Monoclonal antibody for detecting solid particles of coxsackievirus A16 and use of monoclonal antibody
A monoclonal antibody, Coxsackie virus technology, applied in the field of drugs for preventing and/or treating Coxsackie virus A16 infection, degenerate sequence, preparation and diagnosis, detection of Coxsackie virus A16 virus solid particle antigen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Preparation of CA16 virus solid particles
[0039] The cultivation of virus: the CA16 strain used in the present invention is 2007-00190 (GenBankNo.JF420555), and the cell used for cultivating virus is human rhabdoid cell RD ( CCL-136 TM ). First, RD cells were cultured in a 10 cm culture dish (NEST), and the medium was MEM medium (GIBCO) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (PAA). When the cell confluency reaches 80%, the medium is replaced with serum-free MEM medium, and the virus is inoculated according to the amount of MOI=0.1. After culturing at 37°C, the virus was harvested after 3 days after the cells were completely damaged. The virus harvesting method is as follows: the cells are scraped off and then frozen and thawed three times, and the cell debris is removed by centrifugation, and the cell lysate supernatant is taken, filtered through a 0.22 μm filter membrane to obtain a virus stock solution, and stored at -80°C for later use.
[0040] Sucrose ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2: Preparation of monoclonal antibody
[0043] The CA16 virus stock solution prepared in Example 1 was mixed and emulsified evenly with Freund's complete adjuvant, and multi-point injections were performed on 6-8 week-old BALB / c female mice, including back subcutaneous injection, groin subcutaneous injection, foot pad injection, limb muscle injection The immunogen was injected by injection and other ways, and the injection dose was 500 μL / time. After that, boost once every 2 weeks, and boost immunization in the same way. The immunogen is the mixture of the CA16 virus stock solution prepared in Example 1 and Freund's incomplete adjuvant. Before each immunization, 20 μL of tail vein blood or 200 μL of ocular vein blood were collected for titer determination. The serum titer was determined by indirect ELISA. When the serum titer of the mice reached the plateau, the mice were stopped from immunization and rested for two months before fusion. 72 hours before the...
Embodiment 3
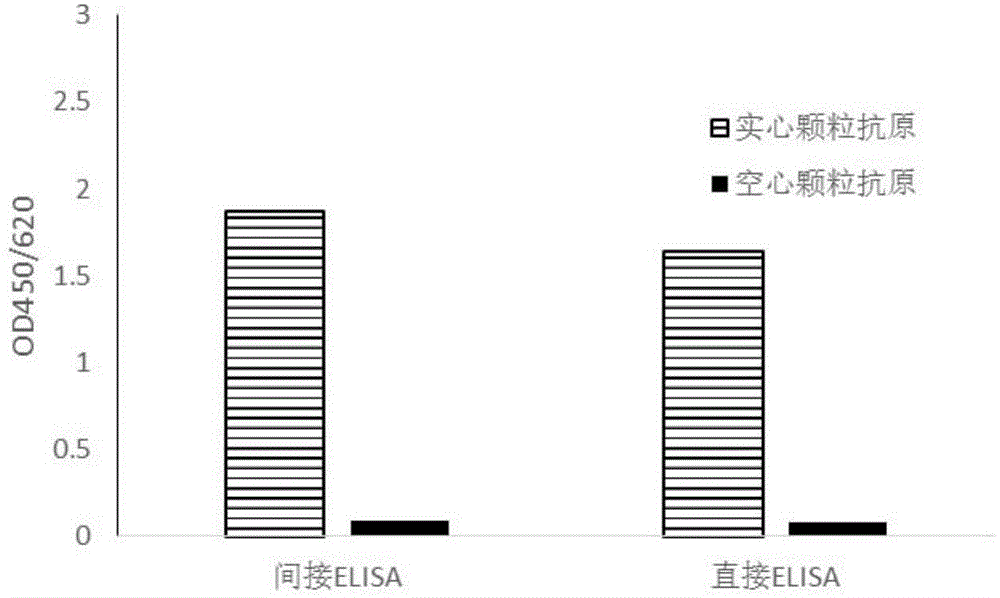
[0045] Example 3: Screening of antibodies that can specifically bind CA16 virus solid particle antigens
[0046]Indirect ELISA experiment: The CA16 virus particle antigens prepared in Example 1 were diluted 100 times with 20mMPB7.4 respectively, coated with 96-well microtiter plate, 100μL / well, coated at 37°C for 2 hours, washed once with PBST, Block non-specific binding sites with related blocking solution (20mMPB7.4 containing 150mM NaCL, 0.5% casein, 0.002% gelatin), 200 μL / well, block overnight at 4°C. Dilute the monoclonal antibody sample to be tested (1 mg / mL) prepared in Example 2 by 200 times (the formula of the diluent is the same as that of the blocking solution), add 100 μL to the microtiter plate, and incubate at 37° C. for 1 h. The plate was washed 5 times with PBST, GAM-HRP (horseradish peroxidase-labeled goat anti-mouse antibody, purchased from Bio-rad, USA, the dilution formula was the same as the blocking solution) was added, and incubated at 37°C for 30 min. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com