Down-the-hole impact cone
An impact cone and down-the-hole technology, which is applied to drilling equipment, earthwork drilling, and driving devices for drilling in boreholes, etc., can solve the problems of reduced drilling efficiency, disassembly failure, and large losses, and achieve low processing and use costs , Guarantee the verticality of the drilling hole, and reduce the loss of impact energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] Below by embodiment and in conjunction with accompanying drawing, the present invention will be further described:
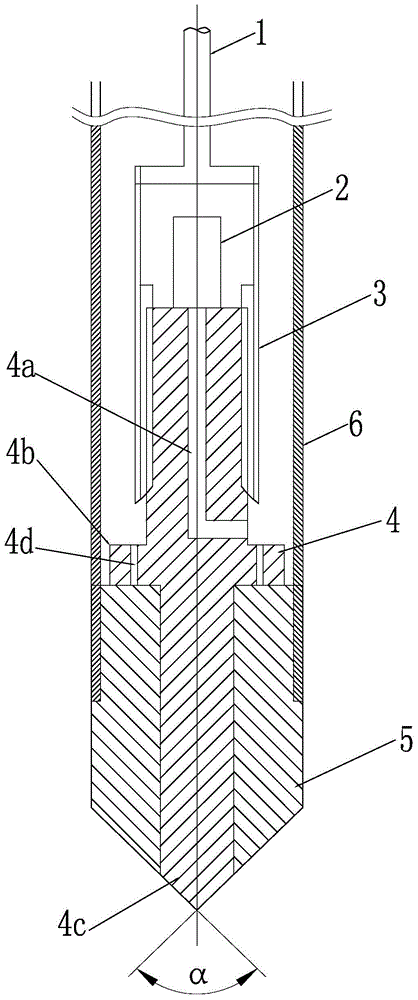
[0030] Such as figure 1 The down-the-hole impact cone shown is mainly composed of a drill pipe 1, a hammer 2, an impactor 3, an impact cone 4, an impact shoe 5, and a casing 6.
[0031] The drill pipe 1 and the impactor 3 with the built-in hammer 2 can be directly purchased as finished products for installation, and the lower end of the drill pipe 1 is connected with the upper end of the impactor 3 by threads. The drill pipe 1 is provided with an air supply channel, which sends air into the inner chamber of the impactor 3. When the inner chamber is closed, the impactor 3 starts immediately due to the increase in the pressure in the inner chamber, so that the built-in hammer 2 goes up and down at a high frequency. strike. This part follows the structure and connection method of the drill pipe 1 and the impactor 3 in the traditional down-the-hole hammer, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com