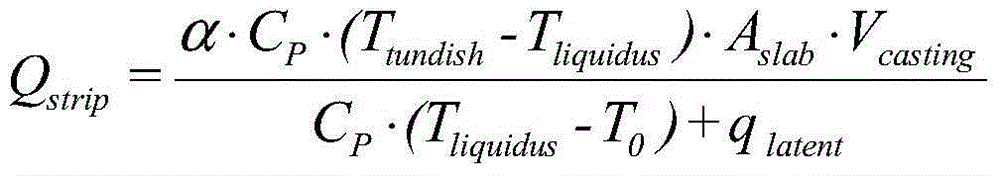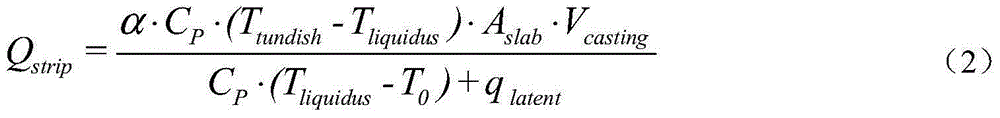Method for determining steel belt feeding process parameter of crystallizer in thick slab continuous casting process
A technology for determining process parameters and methods, which is applied in the field of thick slab continuous casting, and can solve problems such as increased difficulty in smelting, rising smelting costs, and insignificant effects of thick slabs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
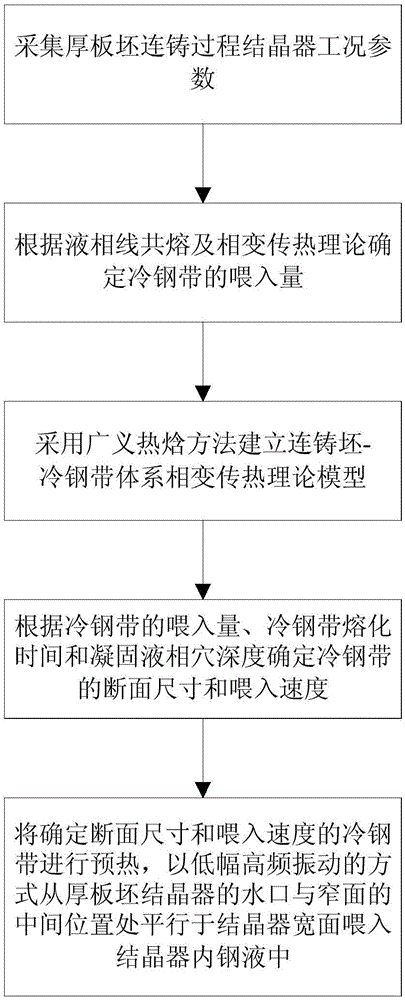
[0025] The present invention proposes a method for determining the technical parameters of the crystallizer feeding strip in the thick slab continuous casting process, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0026] Step 1: Collect the working condition parameters of the mold in the thick slab continuous casting process. The working condition parameters include the molten steel temperature at the outlet of the tundish, the working casting speed, the cross-sectional area of the thick slab, the initial temperature of the cold steel strip, and the molten steel chemical composition.
[0027] In this embodiment, the cross-sectional area A of casting a thick slab on a straight-arc continuous casting machine is adopted. slab 220mm×1800mm low-carbon steel continuous casting slab, the temperature T of molten steel at the outlet ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com